Iwilfin: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: eflornithine hydrochloride
Dosage form: tablet
Drug class: Miscellaneous antineoplastics
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Dec 17, 2024.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Use In Specific Populations
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
Highlights of Prescribing Information
IWILFIN™ (eflornithine) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2023
Recent Major Changes
| Dosage and Administration (2.3) | 11/2024 |
Indications and Usage for Iwilfin
IWILFIN is an ornithine decarboxylase inhibitor indicated to reduce the risk of relapse in adult and pediatric patients with high-risk neuroblastoma (HRNB) who have demonstrated at least a partial response to prior multiagent, multimodality therapy including anti-GD2 immunotherapy. (1)
Iwilfin Dosage and Administration
- Prior to initiation of IWILFIN, perform baseline audiogram, complete blood count, and liver function tests. (2.1, 5.3)
- Recommended dosage of IWILFIN is based on body surface area (see Table 1). (2.2)
- IWILFIN is taken orally twice daily with or without food until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or for a maximum of two years. (2.2)
- IWILFIN tablets may be swallowed whole, chewed, or crushed and mixed with soft food or liquid. (2.5)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 192 mg (3)
Contraindications
None (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Myelosuppression: Monitor blood counts before and during treatment with IWILFIN. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity. (5.1)
- Hepatotoxicity: Monitor liver function tests before and during treatment with IWILFIN. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity. (5.2)
- Hearing Loss: Monitor hearing before and during treatment with IWILFIN. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity. (5.3)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.4, 8.1, 8.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5%) are hearing loss, otitis media, pyrexia, pneumonia, and diarrhea. (6.1)
- Most common Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (incidence ≥2%) are increased ALT, increased AST, decreased neutrophil count, and decreased hemoglobin. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact US WorldMeds at 1-877-IWILFIN or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
Use In Specific Populations
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
Renal Impairment: Reduce the dose in patients with estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR) <30 mL/min. (2.3, 8.5, 12.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 11/2024
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Iwilfin
IWILFIN (eflornithine) is indicated to reduce the risk of relapse in adult and pediatric patients with high-risk neuroblastoma (HRNB) who have demonstrated at least a partial response to prior multiagent, multimodality therapy including anti-GD2 immunotherapy.
2. Iwilfin Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Testing Before Initiating IWILFIN
Prior to initiating IWILFIN, perform complete blood count, liver function tests, and baseline audiogram [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1-5.3)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage of IWILFIN
The recommended IWILFIN dosage, based on body surface area (BSA), is provided in Table 1.
Administer IWILFIN orally twice daily for two years or until recurrence of disease or unacceptable toxicity.
Recalculate the BSA dosage every 3 months during treatment with IWILFIN.
| Body Surface Area (m2) | Dosage |
|---|---|
| >1.5 | 768 mg (four tablets) orally twice a day |
| 0.75 to 1.5 | 576 mg (three tablets) orally twice a day |
| 0.5 to < 0.75 | 384 mg (two tablets) orally twice a day |
| 0.25 to < 0.5 | 192 mg (one tablet) orally twice a day |
2.3 Dosage Recommendations for Renal Impairment
For the treatment of patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR <30 mL/min), reduce the recommended dose of IWILFIN by 50% as described in Table 2 [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
| Body Surface Area (m2) | Recommended Dosage for Patients with Severe Renal Impairment (eGFR <30 mL/min) |
|---|---|
| >1.5 | 384 mg (two tablets) orally twice a day |
| 0.75 to 1.5 | 384 mg (two tablets) in the morning and 192 mg (one tablet) in the evening |
| 0.5 to < 0.75 | 192 mg (one tablet) orally twice a day |
| 0.25 to < 0.5 | 192 mg (one tablet) once a day |
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
The recommended dose reductions for adverse reactions are provided in Table 3.
| Current Dose | Reduced Dose |
|---|---|
| 768 mg (four tablets) orally twice a day | 576 mg (three tablets) orally twice a day |
| 576 mg (three tablets) orally twice a day | 384 mg (two tablets) orally twice a day |
| 384 mg (two tablets) orally twice a day | 192 mg (one tablet) orally twice a day |
| 192 mg (one tablet) orally twice a day | 192 mg (one tablet) orally once daily |
If subsequent adverse reactions occur, continue dose reduction until reaching the minimum dose of one 192 mg tablet once per day. Permanently discontinue IWILFIN if the patient is unable to tolerate the minimum dose of 192 mg once daily.
The recommended dosage modifications of IWILFIN for the management of adverse reactions are provided in Table 4.
| Adverse Reaction | Severity* | Dosage Modification |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | ||
| Neutrophil count decreased | <500/mm3 | Withhold IWILFIN until recovery to ≥500/mm3.
|
| Platelet count decreased | <25,000/mm3 | Withhold IWILFIN until recovery to ≥25,000/mm3.
|
| Anemia | <8g/dL | Withhold IWILFIN until recovery to ≥8g/dL.
|
| Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | ||
| Aspartate aminotransferase increased or Alanine aminotransferase increased | AST or ALT ≥10 × ULN | Withhold IWILFIN until recovery to <10 × ULN.
|
| Hearing Loss [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] | ||
| Hearing loss | Clinically concerning new or worsening hearing loss compared to IWILFIN baseline audiogram | Continue dosing with IWILFIN and repeat audiogram in 3 weeks.
|
| Other Adverse Reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] | ||
| Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea | Grade 3 | If symptoms respond to supportive treatment (e.g., anti-emetic, anti-diarrheal), continue dosing with IWILFIN at the same dose. If symptoms do not respond to treatment,
|
| Other adverse reactions | Grade 3 or 4 | Withhold IWILFIN until recovery to ≤ Grade 2.
|
| Recurrent Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue IWILFIN. | |
2.5 Administration, Crushed Preparation, and Missed Dose Instructions
Administration
- Administer IWILFIN orally twice daily, with or without food, for two years or until recurrence of disease or unacceptable toxicity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- IWILFIN tablets can be swallowed whole, chewed, or crushed.
Crushed Preparation
- For patients who have difficulty swallowing tablets, IWILFIN can be chewed, or crushed then mixed with two tablespoons of soft food or liquid.
- Visually confirm the entire contents are consumed. If any crushed tablet particles remain in the container, mix with an additional small volume (e.g., no more than one ounce, 30 mL) of soft food or liquid.
- Discard crushed tablet preparation after one hour.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 192 mg eflornithine, white to off-white, round, imprinted with "EFL" on one side and "192" on the other side.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Myelosuppression
IWILFIN can cause myelosuppression. In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia occurred in 4.2% of patients. Febrile neutropenia occurred in 0.6% of patients. Bone marrow failure occurred in 1 patient. Grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia occurred in 1.4% of patients. Grade 3 anemia occurred in 3.3% of patients.
Monitor blood counts including neutrophil count, platelet count, and hemoglobin level prior to administration of IWILFIN and periodically during treatment. Withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue IWILFIN based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.2 Hepatotoxicity
IWILFIN can cause hepatotoxicity. In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], Grade 3 or 4 events of increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT) occurred in 11% of patients. Grade 3 or 4 events of increased aspartate aminotransferase (AST) occurred in 6% of patients. Grade 3 or 4 events of increased bilirubin occurred in 0.3% of patients. Increased ALT/AST leading to dose interruption or reduction occurred in 2.5% of patients. IWILFIN was discontinued due to increased ALT/AST in 0.6% of patients.
Perform liver function tests (ALT, AST, and total bilirubin) prior to the start of IWILFIN, every month for the first six months of treatment, then once every 3 months or as clinically indicated, with more frequent testing in patients who develop transaminase or bilirubin elevations. Withhold and reduce the dose or permanently discontinue IWILFIN based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.3 Hearing Loss
IWILFIN can cause hearing loss. In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], 81% of patients had an abnormal audiogram at baseline. New or worsening hearing loss occurred in 13% of patients who received IWILFIN; hearing loss worsened from baseline to Grade 3 or 4 in 12% of patients. Tinnitus occurred in 1 patient. Hearing loss leading to dose interruption or reduction occurred in 4% of patients. New or worsening hearing loss requiring new use of hearing aids occurred in 7% of patients. IWILFIN was discontinued due to hearing loss in 1.4% of patients. Among all patients with new or worsening hearing loss during IWILFIN treatment, the hearing loss resolved to baseline in 9% of patients. Among 18 patients who experienced new or worsening hearing loss and had dose modifications, 67% (N=12) improved or resolved to baseline.
Perform audiogram prior to initiation of therapy and at 6 month intervals, or as clinically indicated, to monitor for potential hearing loss. Withhold and reduce the dose or permanently discontinue IWILFIN based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.4)].
5.4 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action, IWILFIN can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of eflornithine to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in embryolethality at doses equivalent to the recommended human dose.
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with IWILFIN and for 1 week after the last dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with IWILFIN and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hearing Loss [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect rates observed in clinical practice.
The pooled safety population described in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflect exposure to IWILFIN as a single agent, taken orally at doses ranging from 192 - 768 mg twice daily, based on body surface area (BSA), until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or for a maximum of 2 years in patients who demonstrated at least a partial response to prior multiagent, multimodality therapy for newly diagnosed or relapsed/refractory high-risk neuroblastoma in Study 3b (n=101; NCT02395666) and Study 14 (n=259; NCT02679144). Among 360 patients who received IWILFIN, 84% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 73% were exposed for greater than one year. In this pooled safety population, the most common (≥5%) adverse reactions were hearing loss (11%), otitis media (10%), pyrexia (7%), pneumonia (5%), and diarrhea (5%). The most common (≥2%) Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities were increased ALT (11%), increased AST (6%), decreased neutrophils (4.2%), and decreased hemoglobin (3.3%).
Study 3b
The safety of IWILFIN was evaluated in Study 3b [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Eligible patients were pediatric patients with high-risk neuroblastoma (HRNB) who demonstrated at least a partial response to prior multiagent, multimodality therapy including induction, consolidation, and anti-GD2 immunotherapy. Patients received IWILFIN as a single agent taken orally at doses ranging from 192 - 768 mg twice daily, based on body surface area (BSA), until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or for a maximum of 2 years (N=85). Among patients who received IWILFIN, 93% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 89% were exposed for greater than one year.
The median age of patients who received IWILFIN was 4 years (range: 1 to 17); 59% male; 85% White, 7% Black, 1% Asian, 8% Hispanic or Latino; 87% had International Neuroblastoma Staging System Stage 4 disease; 47% had neuroblastoma with known MYCN-amplification.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 12% of patients who received IWILFIN. Serious adverse reactions in >1 patient included skin infection (3 patients).
Permanent discontinuation of IWILFIN due to an adverse reaction occurred in 11% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of IWILFIN in >1 patient included hearing loss.
Dose reductions of IWILFIN due to an adverse reaction occurred in 8% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dose reductions in >1 patient included hearing loss.
The most common (≥5%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, were otitis media, diarrhea, cough, sinusitis, pneumonia, upper respiratory tract infection, conjunctivitis, vomiting, pyrexia, allergic rhinitis, decreased neutrophils, increased ALT, increased AST, hearing loss, skin infection, and urinary tract infection.
Table 5 summarizes the adverse reactions in Study 3b.
| Adverse Reaction* | IWILFIN (n=85) |
|
|---|---|---|
| All Grades†,‡
(%) | Grade 3 (%) |
|
| Infections | ||
| Otitis media | 32 | 2.4 |
| Sinusitis | 13 | 0 |
| Pneumonia | 12 | 1.2 |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 11 | 0 |
| Conjunctivitis | 11 | 0 |
| Skin infection | 7 | 4.7 |
| Urinary tract infection | 6 | 1.2 |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||
| Diarrhea§ | 15 | 3.5 |
| Vomiting | 11 | 1.2 |
| Respiratory Disorders | ||
| Cough | 15 | 0 |
| Allergic rhinitis | 11 | 0 |
| General Disorders | ||
| Pyrexia | 11 | 1.2 |
| Ear and Labyrinth Disorders | ||
| Hearing loss | 7 | 7 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in <5% of patients who received IWILFIN included rash, extremity pain, and alopecia.
Table 6 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in Study 3b.
| Laboratory Abnormality* | IWILFIN (n=85) |
|
|---|---|---|
| All Grades†,‡
(%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) |
|
| Chemistry | ||
| Increased ALT | 9 | 7§ |
| Increased AST | 8 | 6§ |
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 4.7 | 2.4§ |
| Decreased potassium | 2.4 | 2.4§ |
| Decreased glucose | 2.4 | 1.1 |
| Decreased sodium | 2.4 | 2.4§ |
| Increased potassium | 1.2 | 0 |
| Increased glucose | 1.2 | 0 |
| Hematology | ||
| Decreased neutrophils | 9 | 8 |
| Decreased hemoglobin | 4.7 | 2.4§ |
| Decreased white blood cells | 2.4 | 0 |
| Decreased platelets | 1.2 | 0 |
Related/similar drugs
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], IWILFIN can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of eflornithine to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in embryolethality at doses equivalent to the recommended human dose [see Data]. There are no available data on the use of IWILFIN in pregnant women. Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal development study, once daily oral administration of 30, 80 or 200 mg/kg/day eflornithine to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis (gestation day 6 to 7) resulted in reduced fetal body weights and an increase in the incidence of skeletal variations (presence of a 14th rudimentary rib, 14th full rib, 27th presacral vertebrae) at 200 mg/kg/day [approximately 0.8 to 2 times the recommended human dose of 1152 ± 384 mg/m2/day based on body surface area (BSA)]. In a dose range-finding embryo-fetal development study, pregnant rats receiving oral administration of up to 2000 mg/kg/day eflornithine during the period of organogenesis exhibited increased early resorptions and post-implantation loss beginning at 300 mg/kg/day (approximately 1 to 2 times the recommended human dose of 1152 ± 384 mg/m2/day based on BSA), with 100% post-implantation loss and no viable fetuses at ≥800 mg/kg/day (approximately ≥3 to 6 times the recommended human dose of 1152 ± 384 mg/m2/day based on BSA).
In an embryo-fetal development study in rabbits, once daily oral administration of 15, 45 or 135 mg/kg/day eflornithine to pregnant animals during the period of organogenesis (gestation day 7 to 20) resulted in reduced gravid uterine weight accompanied by increased pre-implantation and post-implantation loss, increased early resorptions, and reduced fetal body weights at 135 mg/kg/day (approximately 1 to 2 times the recommended human dose of 1152 ± 384 mg/m2/day based on BSA). Eflornithine resulted in abortions in one animal at 15 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.1 to 0.2 times the recommended human dose of 1152 ± 384 mg/m2/day based on BSA) and one animal at 135 mg/kg/day. In a dose range-finding embryo-fetal development study, pregnant rabbits receiving oral administration of up to 500 mg/kg/day eflornithine during the period of organogenesis exhibited 100% post-implantation loss and no viable fetuses at 500 mg/kg/day (approximately 4 to 8 times the recommended human dose of 1152 ± 384 mg/m2/day based on BSA). There was no clear evidence of eflornithine-related fetal malformations in rats or rabbits.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of eflornithine in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed children, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with IWILFIN and for 1 week after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Based on animal data and its mechanism of action, IWILFIN can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating IWILFIN [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of IWILFIN have been established to reduce the risk of relapse in pediatric patients with high-risk neuroblastoma (HRNB) who have demonstrated at least a partial response to prior multiagent, multimodality therapy including anti-GD2 immunotherapy. Use of IWILFIN for this indication is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies in pediatric patients with a median age of 4 years (range: 1 to 17) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), Clinical Studies (14.1)].
The safety and effectiveness of IWILFIN have not been established in pediatric patients for other indications [see Indications and Usage (1)].
8.5 Renal Impairment
Patients with moderate (eGFR <60 mL/min) and severe (eGFR <30 mL/min) renal impairment have a higher exposure to eflornithine than patients with normal renal function which can increase the risk for toxicity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Reduce the dose in patients with severe renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Monitor patients with moderate renal impairment closely for increased adverse reactions including hepatotoxicity, myelosuppression, and hearing loss [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
11. Iwilfin Description
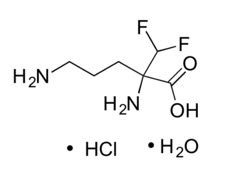
IWILFIN is an ornithine decarboxylase inhibitor. The chemical name of eflornithine hydrochloride is 2,5-diamino-2-(difluoromethyl) pentanoic acid hydrochloride hydrate with a molecular formula of C6H12F2N2O2∙HCl∙H2O. Its molecular weight is 236.65g/mol for the salt and hydrate form and 182.17 g/mol for the anhydrous free base form. Eflornithine hydrochloride is a white to off-white powder, freely soluble in water and sparingly soluble in ethanol. The chemical structure of eflornithine hydrochloride is:
IWILFIN is available as a round, white to off-white tablet for oral administration. Each tablet contains 192 mg eflornithine, equivalent to 250 mg of eflornithine hydrochloride, and the following inactive ingredients: 220 mg silicified microcrystalline cellulose, 25 mg partially pregelatinized maize starch, 2.5 mg colloidal silicon dioxide, and 2.5 mg vegetable source magnesium stearate.
12. Iwilfin - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Eflornithine is an irreversible inhibitor of the enzyme ornithine decarboxylase (ODC), the first and rate-limiting enzyme in the biosynthesis of polyamines and a transcriptional target of MYCN. Polyamines are involved in differentiation and proliferation of mammalian cells and are important for neoplastic transformation. Inhibition of polyamine synthesis by eflornithine restored the balance of the LIN28/Let-7 metabolic pathway, which is involved in regulation of cancer stem cells and glycolytic metabolism, by decreasing expression of the oncogenic drivers MYCN and LIN28B in MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma. In vitro, eflornithine induced senescence and suppressed neurosphere formation in MYCN-amplified and MYCN non-amplified neuroblastoma cells, indicating a cytostatic effect. Treatment with eflornithine prevented or delayed tumor formation in mice injected with limiting dilutions of MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma cells.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Eflornithine exposure-response relationships and the time course of pharmacodynamic responses are unknown.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following oral administrations of IWILFIN, peak plasma concentrations of eflornithine (Cmax) were achieved (Tmax) 3.5 hours post dosing.
Distribution
Eflornithine does not specifically bind to human plasma proteins. Eflornithine volume of distribution (Vz/F) is 24.3 L.
Specific Populations
Pharmacokinetic analyses from patients in Study 14 suggested that age (1 year to 19 years), sex, or body surface area (0.4 m2 to 2 m2), and mild hepatic impairment (bilirubin ≤ULN and AST>ULN or bilirubin >1 × ULN and any AST) had no clinically meaningful effects on eflornithine exposure.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a 2-year carcinogenicity study, once daily oral administration of eflornithine to female rats did not result in drug-related neoplasms at doses up to 600 mg/kg/day (10.5 times the human Cmax at the recommended clinical dose of 1152 ± 384 mg/m2).
Eflornithine was not mutagenic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay.
Dedicated fertility studies were not conducted with eflornithine.
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of IWILFIN is based on an externally controlled trial comparison of Study 3b (investigational arm) and Study ANBL0032 (clinical trial-derived external control arm).
Study 3b
Study 3b (NCT02395666) was a multi-center, open label, non-randomized trial with two cohorts. Eligible patients in one cohort (Stratum 1) were pediatric patients with high-risk neuroblastoma (HRNB) who demonstrated at least a partial response to prior multiagent, multimodality therapy, including induction, consolidation, and anti-GD2 immunotherapy. A total of 105 eligible patients received IWILFIN orally twice daily, dosage based on body surface area (BSA) until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or for a maximum of 2 years [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. Tumor assessments were performed at 3, 6, 9, 12, 18 months, completion of treatment, and as clinically indicated. Following completion of IWILFIN therapy, patients were followed for a total duration of 7 years. The major efficacy outcome measure was event free survival (EFS), defined as disease progression, relapse, secondary cancer, or death due to any cause. An additional efficacy outcome measure was overall survival (OS), defined as death due to any cause. Study 3b was prospectively designed to compare outcomes to the historical EFS rate from Study ANBL0032 reported in published literature.
External Comparator: ANBL0032
The external control arm was derived from 1,241 patients on the experimental arm of Study ANBL0032, a multi-center, open-label, randomized trial of dinutuximab, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, interleukin-2, and cis-retinoic acid compared to cis-retinoic acid alone in pediatric patients with HRNB previously treated with induction and consolidation therapy who achieved at least a partial response to prior autologous stem cell transplant. Tumor assessments were performed post-immunotherapy at 3, 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 30, and 36 months, then per standard of care for a total of 10 years.
Externally Controlled Trial
The efficacy population for the comparative analysis of Study 3b and ANBL0032 included patients from both studies who were less than 21 years of age with histologic verification of HRNB and who demonstrated at least a partial response based on imaging, with no evidence of disease in the bone marrow, at the end of immunotherapy, and did not experience an EFS event prior to starting IWILFIN maintenance therapy (for Study 3b), or for at least 30 days from the end of immunotherapy (for ANBL0032). Eligible patients on Study 3b received immunotherapy on ANBL0032 or were treated off study according to the ANBL0032 protocol. Patients who met the criteria for the comparison and had complete data for specified clinical covariates were matched (1:3) using propensity scores; the matched efficacy populations for the primary analysis included 90 patients treated with IWILFIN and 270 control patients from ANBL0032. The demographic characteristics of the primary analysis population (N=360) were 59% male; median age at diagnosis 3 years (range: 0.1 to 20.1); 88% White, 6% Black, 4% Asian, 7% Hispanic. The majority of patients had Stage 4 disease (86%) and MYCN amplification was observed in 44% of tumors. End of immunotherapy responses were complete response (CR; 87%), very good partial response (VGPR; 8%), or partial response (PR; 5%).
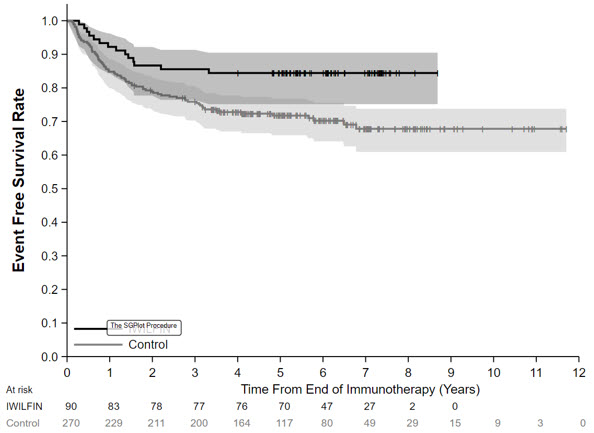
In the protocol-specified primary analysis, the EFS hazard ratio (HR) was 0.48 (95% CI: 0.27, 0.85) and OS HR was 0.32 (95% CI: 0.15, 0.70). The Kaplan-Meier plot for the primary analysis of EFS, with shaded bands for each curve representing the point-wise 95% confidence intervals, is shown in Figure 1. Given the uncertainty associated with the externally controlled study design, supplementary analyses in subpopulations or using alternative statistical methods were performed. In these analyses, the EFS HR ranged from 0.43 (95% CI: 0.23, 0.79) to 0.59 (95% CI: 0.28, 1.27), and the OS HR ranged from 0.29 (95% CI: 0.11, 0.72) to 0.45 (95% CI: 0.21, 0.98).
Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier Curve for Event Free Survival for Protocol-Specified Primary Analysis in the Externally Controlled Trial
16. How is Iwilfin supplied
IWILFIN (eflornithine) is available as 192 mg round, white to off-white tablets imprinted with EFL on one side and 192 on the other side; approximately 11 mm in diameter and supplied as follows:
- Bottle of 100 tablets containing desiccant, NDC 78670-150-01
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Myelosuppression
Inform patients and caregivers of the risk of bone marrow suppression and to promptly report any signs or symptoms of thrombocytopenia, anemia, or infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Hepatotoxicity
Inform patients and caregivers of the risk of hepatotoxicity and to promptly report any signs or symptoms of hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Hearing Loss
Inform patients and caregivers of the risk of hearing loss, and to promptly report any signs or symptoms of new or worsening hearing loss [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Embryofetal Toxicity
Inform patients and caregivers that IWILFIN can be harmful to a developing fetus and cause loss of pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with IWILFIN and for 1 week after the last dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with IWILFIN and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with IWILFIN and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
US WorldMeds®
Distributed by:
USWM, LLC
4441 Springdale Road
Louisville, KY 40241
©2023. IWILFIN™ is a trademark of USWM, LLC.
FPI-0026.1
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Issued: 12/2023 | |
| Patient Information IWILFIN™ (I-WILL-fin) (eflornithine) tablets |
||
| What is IWILFIN?
IWILFIN is a prescription medicine used to reduce the risk of relapse in adults and children with high-risk neuroblastoma (HRNB) who have had at least a partial response to certain prior therapies. |
||
Before you take IWILFIN, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
|
||
How should I take IWILFIN?
|
||
| What are the possible side effects of IWILFIN? IWILFIN may cause serious side effects, including:
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
| The most common side effects of IWILFIN include: | ||
|
|
|
| These are not all the possible side effects of IWILFIN. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
||
How should I store IWILFIN?
|
||
| General information about the safe and effective use of IWILFIN:
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in the Patient Information leaflet. Do not use IWILFIN for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give IWILFIN to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about IWILFIN that is written for health professionals. |
||
| What are the ingredients in IWILFIN? Active ingredient: eflornithine Inactive ingredients: silicified microcrystalline cellulose, partially pregelatinized maize starch, colloidal silicon dioxide, and vegetable source magnesium stearate. Distributed by: USWM, LLC 4441 Springdale Road Louisville, KY 40241 ©2023. IWILFIN™ is a trademark of USWM, LLC. For more information, go to www.IWILFIN.com or call 1-877-IWILFIN. |
||
| IWILFIN
eflornithine hydrochloride tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - USWM, LLC (117542566) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| ScinoPharm Taiwan Ltd. | 657484726 | API MANUFACTURE(78670-150) , ANALYSIS(78670-150) , PACK(78670-150) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| CoreRx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 780516717 | MANUFACTURE(78670-150) , ANALYSIS(78670-150) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quality Chemical Laboratories | 071344167 | ANALYSIS(78670-150) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aphena Pharma Solutions - TN, LLC | 118348161 | LABEL(78670-150) , PACK(78670-150) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| SGS North America | 808308303 | ANALYSIS(78670-150) | |
More about Iwilfin (eflornithine)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Drug images
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- FDA approval history
- Drug class: miscellaneous antineoplastics
- Breastfeeding
- En español