Vykat XR: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: diazoxide choline
Dosage form: tablet, film coated
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 14, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Use In Specific Populations
- Overdosage
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
- Medication Guide
Highlights of Prescribing Information
VYKAT™ XR (diazoxide choline) extended-release tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1973
Indications and Usage for Vykat XR
VYKAT XR is indicated for the treatment of hyperphagia in adults and pediatric patients 4 years of age and older with Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS). (1)
Vykat XR Dosage and Administration
- Prior to initiation, test fasting plasma glucose and HbA1c; optimize blood glucose in patients who have hyperglycemia. (2.1)
- Do not substitute with diazoxide oral suspension. (2.1)
- Administer orally once daily. (2.2)
- Recommended starting dosage and titration schedule is based on patient’s body weight. (2.2)
Weight Starting
DosageTitration
DosageTitration
DosageTarget
Maintenance
DoseWeeks
1 and 2Weeks
3 and 4Weeks
5 and 620 to <30 kg 25 mg 50 mg 75 mg 100 mg 30 to <40 kg 75 mg 150 mg 150 mg 150 mg 40 to <65 kg 75 mg 150 mg 225 mg 225 mg 65 to <100 kg 150 mg 225 mg 300 mg 375 mg 100 to <135 kg 150 mg 300 mg 375 mg 450 mg ≥135 kg 150 mg 300 mg 450 mg 525 mg - The maximum recommended dosage is 5.8 mg/kg/day or 525 mg per day. (2.2)
- Interrupt VYKAT XR or reduce dosage for clinically significant elevations in fasting glucose or HbA1c; consider dosage reduction or interruption for clinically significant fluid overload. (2.3)
- See full prescribing information for VYKAT XR dosage modifications due to drug interactions (2.4)
- Following dosage interruption or a missed dose of 7 days or more, re-titrate according to Table 1 or Table 2. (2.5)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Extended-release tablets: 25 mg, 75 mg, and 150 mg of diazoxide choline. (3)
Contraindications
- Known hypersensitivity to diazoxide, other components of VYKAT XR, or to thiazides. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hyperglycemia: Hyperglycemia, including diabetic ketoacidosis, has been reported. During treatment, monitor fasting glucose and HbA1c. Monitor fasting glucose more frequently during first few weeks of treatment in patients with risk factors for hyperglycemia. (2.3, 5.1)
- Risk of Fluid Overload: Edema, including severe reactions associated with fluid overload, has been reported. Monitor for signs or symptoms of edema or fluid overload. (2.3, 5.2)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥10% and at least 2% greater than in placebo) are hypertrichosis, edema, hyperglycemia, and rash. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Soleno Therapeutics, Inc. at 1-833-765-3661 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
Use In Specific Populations
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 3/2025
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Vykat XR
VYKAT XR is indicated for the treatment of hyperphagia in adults and pediatric patients 4 years of age and older with Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS).
2. Vykat XR Dosage and Administration
2.1 Important Recommendations Prior to VYKAT XR Initiation
Laboratory Testing Prior to VYKAT XR Initiation
Prior to initiating treatment with VYKAT XR, test fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and HbA1c and optimize blood glucose in patients who have hyperglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
For fasting glucose and HbA1c monitoring recommendations during VYKAT XR treatment and for dosage modifications based on results, see Dosage and Administration (2.3).
Important Information Regarding Substitution
Do not substitute VYKAT XR with diazoxide oral suspension because the pharmacokinetic profiles are different [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.2 Dosage and Administration Recommendations
Administer VYKAT XR orally with or without food once daily [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Swallow tablets whole. Do not split, crush, or chew the extended-release tablets because doing so may compromise the extended-release characteristics, efficacy, or safety of VYKAT XR.
The recommended oral dosage of VYKAT XR is based on body weight. The recommended starting dosage and titration schedule of VYKAT XR are shown in Table 1.
| Weight | Recommended Once Daily Dosage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Starting Dosage | Titration Dosage | Titration Dosage | Target Maintenance Dose |
|
| Weeks 1 and 2 | Weeks 3 and 4 | Weeks 5 and 6 | ||
| 20 kg to <30 kg | 25 mg | 50 mg | 75 mg | 100 mg |
| 30 kg to <40 kg | 75 mg | 150 mg | 150 mg | 150 mg |
| 40 kg to <65 kg | 75 mg | 150 mg | 225 mg | 225 mg |
| 65 kg to <100 kg | 150 mg | 225 mg | 300 mg | 375 mg |
| 100 kg to <135 kg | 150 mg | 300 mg | 375 mg | 450 mg |
| ≥135 kg | 150 mg | 300 mg | 450 mg | 525 mg |
The maximum recommended dosage of VYKAT XR is 5.8 mg/kg/day or 525 mg per day. Dosages above 5.8 mg/kg/day or 525 mg per day have not been evaluated in patients with PWS.
2.3 Monitoring and Dosage Modifications Due to Adverse Reactions
Elevations in Fasting Glucose or HbA1c
After initiating treatment with VYKAT XR, monitor:
- Fasting glucose (FPG or fasting blood glucose) at least once every week for the first 2 weeks, then at least once every 4 weeks, and as clinically indicated.
- HbA1c every 3 months and as clinically indicated.
Monitor fasting glucose more frequently during the first few weeks of VYKAT XR treatment in patients with risk factors for hyperglycemia.
If clinically significant elevations in fasting glucose of HbA1c occur during treatment, temporarily interrupt VYKAT XR or reduce the dosage until glycemic parameters are appropriately managed. Consider initiation or adjustment of standard antidiabetic therapy(ies). If clinically significant glucose elevations are noted during titration, titrate over a longer duration and/or to a lower dosage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Fluid Overload
Monitor for signs or symptoms of edema or fluid overload. Consider dosage reduction or temporary dosage interruption in the event of clinically significant fluid overload. If clinically significat fluid overload is noted during titration, titrate over a longer duration and/or to a lower dosage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Titration After Resolution of Fluid Overload or Elevation in Fasting Glucose or HbA1c
If fluid overload or elevations in fasting glucose or HbA1c resolve after a dosage reduction:
- For patients weighing less than 30 kg, titrate the dosage in increments of no more than 25 mg every 2 weeks or titrate over longer duration to a maximum dosage of 5.8 mg/kg/day.
- For patients weighing greater than or equal to 30 kg, titrate the dosage in increments of no more than 75 mg every 2 weeks or titrate over longer duration to a maximum dosage of 5.8 mg/kg/day.
For recommendations on resuming VYKAT XR after dosage interruption, see Dosage and Administration (2.5).
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Concomitant Use with Strong CYP1A2 Inhibitors
VYKAT XR dosage modifications for concomitant use with strong CYP1A2 inhibitors are shown in Table 2[see Drug Interactions (7)].
| Weight | VYKAT XR Recommended Once Daily Dosage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Starting Dosage | Titration Dosage | Titration Dosage | Target Maintenance Dose |
|
| Weeks 1 and 2 | Weeks 3 and 4 | Weeks 5 and 6 | ||
| 20 to <30 kg | 25 mg | 25 mg | 50 mg | 75 mg |
| 30 to <40 kg | 50 mg | 100 mg | 100 mg | 100 mg |
| 40 to <65 kg | 50 mg | 100 mg | 150 mg | 150 mg |
| 65 to <100 kg | 100 mg | 150 mg | 200 mg | 250 mg |
| 100 to <135 kg | 100 mg | 200 mg | 250 mg | 300 mg |
| ≥135 kg | 100 mg | 200 mg | 300 mg | 325 mg |
Based on clinical response, VYKAT XR may be titrated to a maximum recommended dosage of 3.6 mg/kg/day. The VYKAT XR daily dosage should not exceed 325 mg per day.
No dosage modification is recommended when VYKAT XR is concomitantly used with moderate CYP1A2 inhibitors.
2.5 Recommendations Regarding Dosage Interruption, Missed Dose, or Discontinuation of Treatment
Following a dosage interruption or missed dose of:
- Less than 7 days, resume VYKAT XR at the previous dosage
- 7 days or more, re-titrate VYKAT XR according to Table 1 or 2, as appropriate [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.4)]
Treatment with VYKAT XR can be discontinued without tapering.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Extended-release tablets:
- VYKAT XR 25mg of diazoxide choline: white, capsule-shaped, film-coated, waxed tablets, debossed with S-25 on one side.
- VYKAT XR 75 mg of diazoxide choline: white, round, standard convex-shaped, film-coated, waxed tablets, debossed with S-75 on one side.
- VYKAT XR 150 mg of diazoxide choline: white, oval-shaped, film-coated, waxed tablets, debossed with S-150 on one side.
4. Contraindications
VYKAT XR is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to diazoxide, other components of VYKAT XR, or to thiazides. Erythema multiforme has been reported with VYKAT XR [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hyperglycemia
VYKAT XR increases blood glucose, due primarily to an inhibition of insulin release from the pancreas. Hyperglycemia, including severe adverse reactions associated with diabetic ketoacidosis, occurred in VYKAT XR-treated patients during clinical trials [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
Precipitating conditions for diabetic ketoacidosis may include reduction in the dosages of concomitant antihyperglycemic medications, increase in the dosages of concomitant growth hormone, intercurrent illness, surgery, volume depletion or alcohol abuse. Signs and symptoms of ketoacidosis include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, generalized malaise and shortness of breath.
Before initiating VYKAT XR, test fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and HbA1c; optimize blood glucose in patients who have hyperglycemia. After initiating treatment with VYKAT XR, regularly monitor fasting glucose (FPG or fasting blood glucose) and HbA1c [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Monitor fasting glucose more frequently for the first few weeks of treatment with VYKAT XR in patients with risk factors for hyperglycemia, such as obesity, elevated FPG, HbA1c at the upper limit of normal or above, concomitant use of growth hormone, or concomitant use of systemic corticosteroids.
Advise patients of the signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia (e.g., excessive thirst, urinating more often than usual or higher amount of urine than usual, or increased appetite with weight loss). If a patient experiences hyperglycemia after initiating treatment with VYKAT XR, monitor fasting glucose as clinically indicated, and at least twice weekly until fasting glucose decreases to normal levels. Consider monitoring ketones in patients with worsening hyperglycemia.
If hyperglycemia is treated with anti-hyperglycemic medication during VYKAT XR treatment, continue monitoring fasting glucose at least once a week for 8 weeks, followed by once every 2 weeks and as clinically indicated. Consider consultation with a healthcare provider with expertise in the treatment of hyperglycemia and counsel patients on lifestyle changes. Based on the severity of the hyperglycemia, VYKAT XR may require dosage interruption, reduction, or discontinuation in order to avoid progression to ketoacidosis [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.2 Risk of Fluid Overload
Edema, including general, localized, and peripheral edema, occurred in 27% of VYKAT XR-treated patients versus 12% of placebo-treated patients in the placebo-controlled trial with treatment-naïve subjects (Study 1). Severe adverse reactions associated with fluid overload, including pulmonary edema, were reported in VYKAT XR-treated patients during clinical trials [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
The antidiuretic property of diazoxide may lead to significant fluid retention, which may precipitate congestive heart failure in patients with compromised cardiac reserve. VYKAT XR has not been studied in patients with compromised cardiac reserve and should be used with caution in these patients.
Monitor for signs or symptoms of edema or fluid overload and consider appropriate clinical management, which may include VYKAT XR dosage reduction or treatment interruption, if clinically significant [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Hyperglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Risk of Fluid Overload [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
Adverse Reactions from Clinical Studies of VYKAT XR in Patients with PWS
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In the clinical study development program for treatment of hyperphagia in patients aged 4 years and older with PWS, a total of 125 patients received at least 1 dose of VYKAT XR. Patients received dosages of VYKAT XR up to 5.8 mg/kg/day (up to a maximum dosage of 525 mg/day) for up to 4.86 years (median: 3.0 years) in the following studies:
- Study 1: 13-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-arm study in which 126 patients were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to VYKAT XR or placebo and received at least one dose of VYKAT XR.
- Study 2-OLE: A long-term, open-label, maintenance treatment period in 115 patients (mean duration 2.6 years; maximum duration 4.3 years) who had previously been enrolled in Study 1.
- Study 2-RWP: A 16-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized withdrawal treatment period, in which 77 patients who had completed Study 1 and Study 2-OLE were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to VYKAT XR or placebo [see Clinical Studies (14)].
- Study 3: A long-term, open-label, maintenance study in 77 patients who had completed Study 1 and Study 2-OLE.
Adverse reactions leading to discontinuation in VYKAT XR-treated patients included aggression, diabetes mellitus, fluid retention, hirsutism, hyperglycemia, lower respiratory tract infection, peripheral edema, pulmonary edema, and papular rash.
The primary safety analyses are based on Study 1. The most common adverse reactions (10% or more and at least 2% greater than in placebo) in Study 1 were hypertrichosis, edema, hyperglycemia, and rash.
Table 3 presents adverse reactions that occurred in at least 5% of patients in Study 1 receiving VYKAT XR and 2% more frequently in VYKAT XR-treated patients than placebo.
| Adverse Reaction | VYKAT XR (N=84) | Placebo (N=42) |
|---|---|---|
| Hypertrichosis | 36% | 14% |
| Edema* | 27% | 12% |
| Hyperglycemia† | 17% | 5% |
| Rash‡ | 12% | 2% |
| Pyrexia | 6% | 0% |
| Arthralgia | 5% | 2% |
| Influenza | 5% | 2% |
| Nasopharyngitis | 5% | 2% |
In Study 2-RWP, the adverse reactions that occurred most frequently (at least 5%) and to a greater extent than placebo included:
Immune System Disorders: Seasonal allergy
Investigations: Increased weight
Nervous System Disorders: Hyperphagia, anxiety, affect lability, anger, compulsive hoarding, suicidal ideation
Respiratory Disorders: Streptococcal pharyngitis, upper respiratory infection
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Hirsutism
Erythema multiforme was reported in one subject in Study 1. One subject in Study 3 experienced a serious adverse reaction of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Adverse Reactions from Clinical Trials or Postmarketing Experience of Diazoxide in An Unapproved Population
The following adverse reactions associated with use of diazoxide for an unapproved population have been identified in clinical studies or post-marketing reports. Because some of these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Immune System Disorders: Hypersensitivity
Investigations: Increased serum uric acid, transient neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, decreased hemoglobin/hematocrit, eosinophilia
Respiratory Disorders: Pulmonary hypertension
Special Senses: Cataracts
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: Abnormal facial features
Related/similar drugs
7. Drug Interactions
Table 4 displays clinically significant drug interactions with VYKAT XR.
| Strong CYP1A2 Inhibitors* | |
|---|---|
|
|
| Prevention or Management | Reduce the dosage of VYKAT XR when concomitantly used with strong inhibitors of CYP1A2 [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. |
| Mechanism and Clinical Effect(s) | VYKAT XR is a CYP1A2 substrate. Concomitant use of VYKAT XR with strong CYP1A2 inhibitors increases exposure of diazoxide, which may increase the frequency and/or severity of adverse reactions from VYKAT XR [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| CYP1A2 Substrates* | |
| Prevention or Management | Concomitant use of VYKAT XR with CYP1A2 substrates is not recommended. |
| Mechanism and Clinical Effect(s) | VYKAT XR is an inhibitor of CYP1A2. Concomitant use of VYKAT XR with CYP1A2 substrates increases exposure of these substrates. This may increase the frequency and/or severity of adverse reactions from such substrates. |
| Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors* | |
| Prevention or Management | Monitor the frequency and severity of adverse reactions from VYKAT XR. A dosage reduction of VYKAT XR may be needed when used concomitantly with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. |
| Mechanism and Clinical Effect(s) | Concomitant use of VYKAT XR with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors increases exposure of diazoxide, which may increase the frequency and/or severity of adverse reactions from VYKAT XR [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Dual Strong CYP3A4 / Moderate 1A2 Inducers* | |
| Prevention or Management | Concomitant use of VYKAT XR with dual strong CYP3A4/moderate CYP1A2 inducers is not recommended. |
| Mechanism and Clinical Effect(s) | VYKAT XR is a substrate of CYP3A4 and CYP1A2. Concomitant use of VYKAT XR with strong CYP3A4/moderate 1A2 inducers may decrease exposure of VYKAT XR. This may decrease the efficacy of VYKAT XR [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Drugs Highly Bound to Protein | |
| Prevention or Management | Monitor international normalized ratio (INR) in patients who use coumarin or its derivatives concomitantly with VYKAT XR. Dosage modification of coumarin or its derivatives may be needed when used concomitantly with VYKAT XR. Monitor diphenylhydantoin serum levels when VYKAT XR is used concomitantly with diphenylhydantoin. Dosage modification of diphenylhydantoin may be needed when used concomitantly with VYKAT XR. |
| Mechanism and Clinical Effect(s) | Diazoxide is highly bound to serum proteins. Diazoxide may displace other drugs which are also highly bound to protein resulting in higher or lower blood levels of the concomitantly used drugs. The impact of protein binding displacement is expected to be clinically important for drugs with narrow therapeutic range such as coumarin or its derivatives and diphenylhydantoin. Protein binding displacement may result in an increased risk of adverse reactions due to higher blood levels of coumarin or its derivative or loss of efficacy due to lower exposures of diphenylhydantoin. |
| Thiazide or Other Diuretics | |
| Prevention or Management | Monitor for signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] and hyperuricemia when VYKAT XR is used concomitantly with thiazides or other diuretics. Dosage adjustment of VYKAT XR or diuretics may be needed when VYKAT XR is concomitantly used with diuretics. |
| Mechanism and Clinical Effect(s) | Both diazoxide and thiazides or other diuretics may produce hyperglycemia and hyperuricemia. The concomitant use of VYKAT XR with thiazides or other diuretics may potentiate the hyperglycemic and hyperuricemic effects of diazoxide [see Adverse Reactions (6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data from case reports with diazoxide use during pregnancy are insufficient to identify a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal outcomes.
Adverse reactions, including hyperglycemia, alopecia, and hypertrichosis lanuginosa, have been reported in neonates exposed to diazoxide in utero prior to delivery (see Clinical Considerations).
In animal reproduction studies, oral gavage administration of diazoxide choline to pregnant rats during organogenesis at dose exposures equal to the human exposure of 525 mg resulted in no malformations. Maternal and fetal toxicities were observed at a dose approximately equal to the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 525 mg based on AUC (see Data).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the US general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Diazoxide crosses the placenta and has been detected in cord blood. Based on adverse reactions reported in adults, in utero exposure of the infant prior to delivery may produce fetal or neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, thrombocytopenia, altered carbohydrate metabolism, and possibly other adverse reactions. Monitor infants who were exposed to diazoxide in utero for adverse reactions and treat accordingly.
Alopecia and hypertrichosis lanuginosa have occurred in a small number of infants whose mothers received oral diazoxide during the last 19 to 60 days of pregnancy. Abnormal hair growth was first noted at the age of one week and persisted when the infants were last seen at the ages of 5 months to one year. An infant born to a mother who was treated with oral diazoxide, 150 mg daily for 47 days prior to delivery, developed hyperglycemia which resolved after a 6-hour insulin infusion. Because there was an inappropriately low plasma insulin concentration for the degree of hyperglycemia, it was considered compatible with transplacental transfer of diazoxide causing inhibition of release of insulin from the neonatal pancreas.
Labor or Delivery
Intravenous administration of diazoxide during labor may cause cessation of uterine contractions, which may require administration of oxytocic agents to reinstate labor. However, this has not been reported with diazoxide when administered orally. Use caution in administering VYKAT XR during labor.
Animal Data
Diazoxide choline was administered orally to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis at doses of 40, 100, and 160 mg/kg/day (0.3, 0.6, and 1.2 times the MRHD of 525 mg based on AUC). No malformations were observed; however, decreased fetal body weights, delayed skeletal ossification, and increased fetal resorptions were observed at 160 mg/kg/day (a dose approximately equal to the MRHD based on AUC) which was a maternally toxic dose.
In a study in which rabbits were administered diazoxide intravenously, evidence of skeletal and cardiac teratogenic effects was noted at unknown multiples of the MRHD for diazoxide choline.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Diazoxide is present in human milk. There are no data on the effects of diazoxide on the breastfed infant or on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for VYKAT XR and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from VYKAT XR or from the underlying maternal condition.
Clinical Considerations
Because of potential adverse reactions, including hyperglycemia, monitoring the infant’s blood glucose may be advisable, especially during the neonatal period.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of VYKAT XR have been established for the treatment of hyperphagia in pediatric patients 4 years of age and older with PWS. Use of VYKAT XR for this indiction is supported by efficacy data from an adequate and well-controlled study that included pediatric patients with PWS [see Clinical Studies (14)] and safety data from additional studies that included pediatric patients with PWS [see Adverse Reactions (6)], and the information on this use is described throughout the labeling.
The safety and effectiveness of VYKAT XR have not been established for the treatment of hyperphagia in pediatric patients with PWS less than 4 years of age.
Adverse Reactions in Pediatric Patients in an Unapproved Population
The following postmarketing adverse reactions have been reported with the use of other diazoxide products for the treatment of hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia, an unapproved population [see Adverse Reactions (6)]:
- Pulmonary hypertension in pediatric patients less than 6 months of age, including neonates.
- Transient cataracts in association with hyperosmolar coma in a pediatric patient that subsided with correction of the hyperosmolarity.
- Development of abnormal facial features with chronic use in pediatric patients.
VYKAT XR is not approved and is not recommended for the treatment of hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia.
Juvenile Animal Toxicity Data
Diazoxide choline was orally administered at doses of 29, 58, and 145 mg/kg/day to juvenile rats from weaning (postnatal day 21) through adulthood (postnatal day 91). Reduced body weight and body weight gains, correlated with decreased food consumption, occurred at doses ≥ 58 mg/kg/day. Delayed sexual maturation occurred in males at ≥ 58 mg/kg/day and in females at all doses. Decreased motor activity was observed in males at ≥ 58 mg/kg/day, but no effect was observed on learning and memory at any dose in both males and females. The no adverse effect level (NOAEL) was 29 mg/kg/day, which results in exposures less than the clinical exposure at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 525 mg based on AUC.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of VYKAT XR did not include any subjects 65 years of age and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger adult subjects.
10. Overdosage
An overdosage of VYKAT XR may cause marked hyperglycemia, which may be associated with ketoacidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
No specific antidotes for VYKAT XR are known. Monitor ketones in patients with severe hyperglycemia following overdose and consider insulin treatment if necessary. Treat severe hyperglycemia associated with ketoacidosis with prompt insulin administration and restoration of fluid and electrolyte balance. Because of VYKAT XR’s long half-life (approximately 106 hours) in patients with PWS, the symptoms of overdosage (hyperglycemia, with or without ketoacidosis) require prolonged surveillance for periods up to three weeks or until blood sugar levels stabilize within the patient’s normal range. Consider contacting a Poison Help line (1-800-222-1222) or a medical toxicologist for overdosage management recommendations for VYKAT XR.
11. Vykat XR Description
VYKAT XR contains diazoxide choline. Diazoxide choline is very slightly soluble to soluble in solvents dichloromethane, tetrahydrofuran, acetonitrile, and methanol and practically insoluble in solvents methyl tert-butyl ether. The pKa is 8.44 ± 0.01
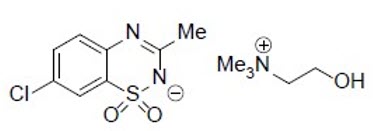
Diazoxide choline is 7-Chloro-3-methyl-1λ6, 2,4-benzothiadiazin-2-ide 1,1-dioxide 2- hydroxyethyl(trimethyl)azanium. The empirical formula is C8H6ClN2O2S•C5H14NO and the molecular weight is 333.83 g/mole. The structural formula is:
VYKAT XR is for oral administration and is available as extended-release tablets in the following strengths: 25 mg tablet contains diazoxide choline 25 mg, equivalent to 17.2 mg diazoxide; 75 mg tablet contains diazoxide choline 75 mg, equivalent to 51.6 mg diazoxide; and 150 mg tablet contains diazoxide choline 150 mg, equivalent to 103.2 mg diazoxide.
Each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: carnauba wax, colloidal silicon dioxide, dibasic calcium phosphate dihydrate, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, polyethylene oxide, silicified microcrystalline cellulose, talc, titanium dioxide, and triacetin.
12. Vykat XR - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The exact mechanism of action of diazoxide choline in the treatment of hyperphagia in patients 4 years of age and older with Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) is unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
VYKAT XR resulted in a reduction in fasting plasma insulin from baseline through 1 year of treatment.
Diazoxide increases blood glucose, due primarily to an inhibition of insulin release from the pancreas.
Other pharmacodynamic effects of VYKAT XR include increased uric acid, renin secretion and IgG concentrations, and decreased cortisol secretion.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following oral administration, diazoxide choline is hydrolyzed to diazoxide prior to absorption. Peak diazoxide concentrations occur after 16 hours. VYKAT XR is expected to reach steady state after 7 days.
Effect of Food
Following administration of 150 mg diazoxide choline to healthy subjects, the Cmax increased by 39% and AUCinf was unchanged with a high-fat meal, compared to fasted conditions. The median Tmax was 12 hours in the fasted state, and 8 hours in the fed state.
Distribution
The volume of distribution of diazoxide following oral administration is about 44.9 L. Diazoxide is extensively bound (91% to 93%) to plasma proteins (primarily human albumin), and crosses the blood-brain barrier.
Elimination
Metabolism
Diazoxide is mainly metabolized by CYP1A2 and to a minor extent by CYP3A4. Diazoxide is metabolized by oxidation or sulfate conjugation at the methyl group resulting in two inactive metabolites. Following long term administration in patients with PWS, only metabolite M1(3-hydroxymethyl-7-chloro-1,2,4- benzothiadiazine-1,1-dioxide) is detectable in circulation.
Excretion
Diazoxide is excreted almost exclusively in urine as free or conjugated compound. In humans, following administration of radiolabeled diazoxide, 85 to 92% of the total dose was recovered in urine, with about 31% eliminated as unchanged drug. About 2% of the dose is eliminated in the feces. The terminal half-life following single-dose administration in healthy subjects was 28.7 to 32.4 hours. In patients with PWS, the estimated terminal half-life is 106 hours.
Specific Populations
Pediatric Patients
Approximately 72% of the patients with PWS were under 17 years of age at enrollment. There were no clinically relevant differences in pharmacokinetics in these participants compared to those observed in adult participants.
Male and Female Patients
No sex-related differences in pharmacokinetics have been observed in clinical trials of VYKAT XR in patients with PWS who have hyperphagia.
Patients with Renal or Hepatic Impairment
VYKAT XR has not been studied in patients with renal or hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6, 8.7)].
Drug Interaction Studies
Drugs That Inhibit CYP1A2
VYKAT XR is metabolized by CYP1A2 and coadministration with a strong CYP1A2 inhibitor may increase exposure of diazoxide and decrease concentrations of diazoxide metabolites. In a clinical study with fluvoxamine (a strong CYP1A2 inhibitor), coadministration with fluvoxamine at an inhibitory dose increased single dose diazoxide Cmax by 17.5% and AUC0-inf by 60% compared to the same parameter measured on single dose in the absence of fluvoxamine co-administration [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitor
Physiology-based pharmacokinetic model-based analysis suggests that concomitant use of VYKAT XR with itraconazole (a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor) may increase the AUCinf of VYKAT XR by 1.1 to 2-fold, compared to VYKAT XR alone. Itraconazole did not appreciably affect the Cmax of VYKAT XR [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Strong CYP3A4 Inducers
Physiology-based pharmacokinetic model-based analysis suggests that concomitant use of VYKAT XR with rifampin (a strong CYP3A4 inducer and moderate CYP1A2 inducer) may decrease the Cmax and AUCinf of VYKAT XR by 14% to 30% and 40% to 70%, respectively, compared to VYKAT XR alone [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Drugs that Alter Gastric pH
Use of VYKAT XR with gastric pH adjusting-drugs is not expected to affect the pharmacokinetics of diazoxide. Based on population pharmacokinetic modeling, use of VYKAT XR with gastric pH adjusting drugs did not significantly affect relative bioavailability or apparent clearance of diazoxide.
Protein Binding Displacement
VYKAT XR may also displace bilirubin bound to serum protein, thus resulting in higher blood levels of bilirubin.
In Vitro Studies
Enzyme systems: Diazoxide choline is an inhibitor of CYP1A2. It is not an inhibitor of CYP2B6, 2C19, 2C8, 2C9, 2D6 or 3A4. It does not induce CYP1A2, CYP2B6 or CYP3A4 at the therapeutic dose range.
Transporter systems: Diazoxide choline is a substrate for OAT1, OAT3, and BCRP. It is an inhibitor of OAT1/3. It is not an inhibitor of P-gp, BCRP, MATE1/2-K, OATP1B1/3, OCT1/2 at the therapeutic dose range.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenicity studies have not been performed with diazoxide choline.
Mutagenesis
Diazoxide choline was not mutagenic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames test) and in the mouse lymphoma assay. Diazoxide choline was not clastogenic in the in vivo rat micronucleus assay.
Impairment of Fertility
Diazoxide choline was orally administered to male and female rats at doses of 58, 116, and 232 mg/kg/day (1, 2, and 4 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) on a mg/m2 basis). Females were treated two weeks prior to mating and continuing through conception and implantation and males were treated for four weeks prior to mating continuing for 35 days after mating. No effects on male or female fertility parameters were observed. Decreases in the mean number of corpora lutea, implantation sites, and live embryos occurred at 4 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis.
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of VYKAT XR for the treatment of hyperphagia in adults and pediatric patients ages 4 years and older with PWS was established in a 16-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized withdrawal study period (Study 2-RWP; NCT03714373) that followed an open-label study period of VYKAT XR. During Study 2-RWP, 77 patients with hyperphagia and PWS were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to continue their current oral dosage using a weight-based dosage regimen of VYKAT XR or placebo [see Dosage and Adminstration (2.2)]. Prior to participating in Study 2-RWP, patients received double-blind and/or open-label VYKAT XR for a mean duration of 3.3 years (range 2.5 to 4.5 years; Study 1 and Study 2-OLE). Results from Study 2-RWP are presented below.
Demographic and baseline disease characteristics were similar for the VYKAT XR and placebo groups. The mean age was 14.9 years of age (range 7 to 29 years of age). Most of the participants were White (86%), 7% were Black or African American, and 8% were of multiple races. The majority of participants were non-Hispanic (91%) and female (56%).
The primary efficacy endpoint was the Change from Baseline in the Hyperphagia Questionnaire for Clinical Trials (HQ-CT) Total Score at Week 16. The HQ-CT is a 9-item, observer-reported outcome measure that assesses a range of hyperphagic and food-related behaviors during the prior 2 weeks. An item score of 0 indicates an absence of behaviors, with a score of 4 indicating the most frequent or severe behaviors. The HQ-CT Total Score may range from 0 to 36, with higher scores indicating greater overall severity of hyperphagic and food-related behaviors.
At the end of the 16-week randomized withdrawal study period, there was statistically significant worsening of hyperphagia in the placebo group relative to the VYKAT XR group, as assessed by the HQ- CT Total Score (see Table 5).
| Treatment Group | Number of Patients | Mean Baseline Score (SD) | LS Mean Change from Baseline (SE) | LS Mean Difference* (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CI, confidence interval; HQ-CT, Hyperphagia Questionnaire for Clinical Trials; LS Mean, least squares mean; RWP, randomized withdrawal period; SD, standard deviation; SE, standard error | ||||
|
||||
| VYKAT XR | 38 | 9.0 (6.3) | 2.6 (1.1) | -5.0 (-8.1, -1.8) |
| Placebo | 39 | 8.1 (5.1) | 7.6 (1.1) | |
16. How is Vykat XR supplied
How Supplied
VYKAT XR is supplied as follows:
| Strength | Description | Package Configuration | NDC Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg diazoxide choline | White, capsule-shaped tablets, debossed with "S-25" on one side | 30-count bottles | 83860-025-01 |
| 75 mg diazoxide choline | White, round, standard convex tablets, debossed with "S-75" on one side | 30-count bottles | 83860-075-01 |
| 150 mg diazoxide choline | White, oval-shaped tablets, debossed with “S-150” on one side. | 30-count bottles | 83860-150-01 |
Storage and Handling
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15° and 30°C (59° and 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Keep in tightly closed container. Protect from humidity. Do not remove desiccant.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Administration Instructions
Advise patients to swallow tablets whole and not to split, crush, or chew VYKAT XR [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Hyperglycemia
Advise the patient or caregiver that VYKAT XR can cause hyperglycemia, sometimes leading to diabetic ketoacidosis, and that the patient will have monitoring of blood glucose before and during VYKAT XR treatment. Advise patients or caregivers on the signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia (e.g., excessive thirst, urinating more often than usual or higher amount of urine than usual, or increased appetite with weight loss) and ketoacidosis (e.g., nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, generalized malaise and shortness of breath) and to contact their healthcare provider if these signs or symptoms occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Risk of Fluid Overload
Advise the patient or caregiver that VYKAT XR may cause edema, including severe adverse reactions associated with fluid overload. Advise patients or caregivers on the signs and symptoms of edema and to contact their healthcare provider if signs or symptoms of edema occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Manufactured for:
Soleno Therapeutics, Inc.
100 Marine Parkway, Suite 400
Redwood City, CA 94065
© 2025 Soleno Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved.
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Issued: 3/2025 | ||
| MEDICATION GUIDE VYKAT™ XR (vye kat ex ar) (diazoxide choline) extended-release tablets, for oral use |
|||
| What is the most important information I should know about VYKAT XR? VYKAT XR may cause serious side effects, including:
|
|||
| What is VYKAT XR?
VYKAT XR is a prescription medicine used to treat extreme hunger, constant thoughts about food, and constant urge to eat that cannot be satisfied with food (hyperphagia) in adults and children 4 years of age and older with Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS). It is not known if VYKAT XR is safe and effective in children under 4 years of age. |
|||
| Who should not take VYKAT XR?
Do not take VYKAT XR if you are allergic to diazoxide, any ingredients in VYKAT XR, or medicines called thiazides. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in VYKAT XR. |
|||
Before taking VYKAT XR, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Do not change your dose or stop any medicines you take or start any new medicines without talking to your healthcare provider first during treatment with VYKAT XR. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:
|
|||
How should I take VYKAT XR?
|
|||
What are the possible side effects of VYKAT XR?
|
|||
How should I store VYKAT XR?
|
|||
| General information about the safe and effective use of VYKAT XR.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use VYKAT XR for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give VYKAT XR to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about VYKAT XR that is written for health professionals. |
|||
| What are the ingredients in VYKAT XR?
Active ingredient: diazoxide choline Inactive ingredients: carnauba wax, colloidal silicon dioxide, dibasic calcium phosphate dihydrate, hypromellose magnesium stearate, polyethylene oxide, silicified microcrystalline cellulose, talc, titanium dioxide, and triacetin. Manufactured for: Soleno Therapeutics, Inc., 100 Marine Parkway, Suite 400, Redwood City, CA 94065 For more information, call 1-833-765-3661. |
|||
Bottle Label - VYKAT XR - 25 mg
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 83860-025-01
Vykat™ XR
(diazoxide choline)
Extended-Release Tablets
25 mg
Dispense the accompanying
Medication Guide to each patient
Rx only 30 tablets SOLENO®THERAPEUTICS

| VYKAT XR
diazoxide choline tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| VYKAT XR
diazoxide choline tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| VYKAT XR
diazoxide choline tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Soleno Therapeutics, Inc. (030593896) |
| Registrant - Soleno Therapeutics, Inc. (030593896) |



