Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)?
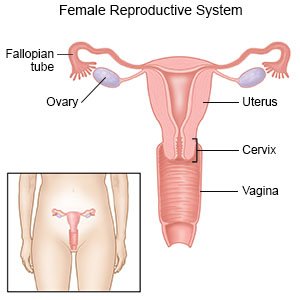
PID is an infection of your reproductive organs. This includes your ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix (lower area of your uterus), and vagina. The infection is caused by bacteria that are sexually transmitted, including gonorrhea and chlamydia. These bacteria spread from your vagina upward through your cervix. The infection may then spread to your uterus, fallopian tubes, or ovaries.
 |
What are the signs and symptoms of PID?
PID may cause mild signs and symptoms or none at all. You may have any of the following:
- Fever or chills
- Pain in your lower abdomen or pelvis
- Heavy discharge from your vagina that may have an unusual or bad smell
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding during or after sex, or bleeding in between your monthly periods
- Pain during sex, especially if your PID is new
- Painful or difficult urination
How is PID treated?
- Antibiotics are given to fight the bacterial infection that caused your PID.
- Surgery may be needed to treat problems related to PID. If you have an abscess on your tubes or ovaries, you may need surgery to drain it. Ask your healthcare provider for more information about surgeries or other procedures you may need.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
What can I do to manage PID?
- Finish your treatment. If you do not finish your treatment for PID, your infection may not go away. You may also have an increased risk for another STI in the future.
- Do not have sex until your healthcare provider says it is okay. You will need to finish treatment before it is safe to have sex.
How can I decrease my risk for PID?
- Use a new condom each time you have sex. Wear a condom during oral, vaginal, and anal sex. Male and female condoms are available. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have questions about the correct use of condoms.
- Get tested for STIs before and after a new sex partner. Ask your partner to get tested before you have sex.
- Do not delay treatment for STIs or vaginal infections. Early treatment can prevent health problems that may lead to PID.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have severe pain in your lower abdomen.
- You have nausea or are vomiting.
- You have chills or a high fever.
- Your symptoms get worse or do not improve after 3 days of treatment.
- Your skin is red, itchy, or you have a new rash.
- You think or know you are pregnant.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
