Tubal Ligation
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
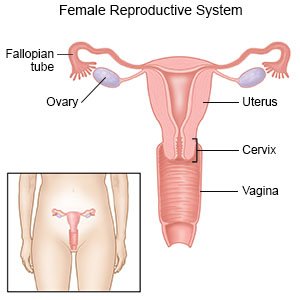
What do I need to know about a tubal ligation?
A tubal ligation is surgery to close your fallopian tubes to prevent pregnancy.
 |
How do I prepare for a tubal ligation?
Your surgeon will talk to you about how to prepare for surgery. He or she may tell you not to eat or drink anything within 8 hours of your surgery. He or she will tell you which medicines to take or not take on the day of your surgery. Arrange for someone to drive you home and stay with you after surgery.
What will happen during a tubal ligation?
- You may be given general anesthesia to keep you asleep and free from pain during surgery. You may instead be given regional anesthesia or local anesthesia. Regional anesthesia numbs the lower part of your body. Local anesthesia numbs the surgery area. With local anesthesia, you may still feel pressure or pushing during surgery, but you should not feel any pain. You may have a minilaparotomy or laparoscopic tubal ligation. During a minilaparotomy, your surgeon will make a small incision in your lower abdomen.
- During laparoscopic tubal ligation, your surgeon will make one or more small incisions in your abdomen. A laparoscope and other instruments will be put into your abdomen through the small incisions. The laparoscope is a long metal tube with a light and camera on the end. Your abdomen will be filled with a gas. This allows your surgeon to see inside your abdomen more clearly. Your fallopian tubes will be cut and closed with thread. Your healthcare provider may instead seal your tubes with heat, or with a clip or ring. After the surgery is done, your incisions are closed with stitches or staples. The incisions may be covered with a bandage.
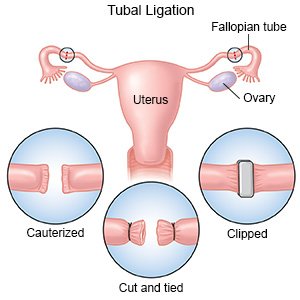
What will happen after a tubal ligation?
You will have abdominal pain and cramps for the first few days after surgery. You may feel dizzy, nauseated, bloated, or have gas. You may also have pain in your shoulders or near your ribs if gas was put in your abdomen.
What are the risks of a tubal ligation?
You may bleed more than expected or get an infection. Blood vessels or organs such as your bowel or bladder could be injured during surgery. Although pregnancy is unlikely after a tubal ligation, there is still a small chance that you may get pregnant. If pregnancy does occur, there is an increased risk for an ectopic pregnancy (tubal pregnancy). You may get a blood clot in your leg or arm. This may become life-threatening.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
