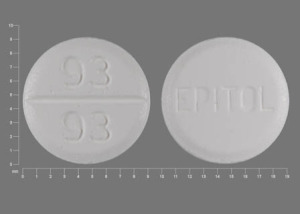
Epitol (Oral)
Generic name: carbamazepine [ kar-ba-MAZ-e-peen ]
Other brand names of carbamazepine include: Carbatrol, Epitol, Equetro, TEGretol, TEGretol-XR
Drug class: Dibenzazepine anticonvulsants
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Mar 9, 2025.
Serious and sometimes fatal dermatologic reactions (including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis) have been reported, especially in patients with the inherited allelic variant HLA-B*1502. Screen genetically at-risk patients prior to receiving carbamazepine. Do not start carbamazepine in patients who test positive for the allele unless the benefit clearly outweighs the risk. Discontinue if you suspect that the patient has a serious dermatologic reaction. Aplastic anemia and agranulocytosis have also been reported. Obtain pretreatment hematological testing and periodically monitor CBC. Consider drug discontinuation if significant bone marrow depression develops .
Uses for Epitol
Carbamazepine is used to treat certain types of seizures (eg, partial seizures, tonic-clonic seizures) and bipolar disorder. It is also used to relieve pain caused by trigeminal neuralgia (tic douloureux).
This medicine is available only with your doctor's prescription.
Before using Epitol
In deciding to use a medicine, the risks of taking the medicine must be weighed against the good it will do. This is a decision you and your doctor will make. For this medicine, the following should be considered:
Allergies
Tell your doctor if you have ever had any unusual or allergic reaction to this medicine or any other medicines. Also tell your health care professional if you have any other types of allergies, such as to foods, dyes, preservatives, or animals. For non-prescription products, read the label or package ingredients carefully.
Pediatric
Appropriate studies performed to date have not demonstrated pediatric-specific problems that would limit the usefulness of Equetro® extended-release capsules in children with partial seizures, generalized tonic-clonic seizures, and mixed seizure patterns. Safety and efficacy have been established.
Appropriate studies have not been performed on the relationship of age to the effects of Equetro® extended-release capsules in children with bipolar disorder and pain of trigeminal neuralgia. Safety and efficacy have not been established.
Appropriate studies performed to date have not demonstrated pediatric-specific problems that would limit the usefulness of Tegretol® chewable tablets, suspension, tablets, or extended-release capsules in children with partial seizures, generalized tonic-clonic seizures, mixed seizure patterns, bipolar disorder, and pain of trigeminal neuralgia.
Geriatric
Appropriate studies on the relationship of age to the effects of carbamazepine have not been performed in the geriatric population, geriatric-specific problems are not expected to limit the usefulness of carbamazepine in the elderly. However, elderly patients are more likely to have confusion, hyponatremia (low sodium in the blood), or agitation and age-related liver, kidney, or heart problems, which may require caution and an adjustment in the dose for patients receiving carbamazepine.
Breast Feeding
There are no adequate studies in women for determining infant risk when using this medication during breastfeeding. Weigh the potential benefits against the potential risks before taking this medication while breastfeeding.
Interactions with Medicines
Although certain medicines should not be used together at all, in other cases two different medicines may be used together even if an interaction might occur. In these cases, your doctor may want to change the dose, or other precautions may be necessary. When you are taking this medicine, it is especially important that your healthcare professional know if you are taking any of the medicines listed below. The following interactions have been selected on the basis of their potential significance and are not necessarily all-inclusive.
Using this medicine with any of the following medicines is not recommended. Your doctor may decide not to treat you with this medication or change some of the other medicines you take.
- Artemether
- Atazanavir
- Boceprevir
- Cabotegravir
- Clorgyline
- Cobicistat
- Daclatasvir
- Darunavir
- Dasabuvir
- Delamanid
- Delavirdine
- Doravirine
- Efavirenz
- Elbasvir
- Elvitegravir
- Fostemsavir
- Furazolidone
- Grazoprevir
- Iproniazid
- Isavuconazonium
- Isocarboxazid
- Lenacapavir
- Linezolid
- Lorlatinib
- Lumefantrine
- Lurasidone
- Maraviroc
- Mavacamten
- Methylene Blue
- Moclobemide
- Nefazodone
- Nialamide
- Nirmatrelvir
- Ombitasvir
- Pacritinib
- Pargyline
- Paritaprevir
- Phenelzine
- Praziquantel
- Procarbazine
- Ranolazine
- Rasagiline
- Rilpivirine
- Ritonavir
- Selegiline
- Telaprevir
- Tenofovir Alafenamide
- Toloxatone
- Tranylcypromine
- Voriconazole
Using this medicine with any of the following medicines is usually not recommended, but may be required in some cases. If both medicines are prescribed together, your doctor may change the dose or how often you use one or both of the medicines.
- Abemaciclib
- Abiraterone Acetate
- Acalabrutinib
- Acetazolamide
- Adagrasib
- Adenosine
- Afatinib
- Alfentanil
- Almotriptan
- Alpelisib
- Alprazolam
- Amiodarone
- Amodiaquine
- Amphetamine
- Amprenavir
- Apixaban
- Apremilast
- Aprepitant
- Aripiprazole
- Artesunate
- Atogepant
- Avacopan
- Avapritinib
- Axitinib
- Bedaquiline
- Belumosudil
- Bendamustine
- Benzhydrocodone
- Benzphetamine
- Berotralstat
- Betrixaban
- Bictegravir
- Bortezomib
- Bosutinib
- Brexpiprazole
- Brigatinib
- Buprenorphine
- Bupropion
- Butorphanol
- Cabozantinib
- Calcifediol
- Cannabidiol
- Capmatinib
- Cariprazine
- Cenobamate
- Ceritinib
- Chloroquine
- Chlorpromazine
- Cisatracurium
- Citalopram
- Clarithromycin
- Clonazepam
- Clozapine
- Cobimetinib
- Codeine
- Conivaptan
- Copanlisib
- Crizotinib
- Cyclophosphamide
- Cyclosporine
- Dabigatran Etexilate
- Daridorexant
- Darolutamide
- Dasatinib
- Deflazacort
- Desmopressin
- Desogestrel
- Desvenlafaxine
- Dexamethasone
- Dextroamphetamine
- Dextromethorphan
- Dienogest
- Dihydrocodeine
- Diltiazem
- Dolasetron
- Dolutegravir
- Doxorubicin
- Doxorubicin Hydrochloride Liposome
- Dronedarone
- Drospirenone
- Duloxetine
- Duvelisib
- Edoxaban
- Elacestrant
- Elexacaftor
- Eliglustat
- Encorafenib
- Entrectinib
- Enzalutamide
- Eravacycline
- Erdafitinib
- Erlotinib
- Erythromycin
- Escitalopram
- Eslicarbazepine Acetate
- Estetrol
- Estradiol
- Ethinyl Estradiol
- Ethynodiol
- Etonogestrel
- Etravirine
- Everolimus
- Exemestane
- Ezogabine
- Fedratinib
- Felodipine
- Fenfluramine
- Fentanyl
- Fexinidazole
- Finerenone
- Fluconazole
- Fluoxetine
- Fluvoxamine
- Fosamprenavir
- Fosaprepitant
- Fosnetupitant
- Fosphenytoin
- Fostamatinib
- Futibatinib
- Gefitinib
- Gepirone
- Gestodene
- Gilteritinib
- Glasdegib
- Glecaprevir
- Granisetron
- Halofantrine
- Hemin
- Hydrocodone
- Hydromorphone
- Hydroxyamphetamine
- Hydroxychloroquine
- Hydroxytryptophan
- Ibrexafungerp
- Ibrutinib
- Idelalisib
- Ifosfamide
- Imatinib
- Indinavir
- Infigratinib
- Irinotecan
- Irinotecan Liposome
- Isoniazid
- Istradefylline
- Itraconazole
- Ivabradine
- Ivacaftor
- Ivosidenib
- Ixabepilone
- Ixazomib
- Ketoconazole
- Lamotrigine
- Lapatinib
- Larotrectinib
- Lasmiditan
- Ledipasvir
- Lefamulin
- Lemborexant
- Leniolisib
- Levoketoconazole
- Levomilnacipran
- Levonorgestrel
- Levorphanol
- Linagliptin
- Lisdexamfetamine
- Lomitapide
- Lopinavir
- Loratadine
- Lorcaserin
- Loxapine
- Lumateperone
- Lurbinectedin
- Macimorelin
- Macitentan
- Manidipine
- Maribavir
- Medroxyprogesterone
- Mefloquine
- Meperidine
- Mestranol
- Metaxalone
- Methadone
- Methamphetamine
- Methotrexate
- Midostaurin
- Mifepristone
- Milnacipran
- Mirtazapine
- Mitapivat
- Mobocertinib
- Morphine
- Morphine Sulfate Liposome
- Nalbuphine
- Naloxegol
- Nelfinavir
- Neratinib
- Netupitant
- Nifedipine
- Nilotinib
- Nimodipine
- Nintedanib
- Nomegestrol
- Norelgestromin
- Norethindrone
- Norgestimate
- Norgestrel
- Olanzapine
- Olaparib
- Olutasidenib
- Omaveloxolone
- Ondansetron
- Orlistat
- Osimertinib
- Oxcarbazepine
- Oxycodone
- Oxymorphone
- Paclitaxel
- Palbociclib
- Paliperidone
- Palonosetron
- Palovarotene
- Panobinostat
- Paroxetine
- Pazopanib
- Pemigatinib
- Pentazocine
- Perampanel
- Pexidartinib
- Phenobarbital
- Phenytoin
- Pibrentasvir
- Pimavanserin
- Piperaquine
- Pirtobrutinib
- Pitolisant
- Ponatinib
- Ponesimod
- Pralsetinib
- Pretomanid
- Primaquine
- Primidone
- Proguanil
- Propoxyphene
- Pyrimethamine
- Quetiapine
- Quinine
- Quizartinib
- Regorafenib
- Relugolix
- Remifentanil
- Ribociclib
- Rimegepant
- Ripretinib
- Risperidone
- Ritlecitinib
- Rivaroxaban
- Rolapitant
- Romidepsin
- Ruxolitinib
- Samidorphan
- Saquinavir
- Segesterone
- Selpercatinib
- Selumetinib
- Sertraline
- Sildenafil
- Simvastatin
- Sirolimus Protein-Bound
- Sofosbuvir
- Sonidegib
- Sotorasib
- Sparsentan
- Stiripentol
- Sufentanil
- Sunitinib
- Tacrolimus
- Tafenoquine
- Tamoxifen
- Tapentadol
- Tasimelteon
- Tazemetostat
- Telithromycin
- Temsirolimus
- Terfenadine
- Tezacaftor
- Thioridazine
- Thiotepa
- Ticagrelor
- Tipranavir
- Tivozanib
- Tofacitinib
- Tolvaptan
- Topiramate
- Trabectedin
- Tramadol
- Trazodone
- Tucatinib
- Ubrogepant
- Ulipristal
- Upadacitinib
- Valbenazine
- Valproic Acid
- Vandetanib
- Velpatasvir
- Vemurafenib
- Venetoclax
- Verapamil
- Vigabatrin
- Vilazodone
- Vincristine
- Vincristine Sulfate Liposome
- Vinflunine
- Voclosporin
- Vonoprazan
- Vorapaxar
- Vortioxetine
- Voxelotor
- Voxilaprevir
- Zanubrutinib
- Zileuton
- Ziprasidone
- Zolpidem
- Zuranolone
Using this medicine with any of the following medicines may cause an increased risk of certain side effects, but using both drugs may be the best treatment for you. If both medicines are prescribed together, your doctor may change the dose or how often you use one or both of the medicines.
- Acetaminophen
- Acetylcysteine
- Aminophylline
- Amitriptyline
- Amoxapine
- Anisindione
- Aripiprazole Lauroxil
- Caspofungin
- Dalfopristin
- Danazol
- Desipramine
- Dicumarol
- Doxepin
- Etretinate
- Felbamate
- Flunarizine
- Furosemide
- Ginkgo
- Haloperidol
- Hydrochlorothiazide
- Imipramine
- Influenza Virus Vaccine
- Levetiracetam
- Lithium
- Methylphenidate
- Methylprednisolone
- Metronidazole
- Mianserin
- Midazolam
- Miokamycin
- Nafimidone
- Niacinamide
- Nortriptyline
- Omeprazole
- Ospemifene
- Phenprocoumon
- Pipecuronium
- Protriptyline
- Psyllium
- Quinupristin
- Remacemide
- Rifampin
- Rifapentine
- Rocuronium
- Rufinamide
- Sabeluzole
- Semaglutide
- Theophylline
- Tiagabine
- Ticlopidine
- Troleandomycin
- Valnoctamide
- Vecuronium
- Viloxazine
- Warfarin
Interactions with Food/Tobacco/Alcohol
Certain medicines should not be used at or around the time of eating food or eating certain types of food since interactions may occur. Using alcohol or tobacco with certain medicines may also cause interactions to occur. The following interactions have been selected on the basis of their potential significance and are not necessarily all-inclusive.
Using this medicine with any of the following is usually not recommended, but may be unavoidable in some cases. If used together, your doctor may change the dose or how often you use this medicine, or give you special instructions about the use of food, alcohol, or tobacco.
- Grapefruit Juice
Using this medicine with any of the following may cause an increased risk of certain side effects but may be unavoidable in some cases. If used together, your doctor may change the dose or how often you use this medicine, or give you special instructions about the use of food, alcohol, or tobacco.
- Black Tea
Other Medical Problems
The presence of other medical problems may affect the use of this medicine. Make sure you tell your doctor if you have any other medical problems, especially:
- Anemia or
- Behavior or mood problems or
- Blood vessel disease or
- Depression, history of or
- Diabetes or
- Glaucoma, or history of or
- Heart block or
- Heart disease or
- Heart rhythm problems, history of or
- Hyponatremia (low sodium in the blood) or
- Increased pressure in the eye, history of or
- Liver disease, history of or
- Porphyria (an inherited disease) or
- Problems with urination or
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome (severe skin disease) or
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis (severe skin disease)—Use with caution. May make these conditions worse.
- Asian ancestry (eg, Chinese, Filipino, Japanese, Korean, Taiwanese)—May increase the risk for serious skin reactions. Your doctor may order a special test before prescribing this medicine.
- Bone marrow depression, history of—Should not be used in patients with this condition.
- Fructose intolerance (rare inherited problem)—Tegretol® oral liquid contains sorbitol and should not be given to patients with this condition.
Proper use of Epitol
Take this medicine exactly as directed by your doctor. Do not take more of it, do not take it more often, and do not take it for a longer time than your doctor ordered. To do so may increase the chance of side effects.
This medicine comes with a Medication Guide. Read and follow the instructions carefully. Ask your doctor if you have any questions.
Tegretol® should be taken with meals to lessen unwanted effects (eg, stomach upset, nausea, vomiting). You may take Equetro® with or without food.
You may swallow the extended-release capsules whole, or open it and sprinkle the contents over a teaspoon of applesauce. Swallow the mixture right away. Do not crush or chew the beads.
Swallow the extended-release tablets whole. Do not crush or chew it. Do not take the extended-release tablets that are damaged or have chips or cracks.
Grapefruit and grapefruit juice may increase the effects of this medicine by increasing the amount in the body. Do not eat grapefruit or drink grapefruit juice while you are taking this medicine.
If you are taking this medicine for pain relief:
- Carbamazepine is not an ordinary pain reliever. It should be used only when a doctor prescribes it for certain kinds of pain. Do not take carbamazepine for any other aches or pains.
If you are taking Tegretol® oral liquid:
- Shake the oral liquid well before each use. Measure your dose with a marked measuring spoon, oral syringe, or medicine cup. The average household teaspoon may not hold the right amount of liquid.
- Do not take any other liquid medicines at the same time that you take your dose of Tegretol® without first checking with your doctor.
Tegretol® tablets work differently than the Tegretol® oral liquid, even at the same dose (number of milligrams). Do not switch from the tablets to the oral liquid unless your doctor tells you to.
Tegretol® may be used alone or together with other seizure medicines. Ask your doctor first before taking any other seizure medicine together with Tegretol®.
Do not take Equetro® capsules if you are also using Tegretol® suspension or tablets. These medicines should not be taken together because both medicines contains carbamazepine. Ask your doctor if you have any questions.
Dosing
The dose of this medicine will be different for different patients. Follow your doctor's orders or the directions on the label. The following information includes only the average doses of this medicine. If your dose is different, do not change it unless your doctor tells you to do so.
The amount of medicine that you take depends on the strength of the medicine. Also, the number of doses you take each day, the time allowed between doses, and the length of time you take the medicine depend on the medical problem for which you are using the medicine.
- For oral dosage form (extended-release capsules):
- For bipolar disorder:
- Adults—At first, 200 milligrams (mg) 2 times a day. Your doctor may increase your dose as needed. However, the dose is usually not more than 1600 mg per day.
- Children—Use and dose must be determined by your doctor.
- For epilepsy:
- Adults and children 12 years of age and older—At first, 200 milligrams (mg) 2 times a day. Your doctor may increase your dose as needed. However, the dose is usually not more than 500 to 800 mg 2 times a day.
- Children younger than 12 years of age—Dose is based on body weight and must be determined by your doctor. However, the dose is usually not more than 1000 mg per day.
- For trigeminal neuralgia:
- Adults—At first, 200 milligrams (mg) once a day. Your doctor may increase your dose as needed and tolerated. However, the dose is usually not more than 1200 mg per day.
- Children—Use and dose must be determined by your doctor.
- For bipolar disorder:
- For oral dosage form (extended-release tablets):
- For epilepsy:
- Adults—At first, 200 mg 2 times a day. Your doctor may adjust your dose if needed. However, the dose is usually not more than 1000 to 1600 mg per day.
- Children 6 to 12 years of age—At first, 100 mg 2 times a day. Your doctor may adjust your dose if needed. However, the dose is usually not more than 1000 mg per day.
- Children younger than 6 years of age—Dose is based on body weight and will be determined by your doctor. The dose is usually 10 to 20 milligram (mg) per kilogram (kg) per day, taken 2 times a day. Your doctor may adjust your dose as needed. However, the dose is usually not more than 35 mg per kg of body weight per day.
- For trigeminal neuralgia:
- Adults—At first, 100 milligrams (mg) 2 times a day. Your doctor may adjust your dose as needed. However, the dose is usually not more than 1200 mg per day.
- Children—Use and dose must be determined by your doctor.
- For epilepsy:
- For oral dosage form (oral liquid):
- For epilepsy:
- Adults—100 milligrams (mg) or 1 teaspoon 4 times a day (400 mg per day). Your doctor may adjust your dose as needed. However, the dose is usually not more than 1000 to 1600 mg per day.
- Children 6 to 12 years of age—At first, 50 milligrams (mg) or one-half teaspoon 4 times a day (200 mg per day). Your doctor may adjust your dose as needed. However, the dose is usually not more than 1000 mg per day.
- Children younger than 6 years of age—Dose is based on body weight and will be determined by your doctor. The dose is 10 to 20 milligrams (mg) per kilogram (kg) of body weight per day, taken 4 times a day. Your doctor may adjust your dose as needed. However, the dose is usually not more than 35 mg per kg of body weight per day.
- For trigeminal neuralgia:
- Adults—At first, 50 milligrams (mg) or one-half teaspoon 4 times a day (200 mg per day). Your doctor may adjust your dose as needed. However, the dose is usually not more than 1200 mg per day.
- Children—Use and dose must be determined by your doctor.
- For epilepsy:
- For oral dosage forms (tablets or chewable tablets):
- For epilepsy:
- Adults—At first, 200 milligrams (mg) 2 times a day. Your doctor may adjust your dose as needed. However, the dose is usually not more than 1000 to 1600 mg per day.
- Children 6 to 12 years of age—At first, 100 mg 2 times a day. Your doctor may adjust your dose as needed. However, the dose is usually not more than 1000 mg per day.
- Children younger than 6 years of age—Dose is based on body weight and will be determined by your doctor. The dose is 10 to 20 milligrams (mg) per kilogram (kg) of body weight per day, taken 3 times a day. Your doctor may adjust your dose as needed. However, the dose is usually not more than 35 mg per kg of body weight per day.
- For trigeminal neuralgia:
- Adults and teenagers—At first, 100 milligrams (mg) 2 times a day. Your doctor may adjust your dose as needed. However, the dose is usually not more than 1200 mg per day.
- Children—Use and dose must be determined by your doctor.
- For epilepsy:
Missed Dose
If you miss a dose of this medicine, take it as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and go back to your regular dosing schedule. Do not double doses.
Storage
Store the medicine in a closed container at room temperature, away from heat, moisture, and direct light. Keep from freezing.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Do not keep outdated medicine or medicine no longer needed.
Ask your healthcare professional how you should dispose of any medicine you do not use.
Precautions while using Epitol
It is very important that your doctor check your or your child's progress at regular visits to make sure this medicine is working properly. Blood and urine tests may be needed to check for unwanted effects.
Using this medicine while you are pregnant can harm your unborn baby. Use an effective form of birth control to keep from getting pregnant. If you think you have become pregnant while using the medicine, tell your doctor right away.
Do not take carbamazepine together with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) or during the first 14 days after you stop taking a MAOI. MAOIs are used for depression and some examples are isocarboxazid (Marplan®), phenelzine (Nardil®), procarbazine (Matulane®), selegiline (Eldepryl®), or tranylcypromine (Parnate®). Do not use this medicine together with nefazodone (Serzone®) and certain medicines for HIV/AIDS (such as delavirdine, efavirenz, Atripla®, Sustiva®, Rescriptor®).
If you plan to have children, talk with your doctor before using this medicine. Some men using this medicine have become infertile (unable to have children).
Carbamazepine may cause some people to be agitated, irritable, or display other abnormal behaviors. It may also cause some people to have suicidal thoughts and tendencies or to become more depressed. If you, your child, or your caregiver notice any of these unwanted effects, tell your doctor right away.
Check with your doctor right away if a fever, sore throat, rash, ulcers in the mouth, nosebleeds, bleeding gums, swollen glands, or small red or purple spots on the skin occur. These could be symptoms of a serious blood problem.
This medicine may cause serious skin reactions (eg, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis), which can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention. Check with your doctor right away if you or your child has blistering, peeling, or loosening of the skin, chills, cough, diarrhea, itching, joint or muscle pain, red irritated eyes, red skin lesions, often with a purple center, sore throat, sores, ulcers, or white spots in the mouth, or on the lips, or unusual tiredness or weakness while you are using this medicine.
This medicine may cause a condition called drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), which is a serious allergic reaction affecting multiple body organs (eg, liver or kidney). Check with your doctor right away if you have fever, dark urine, headache, rash, stomach pain, swollen, painful, or tender lymph glands in the neck, armpit, or groin, unusual tiredness, or yellow eyes or skin.
This medicine may cause some people to be agitated, irritable, or display other abnormal behaviors. It may also cause some people to have suicidal thoughts and tendencies or to become more depressed. If you, your child, or your caregiver notice any of these side effects, tell your doctor or your child's doctor right away.
This medicine may cause serious allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis and angioedema, which can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention. Tell your doctor right away if you or your child have a rash, itching, hoarseness, trouble breathing, trouble swallowing, or any swelling of your hands, face, or mouth after using this medicine.
This medicine will add to the effects of alcohol and other CNS depressants (medicines that cause drowsiness). Some examples of CNS depressants are antihistamines or medicine for hay fever, other allergies, or colds, sedatives, tranquilizers, or sleeping medicine, prescription pain medicine or narcotics, medicine for seizures (eg, barbiturates), muscle relaxants, or anesthetics, including some dental anesthetics. Check with your doctor before taking any of the above while you or your child are using this medicine.
This medicine may cause some people to become drowsy, dizzy, lightheaded, or less alert than they are normally, especially when they are starting treatment or increasing the dose. It may also cause blurred or double vision, weakness, or loss of muscle control in some people. Do not drive or do anything else that could be dangerous until you know how this medicine affects you.
Check with your doctor immediately if blurred vision, difficulty in reading, or any other changes in vision occur during or after treatment. Your doctor may want you to have your eyes checked by an ophthalmologist (eye doctor).
Some people who take carbamazepine may become more sensitive to sunlight than they are normally. Exposure to sunlight, even for brief periods of time, may cause skin rash, itching, redness or other discoloration of the skin, or a severe sunburn. When you begin taking this medicine:
- Stay out of direct sunlight, especially between the hours of 10:00 AM and 3:00 PM, if possible.
- Wear protective clothing, including a hat. Also, wear sunglasses.
- Apply a sun block product that has a sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 15. Some patients may require a product with a higher SPF number, especially if they have a fair complexion. If you have any questions about this, check with your doctor.
- Apply a sun block lipstick that has an SPF of at least 15 to protect your lips.
- Do not use a sunlamp or tanning bed or booth.
If you have a severe reaction from the sun, check with your doctor.
Before having any medical tests, tell the medical doctor in charge that you are taking this medicine. The results of some pregnancy tests may be affected by this medicine.
Do not stop taking this medicine without first checking with your doctor. Your doctor may want you or your child to gradually reduce the amount you are using before stopping it completely. This may help prevent worsening of seizures and reduce the possibility of withdrawal symptoms.
Birth control pills containing estrogen may not work properly if you take them while you are taking carbamazepine. Unplanned pregnancies may occur. Use a different or additional means of birth control while you are taking carbamazepine. If you have any questions about this, check with your doctor.
Do not take other medicines unless they have been discussed with your doctor. This includes prescription or nonprescription (over-the-counter [OTC]) medicines and herbal or vitamin supplements.
Side Effects of Epitol
Along with its needed effects, a medicine may cause some unwanted effects. Although not all of these side effects may occur, if they do occur they may need medical attention.
Check with your doctor immediately if any of the following side effects occur:
More common
- Blurred vision or double vision
- continuous back-and-forth eye movements
Less common
- Actions that are out of control
- behavioral changes (especially in children)
- confusion, agitation, or hostility (especially in the elderly)
- diarrhea (severe)
- discouragement
- drooling
- fear
- feeling of unreality
- feeling sad or empty
- headache (continuing)
- increase in seizures
- irritability
- lack of appetite
- loss of balance control
- loss of interest or pleasure
- muscle trembling, jerking, or stiffness
- nausea (severe)
- other problems with muscle control or coordination
- sense of detachment from self or body
- shakiness and unsteady walk
- shuffling walk
- stiffness of the arm or leg
- sudden, wide mood swings
- talking, feeling, and acting with excitement
- thoughts or attempts of killing oneself
- tiredness
- trouble concentrating
- trouble sleeping
- twisting movements of the body
- uncontrolled movements, especially of the face, neck, and back
- unusual drowsiness
- vomiting (severe)
Rare
- Black, tarry stools
- blood in the urine or stools
- bone or joint pain
- chest pain or tightness
- cough
- darkening of the urine
- difficulty with speaking or slurred speech
- fainting
- frequent urination
- hoarseness
- irregular, pounding, or unusually slow heartbeat
- lower back or side pain
- mental depression with restlessness and nervousness or other mood or mental changes
- muscle or stomach cramps
- nosebleeds or other unusual bleeding or bruising
- numbness, tingling, pain, or weakness in the hands and feet
- pain, tenderness, swelling, or bluish color in the leg or foot
- painful or difficult urination
- pale stools
- pinpoint red spots on the skin
- rapid weight gain
- rigidity
- ringing, buzzing, or other unexplained sounds in the ears
- skin rash, hives, or itching
- sores, ulcers, or white spots on the lips or in the mouth
- swelling of the face, hands, feet, or lower legs
- swollen or painful glands
- sudden decrease in the amount of urine
- trembling
- trouble breathing
- uncontrolled body movements
- unusual tiredness or weakness
- visual hallucinations (seeing things that are not there)
- yellow eyes or skin
Incidence not known
- Blistering, peeling, or loosening of the skin
- chills
- decreased urine output
- dilated neck veins
- extreme tiredness or weakness
- general feeling of discomfort or illness
- irregular breathing
- irregular heartbeat
- joint or muscle pain
- red skin lesions, often with a purple center
- red, irritated eyes
- sore throat
- swelling of the face, fingers, feet, or lower legs
- thickening of bronchial secretions
- unusual bleeding or bruising
- weight gain
Some side effects may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects. Check with your health care professional if any of the following side effects continue or are bothersome or if you have any questions about them:
More common
- Dizziness (mild)
- drowsiness (mild)
- lightheadedness
- nausea (mild)
- vomiting (mild)
Incidence not known
- Accidental injury
- aching joints or muscles
- back pain
- belching
- constipation
- dryness of the mouth
- headache
- heartburn
- increased sensitivity of the skin to sunlight (skin rash, itching, redness or other discoloration of the skin, or severe sunburn)
- increased sweating
- indigestion
- irritation or soreness of the tongue or mouth
- lack or loss of strength
- loss of hair
- loss of memory
- problems with memory
- sexual problems in males
- sleepiness
- stomach pain, upset, or discomfort
Other side effects not listed may also occur in some patients. If you notice any other effects, check with your healthcare professional.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Related/similar drugs
Commonly used brand name(s)
In the U.S.
- Carbatrol
- Epitol
- Equetro
- TEGretol
- TEGretol-XR
In Canada
- APO-carBAMazepine
- APO-carBAMazepine CR
- Dom-carBAMazepine CR
- Gen-carBAMazepine CR
- Mazepine
- Mylan-carBAMazepine CR
- NU-carBAMazepine
- Sandoz-carBAMazepine
- Sandoz-carBAMazepine CR
- Taro-carBAMazepine
- TEGretol CR
Available Dosage Forms:
- Tablet, Chewable
- Capsule, Extended Release
- Tablet
- Tablet, Extended Release
- Suspension
Therapeutic Class: Anticonvulsant
Chemical Class: Dibenzazepine Carboxamide
More about Epitol (carbamazepine)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (19)
- Drug images
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: dibenzazepine anticonvulsants
- Breastfeeding
- En español
Patient resources
Other brands
Tegretol, Tegretol XR, Carbatrol, Equetro, Carnexiv
Professional resources
Other brands
Tegretol, Carbatrol, Equetro, Carnexiv
Related treatment guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.