Acoustic Neuroma
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
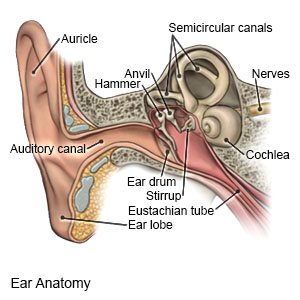
What is an acoustic neuroma (AN)?
AN is a slow growing, benign (not cancer) tumor. The tumor grows on the nerves that control balance, hearing, and feeling in your face. AN also grows on the nerve that moves muscles used for chewing. Rarely, it grows large enough to block fluid from going to your brain. Normally, it only affects one ear.
 |
What causes an acoustic neuroma?
The exact cause is not known. It occurs when your nerve cells grow out of control. This forms the tumor. You may be at higher risk for AN if you have neurofibromatosis 2.
What are the signs and symptoms of an acoustic neuroma?
- Partial or total hearing loss in one ear
- Numbness, weakness, or twitching on one side of your face
- Ringing in your ear
- Dizziness, poor balance, or trouble walking
- Full feeling or pain in your ear
- Headaches or trouble chewing
Related medications
How is AN diagnosed?
- A hearing test checks how sensitive your ears are to sounds at different volumes. This test will check for hearing loss.
- A CT , or CAT scan, takes pictures of your skull and brain. You may be given contrast liquid before the scan. Tell a healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid.
- An MRI of the head takes pictures of your brain, blood vessels, and skull. You may be given contrast liquid to help the pictures show up better. Tell a healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell a healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
How is AN treated?
Treatment depends on how severe your symptoms are and the size of the tumor. Treatment may also depend on your age. You may not need treatment if the tumor is small. Your healthcare provider may want to monitor your AN with regular MRI scans. You may need surgery to remove all or part of your AN. You may, instead, need radiation treatment to shrink your AN.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
When should I contact my healthcare provider?
- Your symptoms get worse.
- Your symptoms return after treatment.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Acoustic Neuroma
Treatment options
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
