Superficial Thrombophlebitis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is superficial thrombophlebitis (STP)?
STP is inflammation of a vein just under your skin (superficial vein). The inflammation causes a blood clot to form in your vein. STP most often happens in your leg but may also happen in your arm or neck.
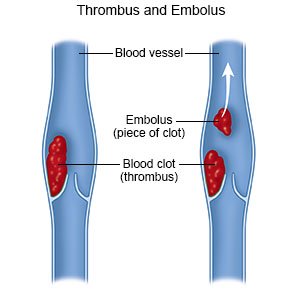 |
What increases my risk for STP?
- A condition that affects your blood vessels, such as varicose veins
- A long-term IV catheter
- Recent surgery
- Injections of prescription or non-prescription drugs into veins
- Obesity, pregnancy, or cancer
- Limited activity caused by bed rest, a leg cast, or sitting for long periods
- A blood disorder that makes your blood clot faster than normal, such as factor V Leiden mutation
- In women, hormone replacement therapy or birth control pills
What are the signs and symptoms of STP?
- A red line on the skin over the vein
- Pain near the vein, and sometimes swelling
- A fever if infection has spread from your vein to others places in your body
- Warm, red skin that is tender to the touch
- A hard area that feels like a knot
How is STP diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will examine you. You may need any of the following:
- Blood tests may be done to check for infection and test how fast your blood clots.
- Doppler ultrasound uses sound waves to check for blood clots or damage to your vein.
How is STP treated?
Treatment may not be needed. STP usually goes away on its own. You may need any of the following for STP that continues:
- Medicines may be given to treat an infection and decrease swelling and pain. Medicine may also be given to prevent more blood clots.
- Removal of an IV catheter may be needed if your IV is infected.
- Surgery may be needed to remove the blood clot or part of your vein. Surgery may also be needed to remove a collection of infected fluid from your vein.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
What can I do to manage STP?
- Apply a warm compress to your arm or leg. This will help decrease swelling and pain. Wet a washcloth in warm water. Do not use hot water. Apply the warm compress for 10 minutes. Repeat this 4 times each day.
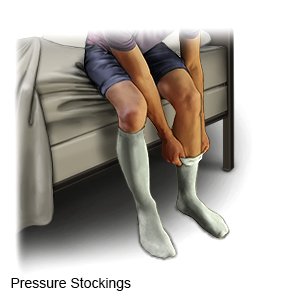
- Wear pressure stockings as directed. Pressure stockings improve blood flow and help prevent clots in your legs. Wear the stockings during the day. Do not wear them when you sleep.
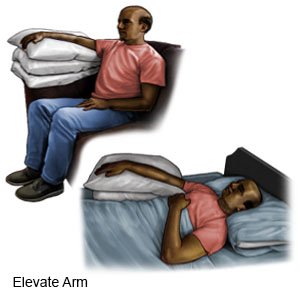
- Elevate your leg or arm above the level of your heart as often as you can. This will help decrease swelling and pain. Prop your leg or arm on pillows or blankets to keep it elevated comfortably.

What can I do to prevent STP?
- Maintain a healthy weight. This will help decrease your risk for another blood clot. Ask your healthcare provider what a healthy weight is for you. Ask him or her to help you create a weight loss plan if needed.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can damage blood vessels and increase your risk for blood clots. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
- Change your body position or move around often. Move and stretch in your seat several times each hour if you travel by car or work at a desk. In an airplane, get up and walk every hour. Move your legs by tightening and releasing your leg muscles while sitting. You can move your legs while sitting by raising and lowering your heels. Keep your toes on the floor while you do this. You can also raise and lower your toes while keeping your heels on the floor.
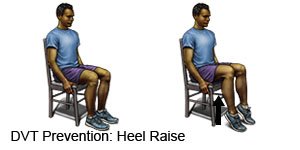
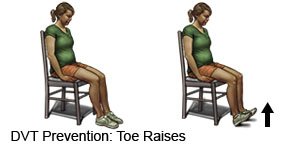
- Exercise regularly to help increase your blood flow. Walking is a good low-impact exercise. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best exercise plan for you.

- Do not inject non-prescription drugs. Talk to your healthcare provider if you need help to quit.
Related medications
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You feel lightheaded, short of breath, and have chest pain.
- You cough up blood.
When should I seek immediate care?
- Your arm or leg feels warm, tender, and painful. It may look swollen and red.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Superficial Thrombophlebitis
Treatment options
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
