Methylene Blue Injection: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Dosage form: injection, solution
Drug classes: Antidotes, Miscellaneous diagnostic dyes
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jun 23, 2025.
On This Page
WARNING: SEROTONIN SYNDROME WITH CONCOMITANT USE OF SEROTONERGIC DRUGS
Methylene Blue Injection may cause serious or fatal serotonergic syndrome when used in combination with serotonergic drugs. Avoid concomitant use of Methylene Blue Injection with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (see WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions).
Methylene Blue Injection Description
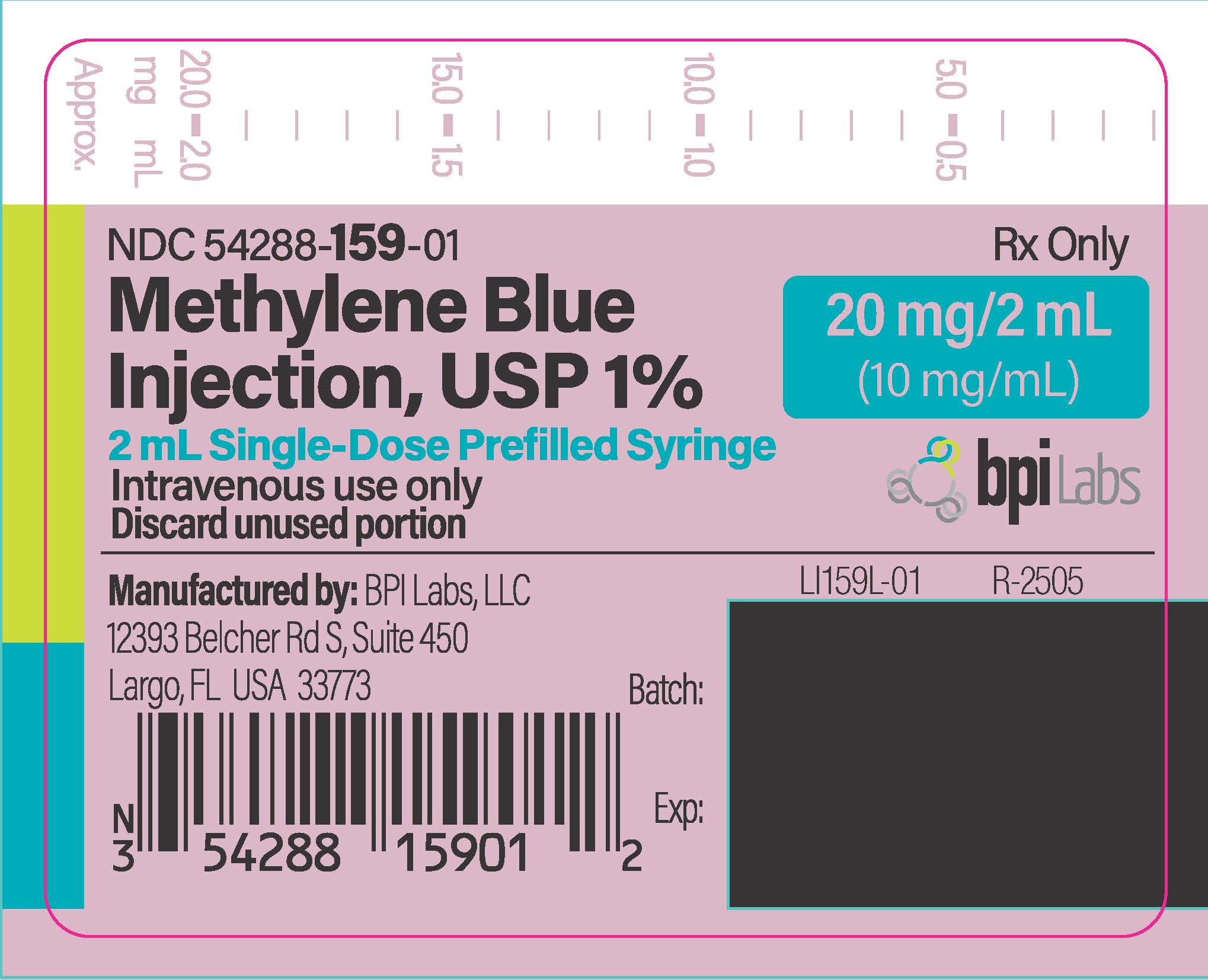
Methylene Blue Injection is a sterile solution of Phenothiazin-5-ium, 3, 7-bis (dimethylamino)-, chloride, trihydrate. Each mL contains methylene blue, 10 mg in water for injection q.s. pH adjusted with sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid when necessary.
The structural formula is:
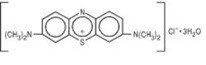
The molecular formula is:
C16H18ClN3S•3H2O MW = 373.90
Methylene Blue Injection - Clinical Pharmacology
Methylene blue will produce two opposite actions on hemoglobin. Low concentrations will convert methemoglobin to hemoglobin. High concentrations convert the ferrous iron of reduced hemoglobin to ferric iron which results in the formation of methemoglobin.
Methylene blue is metabolized in the body to leukomethylene blue which is excreted primarily in the urine. Some unchanged drug is also excreted in the urine. (1)
Contraindications
Methylene blue can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. An association exists between the use of methylene blue in amniocentesis and atresia of the ileum and jejunum, ileal occlusions, and other adverse effects in the neonate. (2, 3)
Methylene blue is contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
Intraspinal and subcutaneous injections are contraindicated.
Methylene blue is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to the drug.
Warnings
Methylene blue should not be given by subcutaneous or intrathecal injection.
Methylene blue is a potent monoamine oxidase inhibitor:Methylene blue has been demonstrated to be a potent monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) and may cause potentially fatal serotonin toxicity (serotonin syndrome) when combined with serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SRIs). (4) (see DRUG INTERACTIONS.) Serotonin toxicity is characterized by development of neuromuscular hyperactivity (tremor, clonus, myoclonus, and hyperreflexia, and, in the advanced stage, pyramidal rigidity); autonomic hyperactivity (diaphoresis, fever, tachycardia, tachypnoea, and mydriasis); and altered mental status (agitation, excitement, and in the advanced stage, confusion). If methylene blue is judged to be indicated, SRIs must be ceased, prior to treatment/procedure/surgery.
Precautions
Drug Interactions:Methylene blue may interact with any drug that acts as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SRI) including, amongst others, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors (NDRIs), triptans and ergot alkaloids; such combinations may have the consequence of potentially fatal serotonin toxicity (serotonin syndrome). Methylene blue should not be co- administered with any drug that acts as an SRI.
Pregnancy: Pregnancy Category X:Epidemiologic evidence exists that methylene blue is a teratogen. An association exists between the use of methylene blue in amniocentesis and atresia of the ileum and jejunum, ileal occlusions, and other adverse effects in the neonate. (2,3) Methylene blue injection should not be administered to pregnant women during amniocentesis due to the risk of teratogenicity and other newborn adverse effects (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency (G6PD Deficiency):Methylene blue should be avoided in patients with G6PD deficiency due to the risk of paradoxical methemoglobinemia and hemolysis. (5,6)
Renal Failure:Methylene blue should be used with caution in patients with severe renal impairment (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
Methylene blue must be injected intravenously very slowly over a period of several minutes to prevent local high concentration of the compound from producing additional methemoglobin. Do not exceed recommended dosage.
Large intravenous doses of methylene blue produce nausea, abdominal and precordial pain, dizziness, headache, profuse sweating, mental confusion, and the formation of methemoglobin.
Related/similar drugs
Methylene Blue Injection Dosage and Administration
0.1 to 0.2 mL per kg body weight (0.045 to 0.09 mL per pound body weight). Inject methylene blue intravenously very slowly over a period of several minutes.
Methylene blue must be injected intravenously very slowly over a period of several minutes to prevent local high concentration of the compound from producing additional methemoglobin. Do not exceed recommended dosage. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration, whenever solution and container permit.
How is Methylene Blue Injection supplied
Methylene Blue Injection, USP 1% is supplied as follows:
NDC 54288-159-05
Five 2 mL Single-Dose Prefilled Syringes packed in a carton
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact BPI Labs LLC at 727-471-0850 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
References
- DiSanto AR, Wagner JG. Pharmacokinetics of highly ionized drugs II: methylene blue – absorption, metabolism, and excretion in man and dog after oral administration. J Pharm Sci. 1972; 61:1086- 1090.
- Cragan JD. Teratogen update: methylene blue. Teratology. 1999; 60:42-48.
- Kidd SA, Lancaster PA, Anderson JC, Boogert A, Fisher CC, Robertson R, et al. Fetal death after exposure to methylene blue dye during mid-trimester amniocentesis in twin pregnancy. Prenat Diagn. 1996; 16:39-47.
- Ramsay RR, Dunford C, Gillman PK. Methylene blue and serotonin toxicity: inhibition of monoamine oxidase A (MAOA) confirms a theoretical prediction. Br J Pharmacol. 2007; 152:946-51.
- Beutler E. G6PD Deficiency. Blood. 1994; 84:3613-3636.
- Youngster I, Arcavi L, Schechmaster R, Akayzen Y, Popliski H, Shimonov J, Beig S, Berkovitch M. Medications and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency: an evidence-based review. Drug Saf. 2010; 33:713-726.
| METHYLENE BLUE
methylene blue injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - BPI LABS LLC (078627620) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| BPI LABS LLC | 078627620 | analysis(54288-159) , manufacture(54288-159) , label(54288-159) | |
Frequently asked questions
More about methylene blue
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (2)
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: antidotes
- En español