Sephience: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: sepiapterin
Dosage form: oral powder
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Sep 16, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Use In Specific Populations
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
Highlights of Prescribing Information
SEPHIENCE (sepiapterin) oral powder
Initial U.S. Approval: 2025
Indications and Usage for Sephience
SEPHIENCE is a phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) activator indicated for the treatment of hyperphenylalaninemia (HPA) in adult and pediatric patients 1 month of age and older with sepiapterin-responsive phenylketonuria (PKU). SEPHIENCE is to be used in conjunction with a phenylalanine (Phe)- restricted diet. (1)
Sephience Dosage and Administration
- Patients treated with SEPHIENCE should be on a dietary protein and a Phe-restricted diet. (2.1)
- Administer SEPHIENCE orally once daily with food. (2.2)
- The recommended starting dosage of SEPHIENCE is: (2.2)
Age SEPHIENCE (mg/kg) per day Less than 6 months 7.5 mg/kg 6 months to less than 1 year 15 mg/kg 1 year to less than 2 years 30 mg/kg 2 years and older 60 mg/kg - Important Administration Information: prepare SEPHIENCE calculated daily doses of < 1,000 mg as a liquid mixture (25 mg/mL), and administer exact prescribed dose volume (mL). (2.2, 2.3)
- See full prescribing information for complete preparation and administration instructions. (2.3)
Contraindications
None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Increased Bleeding: SEPHIENCE may increase the risk of bleeding. Consider treatment interruption in patients with active bleeding. (5.1)
- Hypophenylalaninemia: Some pediatric PKU patients experienced hypophenylalaninemia; monitor patients blood Phe levels during treatment. (5.2)
- Interaction with Levodopa: Seizures, over-stimulation or irritability may occur; monitor patients for a change in neurologic status. (5.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions with SEPHIENCE (≥2% and greater than placebo) were diarrhea, headache, abdominal pain, hypophenylalaninemia, feces discoloration, and oropharyngeal pain. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact PTC Therapeutics, Inc. at 1-866-562-4620 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
Dihydrofolate Reductase (DHFR) Inhibitors: Avoid concomitant use (e.g., trimethoprim, methotrexate, trimetrexate, pemetrexed, pralatrexate, raltitrexed, or piritrexim). (7.1)
Sepiapterin Reductase (SR) Inhibitors: Avoid concomitant use (e.g. sulfasalazine or sulfamethoxazole). (7.1)
Interaction with Levodopa: Monitor patients for a change in neurologic status. (7.2)
Drugs Affecting Nitric Oxide-Mediated Vasorelaxation: Potential for vasorelaxation; monitor blood pressure (e.g., PDE-5 inhibitors). (7.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 7/2025
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Sephience
SEPHIENCE is indicated for the treatment of hyperphenylalaninemia (HPA) in adult and pediatric patients 1 month of age and older with sepiapterin-responsive phenylketonuria (PKU). SEPHIENCE is to be used in conjunction with a phenylalanine (Phe)-restricted diet.
2. Sephience Dosage and Administration
2.1 Important Recommendation Prior to SEPHIENCE Treatment
Treatment with SEPHIENCE should be directed by physicians knowledgeable in the management of PKU.
Biochemical response to SEPHIENCE treatment cannot generally be pre-determined by laboratory testing (e.g., molecular testing), and should be determined through a therapeutic evaluation of SEPHIENCE [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Studies (14.1)].
Obtain baseline blood Phe concentration before initiating treatment.
All patients with PKU who are treated with SEPHIENCE should be on a dietary protein and Phe-restricted diet that is based on blood Phe levels. Patients should undergo regular dietary assessments, including protein and Phe intake, by their healthcare provider [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage and Administration
The recommended starting dosage of SEPHIENCE is based on the patient’s age and is administered orally once daily (see Table 1).
Administer SEPHIENCE with food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
| *For calculated daily doses less than 1,000 mg, the final concentration of prepared SEPHIENCE liquid mixture is 25 mg/mL [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. **60 mg/kg is the maximum daily dose for all patients. |
|
| Age | SEPHIENCE (mg/kg) per day** |
| Less than 6 months | 7.5 mg/kg |
| 6 months to less than 1 year | 15 mg/kg |
| 1 year to less than 2 years | 30 mg/kg |
| 2 years and older | 60 mg/kg |
Evaluation Period
Dosage Titration in Patients Less than 2 Years of Age
After initiating treatment at the starting dosage by age (Table 1), check blood Phe levels to determine response to treatment within 2 weeks. If blood Phe does not decrease, SEPHIENCE dosage may be titrated incrementally based on blood Phe levels to a maximum daily dosage of 60 mg/kg. Existing dietary protein and Phe intake should not be modified during the evaluation period.
Discontinuation for Lack of Biochemical Response
Discontinue SEPHIENCE in patients whose blood Phe does not decrease after 2 weeks of treatment at the maximum daily dosage of 60 mg/kg.
Dosage Modification and Monitoring
Monitor blood Phe levels during treatment, and if needed, modify the daily dosage of SEPHIENCE within the range of 7.5 mg/kg to 60 mg/kg and/or dietary protein and Phe intake to ensure adequate blood Phe level control. Frequent blood Phe monitoring is recommended in the pediatric population [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Missed Dose
A missed dose should be taken as soon as possible but 2 doses should not be administered on the same day. Resume the normal dosing schedule the following day.
2.3 Preparation and Administration Instructions
Doses Less Than 1,000 mg (administration based on 25 mg/mL concentration)
- Determine the required number of SEPHIENCE packets and the required volume of water or apple juice to achieve a concentration of 25 mg/mL mixture (see Table 2).
| Abbreviations: mg, milligrams; mL, milliliters a For calculated daily doses less than 1,000 mg, round the dose up to the nearest 250 mg to determine the number of SEPHIENCE packets and prepare each 250 mg packet with 9 mL of water or apple juice. |
|||
| Daily Dose (mg) | Number of 1,000 mg packetsa | Number of 250 mg packetsa | Volume of water or apple juice (mL) |
| 250 mg or less | 0 | 1 | 9 mL |
| 251 mg to 500 mg | 0 | 2 | 18 mL |
| 501 mg to 750 mg | 0 | 3 | 27 mL |
| 751 mg to 999 mg | 1 | 0 | 36 mL |
- Calculate the prescribed dose volume to the nearest 0.2 mL.
- Divide the calculated daily dose (mg) by the final concentration (25 mg/mL) of SEPHIENCE liquid mixture for doses less than 1,000 mg.
Prescribed dose volume (mL) = SEPHIENCE calculated dose (mg))
25 mg/mL
- Divide the calculated daily dose (mg) by the final concentration (25 mg/mL) of SEPHIENCE liquid mixture for doses less than 1,000 mg.
- Prepare a liquid mixture.
- Open and empty the entire content of each SEPHIENCE packet into an appropriate-size container and mix with the required volume of water or apple juice per Table 2.
- Stir the contents for 30 seconds or more until the mixture is uniformly mixed.
- Using a graduated oral dosing syringe, draw up the prescribed dose volume to the nearest 0.2 mL.
- Administer the prescribed dose volume (mL).
- Administer immediately.
- If particles are remaining in the syringe, draw up additional water or apple juice and administer the contents immediately. Repeat if particles still remain.
- Discard unused portion of SEPHIENCE mixture remaining in the container.
- Consume additional food after administration of the prescribed dose volume.
Doses 1,000 mg or Greater (whole packet administration)
- Determine the required number of SEPHIENCE packets and the required volume of water, apple juice, strawberry jam, or applesauce (see Table 3).
| Abbreviations: mg, milligrams; mL, milliliters; Tbsp, tablespoons a For calculated daily doses 1,000 mg or greater, round the dose to the nearest 250 mg to determine the number of SEPHIENCE packets required. b For each 1,000 mg packet, add 2 Tbsp (30 mL) of water, apple juice, strawberry jam, or applesauce, and then add an additional quantity of 2 Tbsp (30 mL) for up to three 250 mg packet(s) and then mix. |
|||
| Daily Dose (mg) | Number of 1,000 mg packetsa | Number of 250 mg packetsa | Volume of water, apple juice, strawberry jam, or applesauceb |
| 1,000 mg to 1,124 mg | 1 | 0 | 2 Tbsp or 30 mL |
| 1,125 mg to 1,374 mg | 1 | 1 | 4 Tbsp or 60 mL |
| 1,375 mg to 1,624 mg | 1 | 2 | |
| 1,625 mg to 1,874 mg | 1 | 3 | |
| 1,875 mg to 2,124 mg | 2 | 0 | |
| 2,125 mg to 2,374 mg | 2 | 1 | 6 Tbsp or 90 mL |
| 2,375 mg to 2,624 mg | 2 | 2 | |
| 2,625 mg to 2,874 mg | 2 | 3 | |
| 2,875 mg to 3,124 mg | 3 | 0 | |
| 3,125 mg to 3,374 mg | 3 | 1 | 8 Tbsp or 120 mL |
| 3,375 mg to 3,624 mg | 3 | 2 | |
| 3,625 mg to 3,874 mg | 3 | 3 | |
| 3,875 mg to 4,124 mg | 4 | 0 | |
| 4,125 mg to 4,374 mg | 4 | 1 | 10 Tbsp or 150 mL |
| 4,375 mg to 4,624 mg | 4 | 2 | |
| 4,625 mg to 4,874 mg | 4 | 3 | |
| 4,875 mg to 5,124 mg | 5 | 0 | |
| 5,125 mg to 5,374 mg | 5 | 1 | 12 Tbsp or 180 mL |
| 5,375 mg to 5,624 mg | 5 | 2 | |
| 5,625 mg to 5,874 mg | 5 | 3 | |
| 5,875 mg to 6,124 mg | 6 | 0 | |
- Prepare a liquid or soft food mixture.
- Open and empty the entire content of each SEPHIENCE packet into a container.
- Mix with the required amount of water, apple juice, strawberry jam, or applesauce per Table 3.
- Stir the contents for 30 seconds or more when mixing SEPHIENCE with water or apple juice or 60 seconds or more when mixing SEPHIENCE with strawberry jam or applesauce until the mixture is uniform.
- Administer the dose.
- Consume the entire mixture immediately.
- If particles are remaining in the container, add additional water or juice to the container and administer the contents immediately. Repeat if particles still remain.
- Consume additional food after administration of the entire mixture.
2.4 Storage Instructions for the Liquid and Soft Food Mixtures
- If the SEPHIENCE liquid or soft food mixture is not administered immediately, cover and store the mixture at controlled room temperature between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) for up to 6 hours or refrigerate between 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for up to 24 hours.
- If the liquid or soft food mixture is stored, stir for at least 30 or 60 seconds, respectively, prior to administration of the prescribed dose.
- Discard unused SEPHIENCE mixture after 6 hours at controlled room temperature or after 24 hours if refrigerated.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Oral powder: 250 mg or 1,000 mg sepiapterin as yellow to orange powder in a unit-dose packet.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Increased Bleeding
SEPHIENCE may increase the risk of bleeding. Bleeding events, including superficial hematomas, prolonged bleeding, and heavy menstrual bleeding have occurred in patients treated with SEPHIENCE [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. One patient with non-traumatic superficial hematomas and prolonged bleeding was re-challenged at a lower dose of SEPHIENCE with recurrence of symptoms, which led to treatment discontinuation. The patient experienced symptoms 15 days after initial exposure and two days after rechallenge. The patient had normal blood counts and coagulation studies at the time of the bleeding. Inform the patient about the increased risk of bleeding associated with SEPHIENCE and to follow up with his/her healthcare provider if he/she experiences any signs of increased bleeding. Consider treatment interruption with SEPHIENCE in patients with active bleeding.
5.2 Hypophenylalaninemia
In clinical trials of SEPHIENCE, some pediatric PKU patients experienced hypophenylalaninemia (low blood Phe), including some patients with multiple low blood Phe levels, during treatment with SEPHIENCE [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Prolonged levels of blood Phe that are too low have been associated with catabolism and endogenous protein breakdown, which has been associated with adverse developmental outcomes.
Monitor blood Phe levels during treatment and if needed, modify the dosage of SEPHIENCE and/or dietary protein and Phe intake to ensure adequate blood Phe level control. Frequent blood Phe monitoring is recommended in the pediatric population [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.3 Interaction with Levodopa
In a 10-year post-marketing safety surveillance program for a non-PKU indication using another drug that is a phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) activator, 3 patients with underlying neurological disorders experienced seizures, exacerbation of seizures, over-stimulation, and irritability during co-administration with levodopa. Monitor patients who are receiving levodopa for changes in neurological status during treatment with SEPHIENCE [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Increased Bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Hypophenylalaninemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of SEPHIENCE was evaluated in Trial 1 [Part 1 (open label); Part 2, (placebo-controlled)]; and Trial 2 (open-label). The two trials included a total of 215 SEPHIENCE-treated patients with PKU: 10 (5%) were <2 years old, 118 (55%) were ≥2 and <17 years old, and 87 (40%) were ≥17 years old. All patients received SEPHIENCE from 7.5 mg/kg/day up to 60 mg/kg/day and the median duration of treatment (in weeks) was 25.5 [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
Trial 1
Trial 1 included a total of 157 patients (85 male and 72 female, aged 1 year to 61 years old) with PKU across both parts of the trial. The patients received dosages from 20 mg/kg up to 60 mg/kg daily and the median duration of treatment was 8 weeks.
Table 4 lists the most common adverse reactions that were reported in ≥2% of patients treated with SEPHIENCE and greater than that of the placebo group in Part 2 of Trial 1.
| a Includes Abdominal pain; Abdominal pain upper, Abdominal discomfort. | ||
| Adverse Reaction | SEPHIENCE N=56 N (%) | Placebo N=54 N (%) |
| Diarrhea | 4 (7) | 1 (2) |
| Headache | 4 (7) | 1 (2) |
| Abdominal paina | 3 (5) | 1 (2) |
| Hypophenylalaninemia | 2 (4) | 0 |
| Feces discoloration | 2 (4) | 0 |
| Oropharyngeal pain | 2 (4) | 1 (2) |
Adverse reactions were similar across both adult and pediatric populations except for hypophenylalaninemia (see Description of Selected Adverse Reactions).
Description of Selected Adverse Reactions
Increased Bleeding
In Trial 1 Part 2, a case of heavy menstrual bleeding was reported in a SEPHIENCE-treated patient. Less than 2% of patients in Trial 2 experienced increased bleeding, which included heavy menstrual bleeding, non-traumatic superficial hematomas, and prolonged bleeding.
Hypophenylalaninemia
In Trial 1 Part 2, hypophenylalaninemia was seen in 5% (2/37) of sepiapterin-treated pediatric patients and in no adult patients. Some pediatric patients in Trial 2 had multiple low blood Phe levels.
Related/similar drugs
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on SEPHIENCE
Avoid concomitant use of drugs known to inhibit folate synthesis dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) (e.g., trimethoprim, methotrexate, trimetrexate, pemetrexed, pralatrexate, raltitrexed, and piritrexim) while taking SEPHIENCE. Concomitant administration of such drugs may reduce sepiapterin metabolism to tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4). If concomitant use is not avoidable, monitor blood Phe levels.
Avoid concomitant use of sepiapterin reductase (SR) inhibitors with SEPHIENCE. Concomitant administration of such drugs may reduce sepiapterin metabolism to BH4. If concomitant use is not avoidable, monitor blood Phe levels.
7.2 Effects of SEPHIENCE on Other Drugs
SEPHIENCE may increase the availability of tyrosine, a precursor of levodopa. Neurologic events were reported postmarketing in patients receiving another PAH activator and levodopa concomitantly for a non-PKU indication. Monitor patients for a change in neurologic status when levodopa is administered with SEPHIENCE [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
7.3 Drugs Affecting Nitric Oxide-Mediated Vasorelaxation
SEPHIENCE and PDE-5 inhibitors induce vasorelaxation, thus concomitant use of SEPHIENCE with PDE-5 inhibitors may reduce blood pressure even further. Monitor for signs and symptoms of hypotension with concomitant use of SEPHIENCE with drugs that affect nitric oxide-mediated vasorelaxation (e.g., PDE-5 inhibitors such as sildenafil, vardenafil, or tadalafil).
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data on the use of SEPHIENCE during pregnancy are insufficient to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Uncontrolled blood Phe concentrations before and during pregnancy are associated with an increased risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes and fetal adverse effects (see Clinical Considerations).
In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of sepiapterin to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis at dose exposures up to 9- and 6- times the human exposure at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 60 mg/kg, respectively, resulted in no adverse developmental effects (see Data).
All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defects, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in pregnant women with PKU who maintain blood Phe concentrations greater than 600 micromol/L during pregnancy is greater than the corresponding background risk for pregnant women without PKU.
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryofetal Risk
Uncontrolled blood Phe concentrations before and during pregnancy are associated with an increased risk of adverse outcomes and fetal adverse effects (see Data). To reduce the risk of hyperphenylalaninemia-induced fetal adverse effects, blood Phe concentrations should be maintained between 120 and 360 micromol/L during pregnancy and during the 3 months before conception [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Human Data
Available data from the Maternal Phenylketonuria Collaborative Study on 468 pregnancies and 331 live births in pregnant women with PKU demonstrated that uncontrolled Phe concentrations above 600 micromol/L are associated with an increased risk for major birth defects (including microcephaly, major cardiac malformations), intrauterine fetal growth retardation, and future intellectual disability with low IQ.
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal development study in rats, SEPHIENCE was administered at dose levels of 100, 300, or 1,000 mg/kg/day via oral gavage to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis from gestation day (GD) 7 to GD 17. There were no maternal or embryo-fetal developmental toxicities noted at doses up to 1,000 mg/kg/day (9-fold the human AUC0-24 at the MRHD).
In an embryo-fetal development study in pregnant rabbits, SEPHIENCE was administered at dose levels of 100, 300, or 1,000 mg/kg/day via oral gavage to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis from gestation day (GD) 7 to GD 19. There were no maternal or embryo-fetal developmental toxicities at doses up to 1,000 mg/kg/day (6-fold the human AUC0-24 at the MRHD).
In the pre- and post-natal development study in rats, SEPHIENCE was administered at dose levels of 30, 100, and 300 mg/kg/day via oral gavage once daily to pregnant rats from GD 6 to lactation day 20. SEPHIENCE did not induce effects on maternal reproductive function or on developmental and reproductive parameters of male and female offspring up to 300 mg/kg (7-fold the human AUC0-24 at the MRHD).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of sepiapterin in either human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for SEPHIENCE and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from SEPHIENCE or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of SEPHIENCE have been established in pediatric patients 1 month of age and older. Use of SEPHIENCE for this indication is supported by evidence from one adequate and well-controlled trial in 63 pediatric patients with PKU aged 1 to <17 years old (Trial 1) and additional safety and efficacy information obtained from an ongoing open label trial in adult and pediatric patients with PKU (Trial 2) [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
In Trial 1 Part 2, hypophenylalaninemia was seen in 5.4% (2/37) of sepiapterin-treated pediatric patients and in no adult patients. Some pediatric patients in Trial 2 had multiple low blood Phe levels [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
The safety and effectiveness of SEPHIENCE for treatment of PKU have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 1 month of age.
11. Sephience Description
SEPHIENCE (sepiapterin) contains the drug substance sepiapterin, a PAH activator. Sepiapterin is a yellow to orange powder. Sepiapterin is slightly soluble in water with the solubility at 1.4 mg/mL.
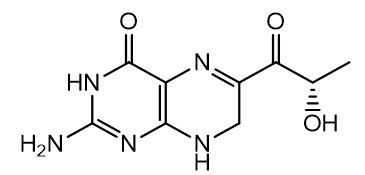
The chemical name of sepiapterin is (S)-2-amino-6-(2-hydroxypropanoyl)-7,8-dihydropteridin-4(3H)-one. The molecular formula is C9H11N5O3 and the molecular weight is 237.22 g/mol. The structural formula is:
SEPHIENCE oral powder contains either 250 mg or 1,000 mg of sepiapterin to be administered orally. The inactive ingredients are: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, isomalt, magnesium stearate, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, sucralose, and xanthan gum.
12. Sephience - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
SEPHIENCE is a precursor of the enzymatic co-factor tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) which activates PAH.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At the recommended SEPHIENCE dose of 60 mg/kg orally once daily, clinically significant QTc interval prolongation was not observed.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following oral administration, sepiapterin reached the maximum concentration in plasma at 2 hours post-treatment and converted to pharmacologically active metabolite BH4 with the exposures of sepiapterin generally less than 2% of those of BH4 (Table 5).
There was no accumulation for BH4 following repeated once daily dose up to 60 mg/kg administered in adult healthy volunteers.
When administered with a high-fat, high-calorie meal in adult healthy volunteers, BH4 exposures increased less than dose proportionally (with slopes 0.87 and 0.84 for Cmax and AUC0-last, respectively) in the dose range 5 to 20 mg/kg and less than dose proportionally (with slopes 0.1957 and 0.3189 for Cmax and AUC0-last, respectively) in the dose range 20 to 60 mg/kg.
The pharmacokinetics of sepiapterin and its active metabolite BH4 following oral administration of sepiapterin at 60 mg/kg with food in adult patients with PKU are summarized in Table 5.
| a Sepiapterin was administered with dietary Phe restriction. NC: not calculated. Sepiapterin plasma concentration quickly declines to below lower limit of quantitation by 12 hours post dose and AUCinf were not estimable for the majority of patients. | |||||
| Analyte | Tmax (hr) Median (Range) | Cmax (ng/mL) Mean (SD) | AUCinf
ng*hr/mL) Mean (SD) | AUC24
(ng*hr/mL) Mean (SD) |
|
| Sepiapterin | N Results | 29 2 (0.5, 6.1) | 29 2.9 (1.6) | NC | 27 19.9 (18.3) |
| BH4 | N Results | 30 4 (2, 8) | 30 432 (177) | 19 3,626 (1267) | 30 3,618 (1,699) |
Absorption
The time to maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) of sepiapterin is approximately 1 to 3 hours after oral administration. Plasma sepiapterin is rapidly metabolized to BH4 and peak BH4 concentrations are achieved approximately 4 hours after the oral administration of sepiapterin.
Effect of Food
Administration of SEPHIENCE with food results in increased exposure to sepiapterin and BH4. When SEPHIENCE was administered at 20 or 60 mg/kg daily with a low-fat meal in healthy adult subjects, BH4 exposures were 169% to 172% higher for Cmax and 162% to 173% higher for AUC0-24h compared to administration under fasted conditions. When sepiapterin at 20 or 60 mg/kg was administered with a high-fat, high-calorie meal, BH4 exposures were 221% to 226% higher for Cmax and 251% to 284% higher for AUC0-24h compared to administration under fasted conditions [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Distribution
Sepiapterin mean human plasma protein binding was 15.4% in the presence of 0.1% dithiothreitol (DTT) in the concentration range of 0.1 to 10 μM. BH4 mean human plasma protein binding was between 24.1% and 41.3% in the concentration range 2 to 15 μM in the presence of 0.5% β-mercaptoethanol. Sepiapterin apparent volume of distribution could not be estimated reliably as sepiapterin is converted to BH4 post oral administration and plasma concentration declines to below lower limit of quantitation generally by 12 hours postdose. BH4 apparent volume of distribution is 11433 (5790) L in adult patients with PKU. Increase of BH4 in cerebrospinal fluid was detected after oral administration of sepiapterin 60 mg/kg QD for 7 days in healthy adult subjects.
Elimination
Following oral administration, sepiapterin is quickly absorbed and converted to BH4. Sepiapterin plasma concentration is remarkably lower than BH4 and declines rapidly to below the limit of quantitation generally by 12 hours post dose. The terminal half-life of BH4 is approximately 5 hours and the apparent clearance is 1498 (848) L/h in adult patients with PKU.
Metabolism
Sepiapterin is metabolized by SR/carbonyl reductase (CR) and DHFR in a 2-step unidirectional process to form pharmacologically active metabolite BH4. BH4 is further metabolized non-enzymatically or enzymatically mediated by aromatic amino acid hydroxylases, such as PAH, tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH), pterin-4α-carbinolamine dehydratase (PCD), dihydropteridine reductase (DHPR), xanthine oxidase (XO), and nitric oxide synthase (NOS) in various tissues.
Extensive metabolism of sepiapterin was observed in humans following a single oral dose of 14C-sepiapterin. Absorbed sepiapterin was converted to the active metabolite BH4, with Cmax and AUC0-24h of sepiapterin generally less than 2% of those of BH4.
Excretion
Following a single oral dose of radiolabeled sepiapterin 4,000 mg to healthy adult subjects, a mean of 6.7% was recovered in urine and 26.2% recovered in feces with a combined total recovery of 32.9% by 240 hours. The low total mass recovery is likely due to formation of volatile metabolites in human intestine. Sepiapterin was a minor component in urine and was one of the prominent radioactive components in feces.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant difference in pharmacokinetics of sepiapterin were observed based on age (range 0.5 to 61 years), sex (female 52%, male 48%), race/ethnicity (White 74%, Asian 16%, Other or not specified 7%, or American Indian or Alaska Native 3%) or ABCG2 genotype (BCRP p.Gln141Lys). The effect of renal impairment, hepatic impairment, or pregnancy on pharmacokinetics of sepiapterin or BH4 is unknown.
Pediatric Patients
The pharmacokinetics of sepiapterin and BH4 following oral administration of sepiapterin at 60 mg/kg with food in PKU patients ≥2 years old are summarized in Table 6.
| a Sepiapterin was administered with dietary Phe restriction. | |||||
| Analyte | Tmax (hr) Median (Range) | Cmax (ng/mL) Mean (SD) | AUCinf
ng*hr/mL) Mean (SD) | AUC24
(ng*hr/mL) Mean (SD) |
|
| Sepiapterin | N Results | 19 1.05 (0.5, 4) | 19 2.5 (2.1) | NA NA | 18 13.8 (15.1) |
| BH4 | N Results | 21 4 (1.9, 8) | 21 350 (191.9) | 16 3,466 (1,792) | 21 3,023 (1,637) |
The pharmacokinetics of sepiapterin have not been evaluated in pediatric patients younger than 2 years of age.
Drug Interaction Studies
Both sepiapterin and BH4 were a substrate and inhibitor of efflux transporter breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) in vitro.
Oral coadministration of curcumin, a BCRP inhibitor, and sepiapterin in healthy adult subjects resulted in increases in mean AUCs and Cmax of BH4 by approximately 20% to 24%, after a single dose.
In healthy adult subjects, oral coadministration of sepiapterin and rosuvastatin, a BCRP substrate, had no impact on rosuvastatin exposures.
The pharmacokinetics of sepiapterin and BH4 following sepiapterin oral administration may be affected by inhibitors of SR and/or DHFR [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Sepiapterin may increase the availability of tyrosine, a precursor of levodopa [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
In a 6-month carcinogenicity study in Tg.rasH2 mice, sepiapterin did not increase the incidence of tumors in male or female transgenic mice at approximately 12- and 16-fold, respectively, the human exposure (AUC0-24h) at the MRHD.
Mutagenesis
Based on the weight of evidence, SEPHIENCE is not genotoxic. SEPHIENCE was negative in the Ames assay. SEPHIENCE was positive in an in vitro chromosomal aberration assay without metabolic activation but not with metabolic activation. SEPHIENCE was negative in the in vivo (micronucleus and comet) assays in rats.
Impairment of Fertility
SEPHIENCE was found to have no effect on fertility and reproductive function of male and female rats when given prior to and throughout mating in male and female rats and continuing to gestation day (GD) 7 in females at oral doses up to 300 mg/kg/day (approximately 7.5-fold the plasma exposure (AUC) at MRHD).
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Repeated administration of SEPHIENCE in rats for 26 weeks at doses greater than 100 mg/kg/day (approximately 3-fold the plasma exposure (AUC) at MRHD) caused renal toxicity, including renal tubular degeneration associated with crystal formation. However, renal toxicity was not noted in monkeys following repeated administration of SEPHIENCE for 39 weeks up to 300 mg/kg/day (approximately 7-fold the plasma exposure (AUC) at MRHD).
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Clinical Studies in PKU
Trial 1 (NCT05099640) was a two-part trial in adult and pediatric patients who had a diagnosis of PKU with hyperphenylalaninemia with at least 2 blood Phe measurements ≥600 μmol/L. Patients in the trial were 54% male, 90% White, 5% American Indian or Alaska Native, and 4% Other by race; 16% were identified as Hispanic or Latino. The mean age of the trial patients was 17 years (range: 1 to 61 years). At trial baseline, 8% of patients had blood Phe levels at <360 μmol/L, 36% at 360-600 μmol/L, 48% at 600-1200 μmol/L, and 8% at >1200 μmol/L.
In Part 1, 157 patients received open-label treatment with SEPHIENCE: 7.5 mg/kg orally in patients 0 to <6 months of age, 15 mg/kg in patients 6 to <12 months of age, 30 mg/kg in patients 12 months to <2 years of age, or 60 mg/kg in patients ≥2 years of age per day for 14 days. In Part 1, 66% of PKU patients showed a biochemical response to SEPHIENCE with a >30% or greater reduction in Phe level. In Part 2, after the 2-week washout period from Part 1, 98 patients aged 2 years and older who demonstrated a ≥30% reduction in blood Phe levels to SEPHIENCE treatment in Part 1 were randomized in a double-blind fashion to either SEPHIENCE 20 mg/kg daily for Weeks 1 and 2, 40 mg/kg daily for Weeks 3 and 4, 60 mg/kg daily for Weeks 5 and 6 (N=49), or placebo (N=49) for 6 weeks to assess efficacy. Twelve additional patients who had shown a 15% to 30% reduction in blood Phe during Part 1 were enrolled in Part 2 but were not included in the primary efficacy analysis.
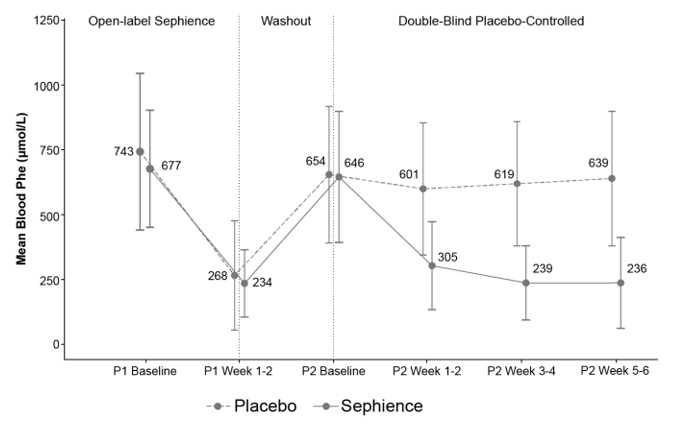
In Part 2, the primary efficacy was assessed in patients who demonstrated a ≥30% reduction in blood Phe levels during Part 1 (N=98) by the mean change in blood Phe level from baseline to Weeks 5 and 6 in the SEPHIENCE-treated group as compared to the mean change in the placebo group, as shown in Table 7.
In Part 2 of Trial 1, 55 patients in the SEPHIENCE group and 54 patients in the placebo group completed the treatment period. One patient in the SEPHIENCE group discontinued treatment.
Table 7 displays a reduction in blood Phe level from baseline to Weeks 5 and 6 in Part 2 of Trial 1 for SEPHIENCE-treated patients relative to placebo. Figure 1 displays the mean blood Phe level over time by treatment group.
| a Baseline is the average of Day -1 and Day 1 blood Phe levels in Part 2. b Blood Phe levels were based on average values during Weeks 5 and 6. † Adjusted mean and standard error, p-value <0.0001 for treatment difference were from a mixed model for repeated measures (MMRM) with change in blood Phe from baseline to post-baseline assessments as the response variable, and fixed effects for treatment, baseline blood Phe, baseline Phe stratum, visit and treatment-by-visit interaction. |
||
| SEPHIENCE (N=49) | Placebo (N=49) |
|
| Baseline Blood Phe Levela (μmol/L) | ||
| Mean (±SD) | 646.1 (253) | 654 (261.5) |
| Percentiles (25th, 75th) | 468.5, 769.5 | 466, 796 |
| Weeks 5 and 6b | ||
| Mean (±SD) | 236 (174.9) | 637.9 (259.9) |
| Percentiles (25th, 75th) | 127.7, 291 | 453, 776 |
| Mean Change in Blood Phe From Baseline to Weeks 5 and 6 (μmol/L) | ||
| Adjusted Mean (±SE)† | -415.8 (24.1) | -19.9 (24.2) |
| Percentiles (25th, 75th) | -544, -296.7 | -86.7, 63.7 |
| Mean Percent Change in Blood Phe From Baseline to Weeks 5 and 6 | ||
| Mean (±SD) | -62.8 (20.7) | 1.4 (29.2) |
| Percentiles (25th, 75th) | -76.9, -60.7 | -12.4, 15 |
| Treatment difference (95% CI) in adjusted mean | -64.2 (-74.1, -54.4) | |
Figure 1: Mean (±SD) Blood Phe Levels Over Time For Patients Who Had a ≥30% Reduction in Blood Phe Levels During Part 1 of Trial 1 (N=98)
Supportive efficacy data were provided from Trial 2, which is an ongoing, multicenter, open-label trial in adult and pediatric patients with a clinical diagnosis of PKU with hyperphenylalaninemia. At the data cutoff date, 169 patients, including 65 adult and 104 pediatric patients (median age: 14 years, range 2 months to 55 years) received treatment with SEPHIENCE. Five patients 2 to <6 months of age received SEPHIENCE 7.5 mg/kg, 9 patients 12 months to <2 years of age received SEPHIENCE 30 mg/kg, and 90 patients 2 to <17 years of age and 65 patients ≥17 years of age received SEPHIENCE 60 mg/kg. Of the 9 patients under the age of 2 years, 6 patients (66%) had a ≥30% decrease in blood Phe from baseline) at Weeks 1 and 2. The baseline Phe level in patients 2 years and under was 311.4 μmol/L and the mean absolute change in Phe from baseline to Weeks 1 and 2 in this age group was -125 μmol/L (standard deviation 265.9 μmol/L).
16. How is Sephience supplied
How Supplied
SEPHIENCE (sepiapterin) oral powder is supplied as a yellow to orange powder in a unit-dose heat-sealed laminated aluminum foil packet. Each packet contains:
250 mg sepiapterin per packet:
NDC 52856-201-03 Carton of 30-unit dose packets
NDC 52856-201-01 Single unit dose packet
1,000 mg sepiapterin per packet:
NDC 52856-301-03 Carton of 30-unit dose packets
NDC 52856-301-01 Single unit dose packet
Storage and Handling
Store SEPHIENCE at room temperature between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursion permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Store SEPHIENCE liquid or soft food mixture either refrigerated or at controlled room temperature [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient and/or caregiver to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Increased Bleeding
Inform the patient about the increased risk of bleeding associated with SEPHIENCE and to follow up with his/her healthcare provider if he/she experiences any symptoms of increased bleeding.
Drug Interactions
Advise the patient to inform his/her healthcare provider if he/she is taking, or plan to take, any prescription or over-the-counter medications and supplements because of the potential for drug interactions [see Drug Interactions (7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Feces Discoloration
Advise patients that SEPHIENCE may cause feces to have a yellow or orange discoloration.
Manufactured by
Allphamed PHARBIL Arzneimittel GmbH
Hildebrand str. 12,
37081 Gottingen,
Germany (DEU)
Manufactured for:
PTC Therapeutics, Inc.
Warren, NJ 07059
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Issued: 07/2025 |
|
PATIENT INFORMATION
SEPHIENCE (seh-FIGH-ence) |
|
|
What is SEPHIENCE? SEPHIENCE is a prescription medicine used to lower blood levels of phenylalanine (Phe) in adults and children 1 month of age and older with a certain type of Phenylketonuria (PKU). SEPHIENCE is used along with a Phe-restricted diet. |
|
|
Before taking or giving SEPHIENCE, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. SEPHIENCE and other medicines may affect each other causing side effects. SEPHIENCE may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how SEPHIENCE works. Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them with you to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. |
|
|
How should I take or give SEPHIENCE?
|
|
|
What are the possible side effects of SEPHIENCE? SEPHIENCE may cause serious side effects including:
The most common side effects of SEPHIENCE include: diarrhea, headache, stomach (abdominal) pain, yellow or orange stool (feces), and throat pain. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all of the possible side effects of SEPHIENCE. Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. You may also report side effects to PTC Therapeutics, Inc. at 1-866-562-4620 or email at usmedinfo@ptcbio.com. |
|
|
How should I store SEPHIENCE?
Keep SEPHIENCE and all medicines out of the reach of children. |
|
|
General information about the safe and effective use of SEPHIENCE. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use SEPHIENCE for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give SEPHIENCE to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about SEPHIENCE that is written for health professionals. |
|
|
What are the ingredients in SEPHIENCE? Active ingredients: sepiapterin Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, isomalt, magnesium stearate, mannitol, Manufactured by: Allphamed PHARBIL Arzneimittel GmbH |
|
|
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
SEPHIENCE (seh-FIGH-ence) |
|
|
This Instructions for Use contains information on how to prepare, take, or give SEPHIENCE. Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you have any questions on how to prepare, take, or give SEPHIENCE. The preparation steps differ based on the prescribed dose. Follow the steps specific to the dose your healthcare provider has prescribed. See the section called:
|
|
|
Each SEPHIENCE carton contains:
|
|
|
|
|
|
Important Information you need to know before taking or giving SEPHIENCE:
|
|
|
Storing SEPHIENCE:
Keep SEPHIENCE and all medicines out of the reach of children. |
|
|
Preparing to mix SEPHIENCE oral powder: |
|
| Instructions for SEPHIENCE Doses Less Than 1,000 mg: | |
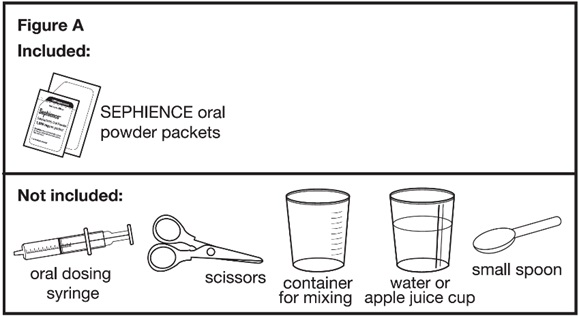
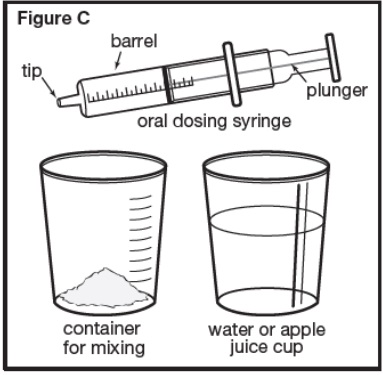
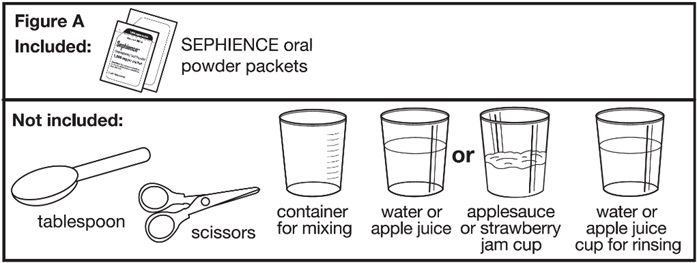
Supplies needed to mix and give SEPHIENCE doses less than 1,000 mg (see Figure A):
|
|
|
Supplies not included with the SEPHIENCE oral powder packet carton(s):
Ask your pharmacist for a container for mixing SEPHIENCE and an oral dosing syringe if you do not have these supplies. | |
|
Step 1: Find a clean, flat work surface. Place the following items on your clean, flat work surface:
| |
|
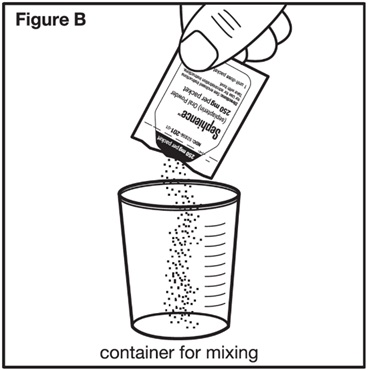
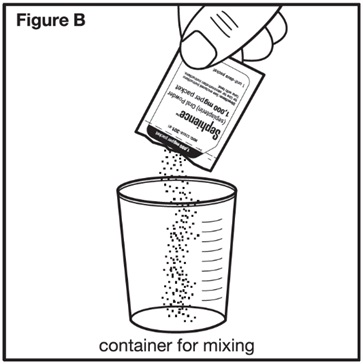
Step 2: Check the label on the SEPHIENCE oral powder packet(s) to make sure you have the number of packets for the prescribed dose. Open the SEPHIENCE oral powder packet(s) by folding and tearing at the tear notch, or using scissors to cut the packet(s) open at the dotted line. Empty the entire contents of each SEPHIENCE oral powder packet(s) into the container for mixing (see Figure B). | |
|
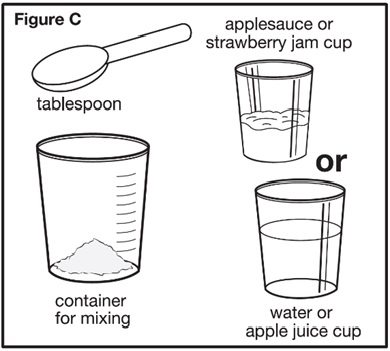
Step 3: Place the tip of the oral dosing syringe into the cup containing the water or apple juice. Pull back on the plunger and draw up the amount of water or apple juice needed to prepare the packet(s) for the prescribed dose. Use 9 mL of water or apple juice for each 250 mg packet. For example:
If you are using one 1,000 mg packet to prepare the prescribed dose, you will need to add 36 mL of water or apple juice. Slowly add the water or apple juice to the container for mixing containing the SEPHIENCE oral powder. Repeat until the entire amount of water or apple juice that is needed to mix the number of SEPHIENCE oral powder packets has been added to the container for mixing (see Figure C). | |
|
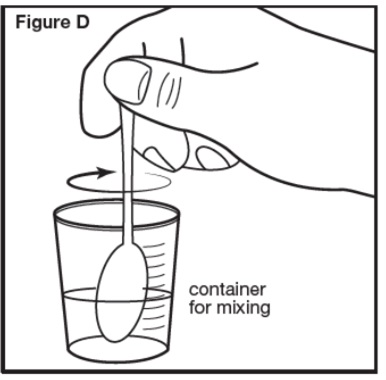
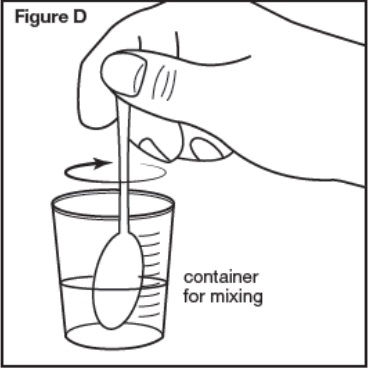
Step 4: Stir the SEPHIENCE oral powder mixed with water or apple juice well for 30 seconds or more with a small spoon until the SEPHIENCE mixture is free of lumps (see Figure D). SEPHIENCE oral powder is not expected to dissolve completely. This is normal. | |
|
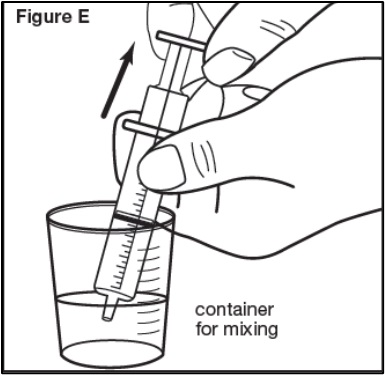
Step 5: Place the tip of the oral dosing syringe into the mixture inside the container used for mixing. Pull back on the plunger until the edge of the plunger lines up with the marking for the dose as instructed by your healthcare provider in mL (milliliters) (see Figure E). | |
|
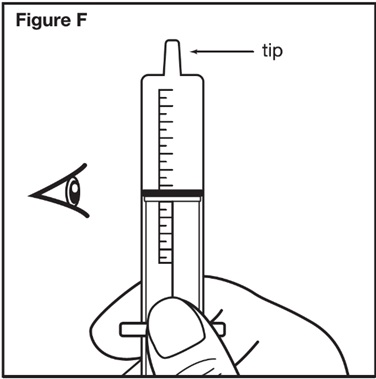
Step 6: Take the oral dosing syringe out of the container used for mixing. Carefully turn the oral dosing syringe so that the tip is pointing up. Check the syringe marking to make sure that the amount of SEPHIENCE mixture in the oral dosing syringe lines up with the prescribed SEPHIENCE dose in mL (milliliters) (see Figure F). Your dose may be different than the dose shown in Figure F. Give SEPHIENCE mixture right away after it is drawn up into the syringe. | |
|
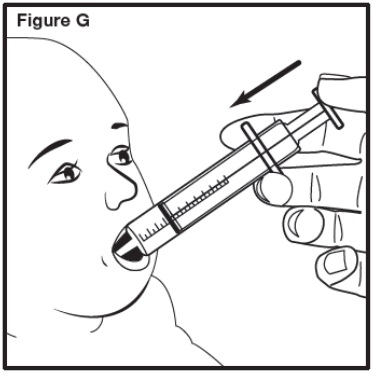
Step 7: Place the tip of the oral dosing syringe into your child’s mouth. Point the tip of the oral dosing syringe toward either cheek (see Figure G). Push on the plunger slowly, until all the mixture in the oral dosing syringe is given. If the prescribed dose is more than 10 mL, repeat Step 5 to Step 7 until you give the total amount of prescribed dose in mL (milliliters) by your healthcare provider. | |
|
Step 8: If there is any mixture left in the oral dosing syringe, draw up more water or apple juice into the oral dosing syringe and give until no mixture is left in the oral dosing syringe. | |
|
Step 9: Throw away any SEPHIENCE mixture remaining in the container used for mixing in the household trash. See Throwing away (disposing of) SEPHIENCE. Remove the plunger from the barrel of the oral dosing syringe. Wash the oral dosing syringe and container used for mixing with warm water and air dry. When the oral dosing syringe is dry, put the plunger back into the barrel. Store the oral dosing syringe and container used for mixing for the next use. |
|
| Instructions for SEPHIENCE Doses 1,000 mg or Greater: | |
|
Supplies needed to mix and take or give SEPHIENCE doses 1,000 mg or greater (see Figure A):
|
|
|
Supplies not included with the SEPHIENCE oral powder packet carton(s):
| |
|
|
| Find your prescribed number of packets: | Choose one of the following:
|
|
|
|
| Amount of water, apple juice, strawberry jam, or applesauce to mix the packet(s) |
| 1 | 0 | 2 Tbsp or 30 mL |
| 1 | 1 | 4 Tbsp or 60 mL |
| 1 | 2 | 4 Tbsp or 60 mL |
| 1 | 3 | 4 Tbsp or 60 mL |
| 2 | 0 | 4 Tbsp or 60 mL |
| 2 | 1 | 6 Tbsp or 90 mL |
| 2 | 2 | 6 Tbsp or 90 mL |
| 2 | 3 | 6 Tbsp or 90 mL |
| 3 | 0 | 6 Tbsp or 90 mL |
| 3 | 1 | 8 Tbsp or 120 mL |
| 3 | 2 | 8 Tbsp or 120 mL |
| 3 | 3 | 8 Tbsp or 120 mL |
| 4 | 0 | 8 Tbsp or 120 mL |
| 4 | 1 | 10 Tbsp or 150 mL |
| 4 | 2 | 10 Tbsp or 150 mL |
| 4 | 3 | 10 Tbsp or 150 mL |
| 5 | 0 | 10 Tbsp or 150 mL |
| 5 | 1 | 12 Tbsp or 180 mL |
| 5 | 2 | 12 Tbsp or 180 mL |
| 5 | 3 | 12 Tbsp or 180 mL |
| 6 | 0 | 12 Tbsp or 180 mL |
Ask your pharmacist for a container for mixing SEPHIENCE if you do not have these supplies.
|
Step 1: Find a clean, flat work surface. Place the following items on your clean, flat work surface:
| |
|
Step 2: Check the label on the SEPHIENCE oral powder packet(s) to make sure you have the number of packets for the prescribed dose. Open the SEPHIENCE oral powder packet(s) by folding and tearing at the tear notch or using scissors to cut the packet(s) open at the dotted line. Empty the entire contents of each SEPHIENCE oral powder packet(s) into the container for mixing (see Figure B). | |
|
Step 3: Mix the SEPHIENCE oral powder packet(s) with water, apple juice, strawberry jam, or applesauce. See Table 1 above. Slowly add the water, apple juice, strawberry jam, or applesauce to the container for mixing containing the SEPHIENCE oral powder. Repeat until the entire amount of water, apple juice, strawberry jam, or applesauce that is needed to mix the number of SEPHIENCE oral powder packets has been added to the container for mixing (see Figure C). | |
|
Step 4: If you used water or apple juice to mix the SEPHIENCE oral powder packet(s), stir the mixture well for 30 seconds or more with the tablespoon until the SEPHIENCE mixture is free of lumps (see Figure D). SEPHIENCE oral powder is not expected to dissolve completely. If you used strawberry jam or applesauce to mix the SEPHIENCE oral powder packet(s), stir the mixture well for 60 seconds or more with the tablespoon. | |
|
Step 5: Give or take all of the SEPHIENCE mixture from the container used for mixing. |
|
|
Step 6: If any SEPHIENCE mixture remains in the container used for mixing, rinse the container with water or apple juice (at least 15 mL). Swallow the rinse right away. Repeat this step until no mixture remains in the container used for mixing. |
|
|
Step 7: Wash the container used for mixing with warm water and air dry. Store the container used for mixing for the next use. |
|
Throwing away (disposing of) SEPHIENCE:
- Ask your pharmacist how to properly throw away (dispose of) SEPHIENCE oral powder packet(s) that are not needed or that have expired.
Manufactured by:
Allphamed PHARBIL Arzneimittel GmbH
Hildebrand str. 12,
37081 Gottingen,
Germany (DEU)
Manufactured for:
PTC Therapeutics, Inc.
Warren, NJ 07059
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Approved: 07/2025
| SEPHIENCE
sepiapterin powder |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| SEPHIENCE
sepiapterin powder |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - PTC Therapeutics Inc. (124371951) |