Garadacimab: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: injection, solution
Drug class: Hereditary angioedema agents
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jul 13, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Use In Specific Populations
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ANDEMBRY® (garadacimab-gxii) injection, for subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2025
Indications and Usage for Garadacimab
ANDEMBRY is an activated Factor XII (FXIIa) inhibitor (monoclonal antibody) indicated for prophylaxis to prevent attacks of hereditary angioedema (HAE) in adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older. (1)
Garadacimab Dosage and Administration
- Recommended Dosage: Initial loading dose of 400 mg (two 200 mg injections) administered subcutaneously followed by maintenance dosage of 200 mg once monthly. (2.1)
- Subcutaneous use only. (2.2)
- Patients may self-administer. See full prescribing information for preparation and administration instructions. (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Contraindications
None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
None. (5)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 7%) are nasopharyngitis and abdominal pain. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact CSL Behring at 1-866-915-6958 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Drug Interference with Laboratory Test: ANDEMBRY can prolong activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) due to an interaction of garadacimab-gxii with the aPTT assay. (7.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 6/2025
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Garadacimab
ANDEMBRY is indicated for prophylaxis to prevent attacks of hereditary angioedema (HAE) in adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older.
2. Garadacimab Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of ANDEMBRY is an initial loading dose of 400 mg (two injections of 200 mg) administered subcutaneously on the first day of treatment followed by a maintenance dosage of 200 mg administered subcutaneously every month.
2.2 Preparation and Administration Instructions for ANDEMBRY Prefilled Autoinjector and Prefilled Syringe with Needle Safety Device
- For subcutaneous use only.
- ANDEMBRY is intended for self-administration or administration by a caregiver. Prior to treatment initiation, train patients/caregivers on proper preparation and subcutaneous (SC) administration technique of ANDEMBRY [see Instructions for Use].
- Prior to administration, remove ANDEMBRY from the refrigerator and allow to sit for 30 minutes at room temperature before use.
- Inspect ANDEMBRY visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. ANDEMBRY is a slightly opalescent to clear, brownish-yellow to yellow solution.
- Administer ANDEMBRY subcutaneously into the thigh or abdomen ensuring to stay 1 inch (2 cm) away from the navel. The upper arm can also be used if a caregiver administers the subcutaneous injection.
- Discard the used ANDEMBRY into a sharps disposal container (closed puncture-resistant container).
- For detailed instructions on the preparation and administration of ANDEMBRY [see Instructions for Use].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: a sterile, preservative-free, slightly opalescent to clear, brownish-yellow to yellow solution available in the following:
- 200 mg/1.2 mL of garadacimab solution in a single-dose prefilled autoinjector
- 200 mg/1.2 mL (167 mg/mL) of garadacimab solution in a single-dose prefilled syringe with needle safety device
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of ANDEMBRY reflects the exposure in a total of 164 adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with hereditary angioedema (HAE) from a placebo-controlled study, VANGUARD [see Clinical Studies (14)], and an open-label clinical study. Among the 164 patients who received at least one dose of ANDEMBRY 200 mg subcutaneously, 153 (93%) patients were exposed for at least one year. The median duration of ANDEMBRY treatment was 2.6 years.
The safety data below is based on the 6-month placebo-controlled study (VANGUARD), in which ANDEMBRY 400 mg was administered subcutaneously as a loading dose followed by 200 mg (N=39) every month in patients with HAE. Demographics of the patients in this study are summarized in Clinical Studies [see Clinical Studies (14)]. The safety of ANDEMBRY was similar across all subgroups of patients, including analysis by age, sex and geographic region.
Table 1 provides the most common adverse reactions with ANDEMBRY with incidence ≥7% and more common than placebo.
| Adverse Reactions | ANDEMBRY (N=39) | Placebo (N=25) |
|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | |
| Nasopharyngitis* | 8 (21) | 3 (12) |
| Abdominal Pain† | 3 (8) | 0 |
Specific Adverse Reaction(s):
Injection Site Reactions
In VANGUARD and an open-label clinical study, which included 57 patients who rolled over from VANGUARD, 164 patients with HAE received ANDEMBRY 200 mg subcutaneously every month. Injection site reactions (e.g., injection site bruising, injection site erythema, injection site hematoma, injection site pruritus, injection site urticaria) were reported in 23 (14%) patients.
Laboratory Abnormalities:
Prolonged Coagulation Tests (aPTT and PT)
In the VANGUARD trial, the incidence of prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), defined as >1.4×ULN, was 3 (8%) patients in the ANDEMBRY group compared to 0 patients in the placebo group. Additionally, the incidence of prolonged prothrombin time (PT) or international normalized ratio (INR), defined as >1.3× ULN, was 6 (15%) patients in the ANDEMBRY group compared to 1 (4%) patient in the placebo group. None of the increases in aPTT, PT and INR were associated with bleeding events [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Related/similar drugs
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Drug Interference with Laboratory Test
Coagulation Tests
ANDEMBRY can prolong activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) due to an interaction of garadacimab-gxii with the aPTT assay. The reagents used in the aPTT laboratory test initiate intrinsic coagulation through the activation of FXII in the contact system, therefore inhibition of plasma FXIIa by ANDEMBRY can prolong aPTT in this assay [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on ANDEMBRY use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Monoclonal antibodies such as garadacimab-gxii are transported across the placenta during the third trimester of pregnancy; therefore, potential effects on a fetus are likely to be greater during the third trimester of pregnancy. In an embryo-fetal development study in pregnant rabbits, garadacimab-gxii produced no evidence of fetal harm at doses up to approximately 100 times the exposure achieved at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 200 mg once monthly. In a pre- and post-natal development study in rabbits, garadacimab-gxii had no effects on survival, growth, or development of F1 offspring at doses resulting in approximately 76 times the exposure achieved at the MRHD (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population(s) is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal development study in pregnant rabbits dosed by the intravenous route every 3 days during the period of organogenesis from gestation days 6 to 18, garadacimab-gxii produced no evidence of fetal harm or maternal toxicity at doses resulting in approximately 100 times the exposure achieved at the MRHD (on an AUC basis with maternal intravenous doses up to 100 mg/kg/dose).
In a pre- and post-natal development study in rabbits dosed by the intravenous or subcutaneous route once every 5 days from the end of implantation (Gestation Day 7) to postpartum day 38 (end of the lactation period), garadacimab-gxii had no effects on survival, growth, or development of F1 offspring at doses resulting in approximately 76 times the exposure achieved at the MRHD (on an AUC basis with a maternal intravenous dose of 100 mg/kg/dose). There was no evidence of maternal toxicity.
Garadacimab-gxii crossed the placenta in rabbits. With a maternal dose of 100 mg/kg garadacimab-gxii on gestation day 29, fetal plasma concentrations were 40.8% of maternal concentrations following subcutaneous administration and approximately equivalent following intravenous administration.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of garadacimab-gxii or its metabolite in either human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Maternal IgG is known to be present in human milk. The effects of local gastrointestinal exposure and limited systemic exposure in the breastfed infant to garadacimab-gxii are unknown.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for ANDEMBRY and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from ANDEMBRY or the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of ANDEMBRY for prophylaxis to prevent attacks of HAE have been established in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older. Use of ANDEMBRY for this indication is supported by evidence from a total of 6 pediatric patients aged 12 years and older enrolled in VANGUARD who received treatment with ANDEMBRY 400 mg loading dose administered subcutaneously followed by a maintenance dosage of 200 mg subcutaneously every month (n=4) or placebo (n=2). Results of the subgroup analysis for pediatric patients aged 12 years and older were consistent with study results for adult patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14)].
The safety and effectiveness of ANDEMBRY have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 12 years of age.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the total number of ANDEMBRY-treated patients in the clinical study for prophylaxis to prevent attacks of HAE, 6 (9%) were 65 years of age and older [see Clinical Studies (14)]. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness of ANDEMBRY have been observed between patients 65 years of age and older and younger adult patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14)].
11. Garadacimab Description
Garadacimab-gxii, an activated Factor XII (FXIIa) inhibitor, is a recombinant, fully human, monoclonal antibody (IgG4/λ-light chain) produced in Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells. Based on the amino acid sequence, the molecular weight of garadacimab-gxii is approximately 148 kDa.
ANDEMBRY (garadacimab-gxii) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, slightly opalescent to clear, brownish-yellow to yellow solution for subcutaneous use.
Each 1.2 mL prefilled autoinjector or prefilled syringe with needle safety device of ANDEMBRY contains 200 mg of garadacimab-gxii, arginine monohydrochloride (37.9 mg), histidine (3.7 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.24 mg), proline (19.3 mg), and water for injection, USP. The pH is 6.1.
12. Garadacimab - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Garadacimab-gxii is an inhibitor of activated FXII that binds to the catalytic domain of activated Factor XII (FXIIa and βFXIIa) and inhibits its catalytic activity. FXII is the first factor activated in the contact activation pathway and initiates the inflammatory bradykinin-producing kallikrein-kinin system. The inhibition of FXIIa decreases the activation of prekallikrein to kallikrein and the generation of bradykinin, which is associated with inflammation and swelling in HAE attacks, thus reducing the cascade of events leading to an HAE attack.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Garadacimab-gxii concentration-dependent inhibition of FXIIa-mediated kallikrein activity was observed in patients with HAE. Inhibition of FXIIa-mediated kallikrein activity was observed after the first dose.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of garadacimab-gxii are provided in Table 2 following subcutaneous administration of a single 200 mg dose to healthy volunteers and are presented as mean (SD), unless otherwise specified.
| Parameter | Garadacimab-gxii |
|---|---|
| Abbreviations: AUC = area under the plasma concentration-time curve; CI = confidence interval; Cmax = maximum plasma concentration; Ctrough,steady state = trough plasma concentration at steady state; Tmax = time to peak concentration | |
| Tmax is reported as median (range) and absolute bioavailability is reported as estimate (95% CI) | |
|
|
| Exposure | |
| Cmax | 18.4 (7.23) mcg/mL |
| AUC0-inf | 11470 (4103) mcg∙h/mL |
| Ctrough,Steady State†,‡ | 8.09 (4.28) to 8.69 (3.93) mcg /mL |
| Absorption | |
| Absolute Bioavailability | 39 (34, 43)% |
| Tmax | 6 (2, 15) days |
| Distribution | |
| Apparent Volume of Distribution | 11.8 (5.17) Liters (L) |
| Elimination | |
| Half-Life‡ | 17.4 (3.14) days |
| Apparent Clearance | 0.02 (0.008) L/h |
| Metabolism | |
| Primary Pathway | Expected to be metabolized into small peptides by catabolic pathways |
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of garadacimab-gxii were observed based on age (age range: 12 to 73 years), gender, race, body weight (range: 43 to 153 kg), and mild to moderate renal impairment (eGFR 30 to <90 mL/min/1.73 m2). The effect of severe renal impairment (eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2) on garadacimab-gxii pharmacokinetics is unknown.
12.6 Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies (ADA) is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those of garadacimab-gxii or other garadacimab products.
In VANGUARD, 2.6% (1/39) of patients who received garadacimab-gxii tested positive for anti- garadacimab-antibodies during the 6-month treatment period.
The development of ADA against garadacimab-gxii did not affect pharmacokinetics (PK), safety, or clinical response.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Animal studies have not been conducted to evaluate the carcinogenic or mutagenic potential of garadacimab-gxii.
Fertility and reproductive performance were unaffected in sexually mature male and female rabbits that received garadacimab-gxii at intravenous doses up to 100 mg/kg once every three days (resulting in exposures in male and female rabbits up to approximately 100 and 80 times the MRHD on an AUC basis).
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of ANDEMBRY for prophylaxis to prevent hereditary angioedema (HAE) attacks was evaluated in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study (VANGUARD [NCT04656418]) of 6 months duration.
VANGUARD enrolled a total of 64 adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older with Type I or Type II HAE who experienced at least 2 investigator-confirmed HAE attacks over a 2-month period prior to treatment with ANDEMBRY or placebo. Patients were randomized in a 3:2 ratio (ANDEMBRY:placebo) to receive an initial loading dose of ANDEMBRY 400 mg administered subcutaneously followed by a maintenance dose of 200 mg every month, or matched placebo. Patients were required to discontinue other prophylactic HAE medications prior to entering the study. All patients were allowed to use on-demand medications for the treatment of HAE attacks during the study.
The demographics and baseline characteristics of patients in VANGUARD are provided in Table 3.
| VANGUARD (N=64) | |
|---|---|
| Female, n (%) | 38 (59) |
| Race, n (%) | |
| Asian | 6 (9) |
| Black or African American | 1 (2) |
| Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander | 1 (2) |
| White | 55 (86) |
| Other | 1 (2) |
| Hispanic or Latino, n (%) | 3 (5) |
| Mean age, years (SD) | 41 (16) |
| ≤ 17 years, n (%) | 6 (9) |
| > 17 years, n (%) | 58 (91) |
| C1-INH HAE Type 1, n (%) | 56 (88) |
| Prior HAE prophylaxis*, n (%) | 21 (33) |
| Baseline HAE attack rate†, n (%) | |
| 1 to < 3 attacks | 26 (41) |
| ≥ 3 attacks | 38 (59) |
The primary endpoint for VANGUARD was the monthly HAE attack rate at 6 months (number of investigator-confirmed HAE attacks per month). As shown in Table 4, the least squares mean for the monthly HAE attack rate was lower with ANDEMBRY compared to placebo.
| Rate of Monthly HAE Attack | ANDEMBRY (N=39) | Placebo (N=25) |
|---|---|---|
| Abbreviations: CI=confidence interval; HAE=hereditary angioedema; LS=least squares | ||
| Note: LS means were obtained from a Poisson model accounting for overdispersion with an offset term for time on treatment and fixed effects for treatment group and HAE attack rate over a 2-month period prior to treatment | ||
|
||
| LS mean (95% CI) | 0.22 (0.11, 0.47) | 2.07 (1.49, 2.87) |
| Percent reduction relative to placebo (95% CI) | 89.2 (75.6, 95.2) | |
| P-value * | < 0.001 | |
The monthly rate of HAE attacks requiring on-demand therapy and the monthly rate of moderate or severe HAE attacks were assessed as secondary endpoints in VANGUARD. There was a 91.2% reduction with ANDEMBRY relative to placebo in the monthly rate of HAE attacks requiring on-demand therapy and a 93.6% reduction with ANDEMBRY relative to placebo in the monthly rate of moderate or severe HAE attacks.
Additional secondary endpoints assessed the proportion of patients with a ≥50%, ≥70%, ≥90%, and 100% (attack-free) reduction in monthly HAE attack rate from the first dose through the end of the 6-month treatment period compared to the 2-month period prior to treatment. The proportion of patients with a ≥50%, ≥70%, ≥90%, and 100% reduction was 95%, 92%, 74%, and 62% on ANDEMBRY versus 33%, 17%, 8%, and 0% on placebo, respectively.
16. How is Garadacimab supplied
How Supplied
ANDEMBRY (garadacimab-gxii) injection is a ready-to-use, slightly opalescent to clear, brownish-yellow to yellow solution in the following presentations, supplied in single-dose prefilled autoinjector or prefilled syringe with needle safety device.
Table 5 provides the available presentations and strengths of ANDEMBRY.
| Presentation | Strength | Unit Count | NDC (Device) | NDC (Carton) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prefilled autoinjector | 200 mg/1.2 mL | 1 | 63833-925-20 | 63833-925-01 |
| Prefilled syringe with needle safety device | 200 mg/1.2 mL (167 mg/mL) | 1 | 63833-920-20 | 63833-920-01 |
Each single-dose prefilled autoinjector or prefilled syringe with needle safety device is supplied in a carton.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Administration Instructions
- Instruct patients that ANDEMBRY is for subcutaneous use and intended for self-administration or administration by caregiver.
- Instruct patients and/or caregivers on the proper preparation and subcutaneous administration techniques of ANDEMBRY [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Instructions for Use].
- Instruct patients and/or caregivers to administer ANDEMBRY subcutaneously into the upper arm, thigh or abdomen ensuring to stay 1 inch (2 cm) away from the navel [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- Instruct patients or caregivers in proper disposal technique for prefilled autoinjector or prefilled syringe with needle safety device and advise them not to reuse these items.
- Instruct patients to dispose of the prefilled autoinjector or prefilled syringe with needle safety device in a sharps disposal container (closed puncture-resistant container).
Manufactured for:
CSL Behring GmbH
Emil-von-Behring-Strasse 76,
35041 Marburg, Germany
US License No. 1765
Manufactured by:
CSL Behring LLC
King of Prussia, PA 19406
US License No. 1767
Distributed by:
CSL Behring LLC
Kankakee, IL 60901
For more information, visit www.ANDEMBRY.com
For Patent information: www.cslbehring.com/products/patents
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised 06/2025 |
| PATIENT INFORMATION ANDEMBRY ® (an-DEM-bree) (garadacimab-gxii) injection, for subcutaneous use |
| Read this Patient Information before you start using ANDEMBRY and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment. |
| What is ANDEMBRY?
ANDEMBRY is a prescription medicine used to prevent attacks of Hereditary Angioedema (HAE) in children 12 years of age and older. It is not known if ANDEMBRY is safe and effective in children under 12 years of age. |
Before you use ANDEMBRY, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
|
How should I use ANDEMBRY?
|
| What are the possible side effects of ANDEMBRY? The most common side effects of ANDEMBRY include:
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
| General information about the safe and effective use of ANDEMBRY
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use ANDEMBRY for a condition for which it is not prescribed. Do not give ANDEMBRY to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about ANDEMBRY that is written for healthcare professionals. |
| What are the ingredients in ANDEMBRY? Active ingredient: garadacimab-gxii Inactive ingredients: arginine monohydrochloride, histidine, polysorbate 80, proline, water for injection. Manufactured for: CSL Behring GmbH Emil-von-Behring-Strasse 76, 35041 Marburg, Germany US License No. 1765 Manufactured by: CSL Behring LLC King of Prussia, PA 19406 US License No. 1767 Distributed by: CSL Behring LLC Kankakee, IL 60901 For Patent information: www.cslbehring.com/products/patents For more information, visit www.ANDEMBRY.com or call 1-866-915-6158. |
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
ANDEMBRY (an-DEM-bree)
(garadacimab-gxii)
injection, for subcutaneous use
Prefilled Autoinjector
| Important:
This autoinjector works differently than other injection devices. Read the Instructions for Use carefully before using it, and each time you get a new autoinjector. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment. Children should inject ANDEMBRY under the supervision of an adult. Make sure you have been trained by your healthcare provider before you use this autoinjector for the first time. |
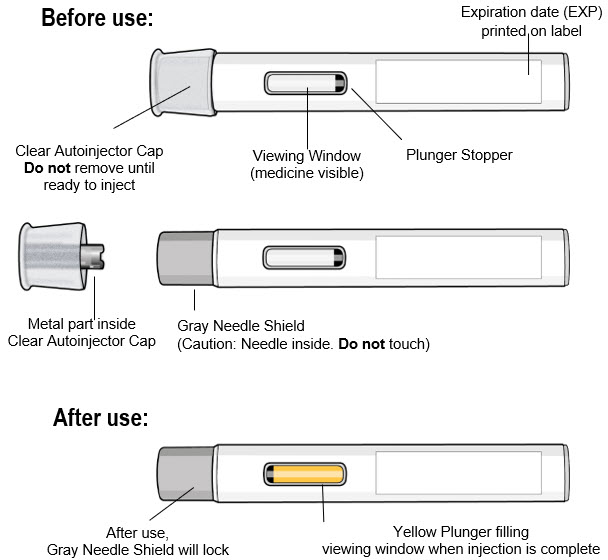
Parts of the Autoinjector (see Figure A):
Continue to the next sections to prepare and perform the injection.
|
|
| Figure A |
Read the Following Safety Information:
- Keep the autoinjector in its original carton box until use, to protect it from light.
- Do not remove the clear autoinjector cap until you are ready to inject.
- Do not put the clear autoinjector cap back on the autoinjector after it has been removed because this could start the injection and cause injury.
- The autoinjector contains 1 dose and is for one time use only. Do not try to reuse the same autoinjector.
- Do not use the autoinjector if the expiration date has passed.
- The autoinjector is for subcutaneous (under the skin) injection only.
- Do not use the autoinjector if it has dropped, looks damaged, has cracks, or is leaking medicine. Throw away the autoinjector as described in Step 11 and use a new one.
- Do not inject through clothing.
- Do not touch or try to remove the gray needle shield at any time.
- Keep ANDEMBRY and all medicines out of reach of children.
Contact your healthcare provider if you have any questions.
How Should I Store ANDEMBRY?
- Store ANDEMBRY autoinjector in a refrigerator, between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) in its original carton box until use, to protect it from light.
- Do not shake
- Do not freeze. If the autoinjector has been frozen, do not use the autoinjector even if it is thawed.
- The refrigerated autoinjector may be used until the expiration date (EXP) printed on the label.
- Take the autoinjector out of the refrigerator 30 minutes before use, allowing it to reach room temperature.
- Do not put the autoinjector back in the refrigerator after it has reached room temperature.
Supplies needed for your Autoinjector Injection (see Figure B):
Included in the carton box:
- 1 Single-dose autoinjector
Required supplies but not included in the carton box:
- 1 Alcohol pad
- 1 Cotton ball or gauze pad
- 1 FDA-cleared sharps container or puncture-resistant container for disposal (see Step 11. Disposing of the Autoinjector)
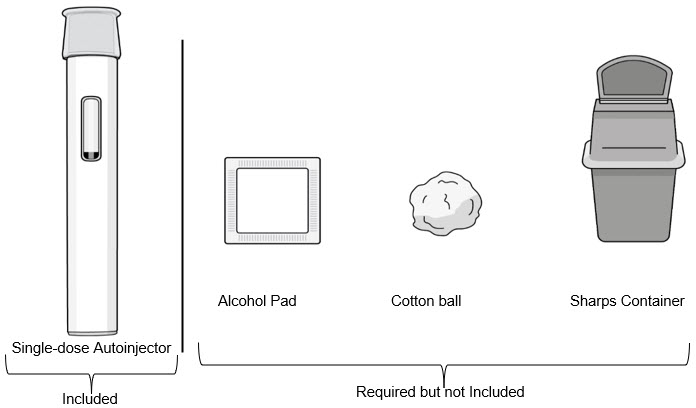 |
| Figure B |
Preparing for an Injection
Do not remove the clear autoinjector cap until immediately before the injection.
Step 1. Let the Autoinjector Reach Room Temperature
- Remove the autoinjector from the carton box and place it laying down on a clean flat surface.
- Wait 30 minutes for the medicine to reach room temperature after taking it out of the refrigerator (see Figure C).
- Injecting the medicine cold could be uncomfortable.
- Do not try to speed up the warming process in any way. For example, do not warm it in a microwave, in hot water, or leave it in direct sunlight.
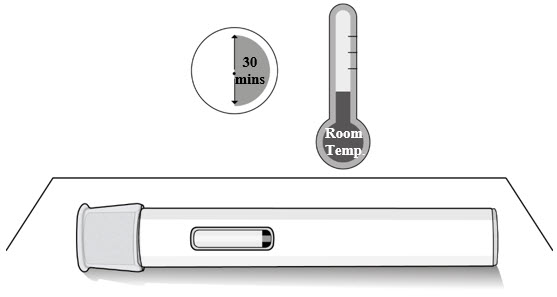 |
| Figure C |
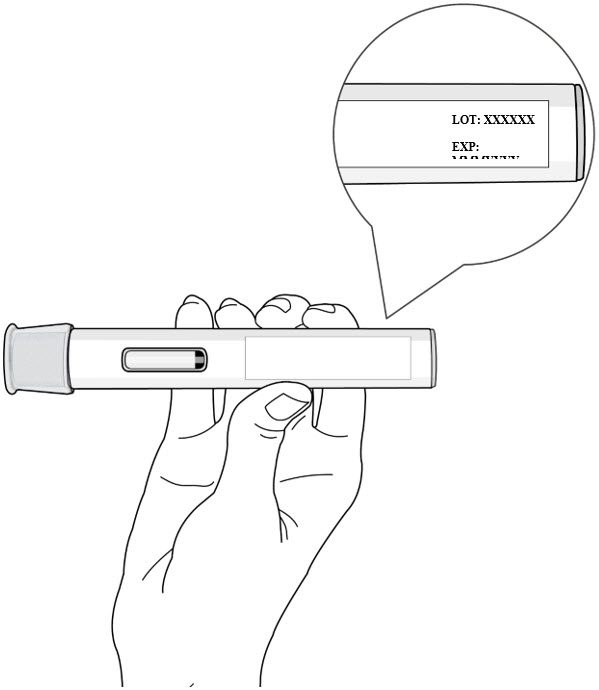
Step 2. Check the Expiration Date
- Check the expiration date on the autoinjector label (see Figure D).
- Do not use the autoinjector if the expiration date has passed.
- If the expiration date has passed, then safely dispose of the autoinjector and get a new one (see Step 11. Disposing of the Autoinjector).
 |
| Figure D |
Step 3. Inspect the autoinjector and the medicine
- Check the autoinjector for damage.
- Check the medicine through the viewing window of the autoinjector (see Figure E).
- It is normal to see air bubbles, do not try to remove the air bubbles.
- The medicine should be brownish-yellow to yellow and may appear slightly opalescent to clear.
-
Do not use the autoinjector, safely dispose and get a new one (see Step 11. Disposing of the Autoinjector) if:
- The medicine is discolored or contains particles
- The autoinjector looks damaged or has cracks
- The autoinjector is leaking
- The autoinjector has been dropped on a hard surface, even if it does not look damaged
 |
| Figure E |
Choose and Prepare an Injection Site
Step 4. Clean your Hands
- Wash your hands well with soap and water or use hand sanitizer (see Figure F).
 |
| Figure F |
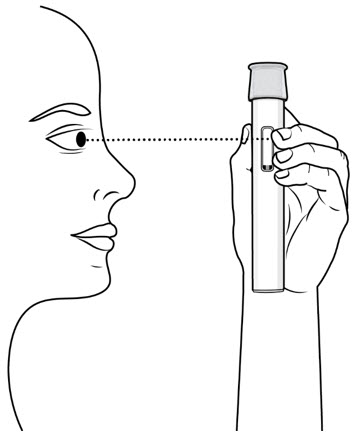
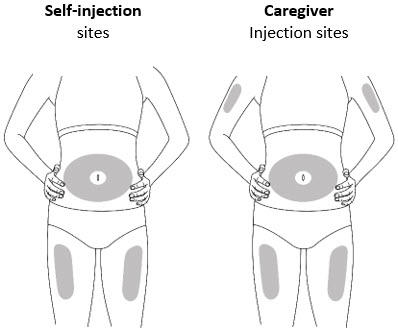
Step 5. Select the Injection Site
- Inject into the thigh or belly (abdomen) area, but stay 1 inch (2 cm) away from the belly button (navel) (see Figure G)
- If somebody else (caregiver) gives you the injection, they can also use the upper arm. Do not try to inject into the upper arm yourself.
- Change (rotate) your injection site with each injection. Do not inject in the same place multiple times if the skin is damaged.
- Do not inject into the belly button, moles, scars or bruises, or into areas where the skin is tender, red, hard, or injured.
 |
| Figure G |
Step 6. Prepare the Injection Site
- Clean the injection site with an alcohol pad (see Figure H).
- Let your skin dry on its own.
- Do not touch this area again before injecting.
- Do not fan or blow on the skin area that you cleaned.
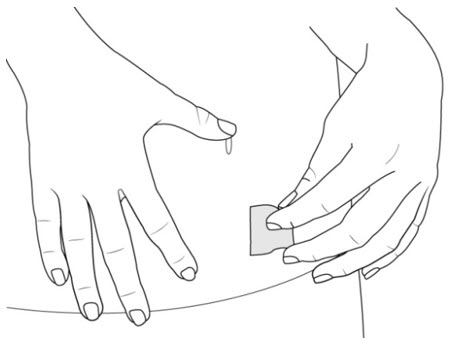 |
| Figure H |
Injecting the Medicine with the Autoinjector
Complete the Injection without stopping. Read all steps first before beginning.
Do not remove the Clear Cap until you are ready to inject.
Step 7. Remove Clear Autoinjector Cap and Dispose of the Cap
- Hold the autoinjector with one hand and pull the Clear Autoinjector Cap straight off with the other hand.
- Do not twist the Clear Cap, (see Figure I). If you cannot remove the Clear Cap, ask a caregiver for help or contact your healthcare provider.
- The Clear Cap has a metal part inside, this is normal.
- Do not put the Clear Cap back on after it has been removed, because this could start the injection and cause injury.
- Dispose of the Clear Cap in an FDA-cleared sharps container.
Important:
- Do not touch the gray needle shield of the autoinjector to avoid injury.
- Do not put the autoinjector down after removing the Clear Cap.
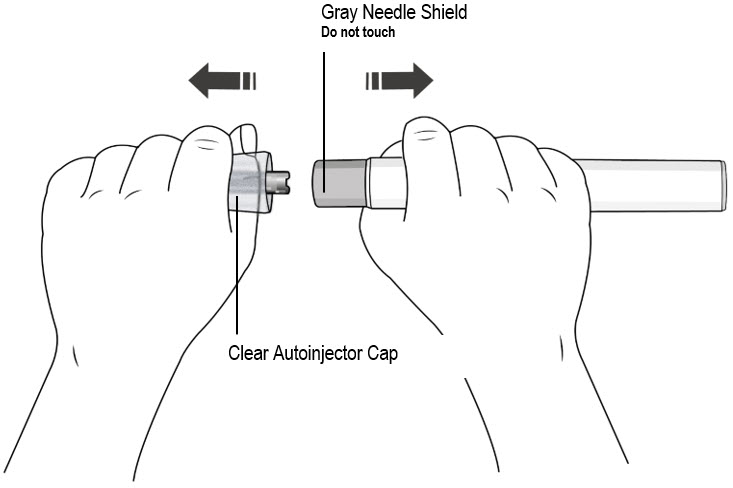 |
| Figure I |
Step 8. Pinch the Skin and place the autoinjector on the injection site
Immediately after removing the clear autoinjector cap, complete the following steps without stopping:
- Gently pinch the area of cleaned skin around the injection site and hold the area firmly until the injection is complete (see Figure J).
- Place the autoinjector at a 90° angle on the cleaned injection site (see Figure J).
- Make sure you can see the viewing window.
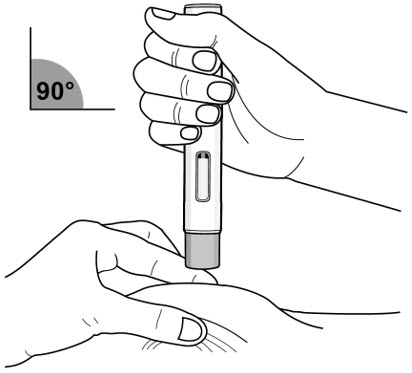 |
| Figure J |
| Step 9. Inject Medicine (see Figure K) | |
 | You Must Read all of Step 9 before injecting. The injection may take up to 15 seconds. To ensure you receive a full dose you must keep the autoinjector firmly pressed against your pinched skin until:
|
| Figure K | ||
| Press the gray needle shield down firmly against the pinched skin to start the injection and keep pressing down until all the steps below are complete. | ||
| Press down to start | Keep Pressing Down | Keep Pressing down for 5 more seconds …1…2…3…4…5 |
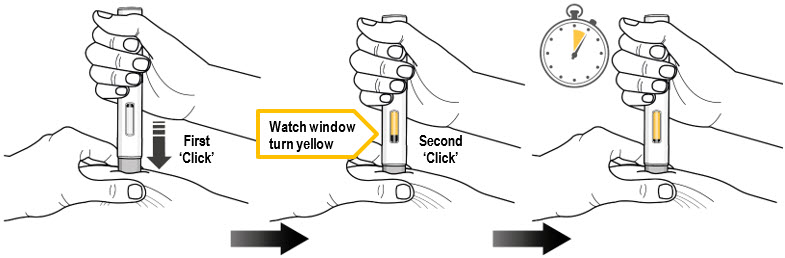 |
||
Press down to start the injection and listen for a First 'Click'.
| Keep pressing the autoinjector down and watch the viewing window.
| Keep pressing the autoinjector down for 5 more seconds to make sure you get the full dose.
Make sure the yellow plunger completely fills the window and has stopped moving before you remove the autoinjector. |
| Keep pressing the autoinjector down. | Keep pressing the autoinjector down. | |
- Do not remove the autoinjector until the yellow plunger has stopped moving and completely filled the viewing window, and 5 seconds has passed after the Second "Click."
- Do not remove, tilt, or rotate the autoinjector during the injection.
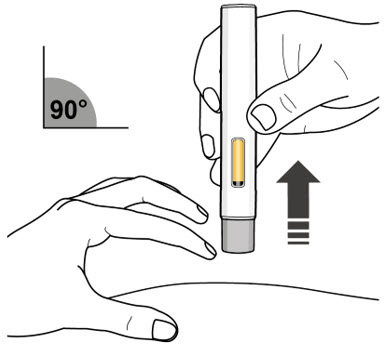
Step 10. Release the Pinch and Remove the Autoinjector
- Release the pinch and remove the autoinjector at a 90° angle from the skin (see Figure L).
- As the autoinjector is lifted from the skin, the gray needle shield returns to the original (before use) position, and will lock into place, covering the needle.
 |
| Figure L |
Important: If you think that you have not received the full dose, contact your healthcare provider right away.
- If there is a little bleeding at the injection site, you can press a cotton ball or gauze over the injection site.
- Do not rub the injection site.
- If needed, you may cover the injection site with a small adhesive bandage.
Disposal
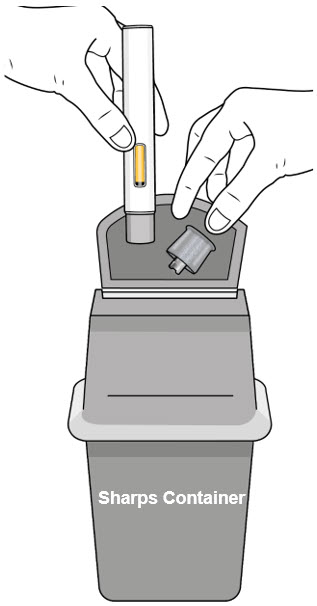
Step 11. Disposing of the autoinjector
- Do not try to reuse the autoinjector.
- After injecting your dose, put the autoinjector into an FDA-cleared sharps container or closed puncture-resistant container (see Figure M).
 |
| Figure M |
- If you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps container, you may use a household container that is:
- Made of heavy-duty plastic
- Can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out
- Upright stable during use
- Leak-resistant
- Properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container
- When your sharps container is almost full, you will need to follow your local guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.
- Do not dispose of your used sharps container in your household trash unless your local guidelines permit this.
- Do not recycle your used sharps container.
Step 12. Keep Track of Your Treatment
- If required by your healthcare provider, record your injection in a diary to help keep track of your medicine.
Manufactured by:
CSL Behring LLC
King of Prussia, PA 19406
US License No. 1767
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
06/2025
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 200 mg Autoinjector Label
NDC 63833-925-20
200 mg
1.2 mL
ANDEMBRY®
garadacimab-gxii
injection
200 mg/1.2 mL
For Subcutaneous Use
1 single-dose Prefilled Autoinjector
Rx only
Manufactured by:
CSL Behring LLC
King of Prussia, PA
19406 USA
US License No. 1767
LOT 0000000000
EXP MMM YYYY
Read the instructions
before use
41126
| ANDEMBRY
garadacimab injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - CSL (326530474) |
Biological Products Related to garadacimab
Find detailed information on biosimilars for this medication.
More about garadacimab
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: hereditary angioedema agents
- En español