Melanoma
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is melanoma?
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer. It forms in cells called melanin that make skin color. Melanoma may appear as a new mole, or in moles you already have. Melanoma can form in the skin, eyes, nose, or throat.
What increases my risk for melanoma?
- Sun exposure or use of tanning beds
- A family history of melanoma
- At least 1 blistering sunburn as a child or teenager
- Light colored skin, hair, or eyes
- Freckles or moles that increase or change
- A weakened immune system
- Skin diseases, such as xeroderma pigmentosum
What are the signs and symptoms of melanoma?
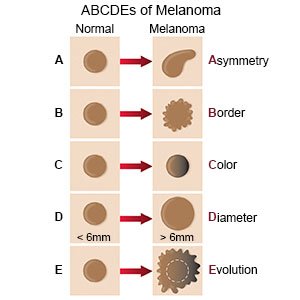
Melanoma is described based on the ABCDE system:
- A symmetry means if a line is drawn through the middle of the mole, the 2 halves are not equal.
- B order means the edges of the mole are not smooth.
- C olors include blue, black, brown, or red.
- D iameter means the size of the mole is larger than a pencil eraser.
- E volution means the mole changes. This may include changes in appearance, changes in symptoms, such as bleeding, or changes in shape, size, or color. The area may also itch or feel hard, lumpy, swollen, or tender.
How is melanoma diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will examine your skin and look at the size, shape, and color of your moles. You may need more than one of the following tests:
- A skin biopsy is done to remove part or all of the mole, sore, or lump. The sample is then sent to a lab to be tested for cancer.
- A CT, MRI, or PET scan may be used to see if the melanoma has spread. You may be given contrast liquid to help the melanoma show up better in pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell a healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
- A sentinel node biopsy may be done to see if the melanoma has spread to lymph nodes close to the mole.
How is melanoma treated?
Treatment depends on the stage of your melanoma. You may need any of the following:
- Surgery is done to remove the melanoma and some of the tissue around it. Surgery may also be done if the cancer has spread into the lymph nodes or other parts of your body.
- Radiation therapy uses x-rays or gamma rays to treat cancer. Radiation kills cancer cells and may stop the cancer from spreading. It is also used to reduce symptoms, such as pain.
- Chemotherapy is medicine given to kill cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy is medicine given to help your immune system fight the cancer.
- Targeted therapy is medicine given to kill cancer cells without harming healthy tissue.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
How should I take care of my skin?
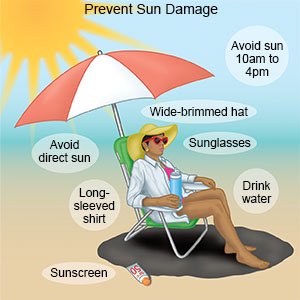
- Protect your skin from the sun's ultraviolet (UVA UVB) rays:
- Wear sunscreen that has an SPF (sun protectant factor) of 30 or higher. Make sure it has UVA and UVB protection. Follow directions when you use sunscreen. Apply sunscreen again if you swim, sweat, or are in the sun for longer than an hour. Protect your lips by using lipsticks or lip balms that contain sunscreen. Apply sunscreen even on cloudy days.
- Stay out of the sun between 10 am and 4 pm. This is when the sun is strongest and most damaging to your skin.
- Wear protective clothing. Long-sleeved shirts and pants will protect your arms and legs when you are out in the sun. A wide-brimmed hat can protect both your face and neck. Wear sunglasses that have UVA and UVB protection.
- Do not use tanning booths. These can damage your skin as much as the sun can.
- Look for new bumps on your skin every week. Check your entire body, including your scalp. Look for moles that change in shape, size, color, or texture. Know what your regular birthmarks and moles look like.
 |
When should I call my doctor?
- You have a mole that changes in shape, size, color, or texture.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Melanoma
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
