Hepatitis A Vaccine for Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
The hepatitis A vaccine
is an injection that helps protect your child from the virus that causes hepatitis A. Hepatitis A is a serious liver disease. The virus is usually spread by person-to-person contact or through food and liquid contaminated with the virus.
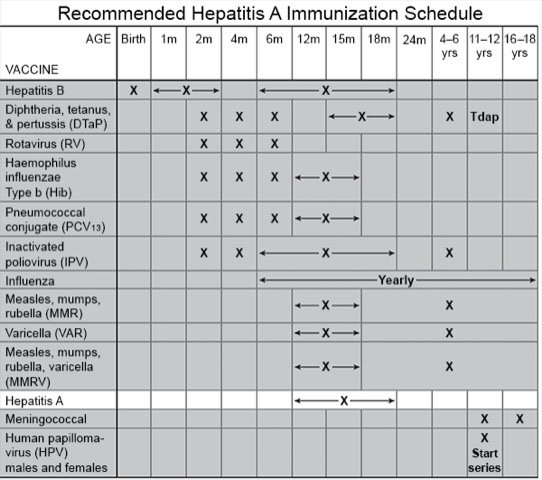
When your child should get the hepatitis A vaccine:
The vaccine is given in 2 doses at least 6 months apart. The vaccine can be given with other vaccines.
- Children 12 to 23 months old should get the vaccine routinely.
- Babies 6 to 11 months old who are traveling outside the United States may be given the vaccine.
- Children and adolescents 2 to 18 years old can still get the vaccine, if needed. Talk to your child's healthcare provider about when to get make-up doses.
- The vaccine is given to pregnant or breastfeeding adolescents who are at risk for hepatitis A. Your adolescent's provider will tell you when the vaccine should be given.
 |
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- Your child has signs of a severe allergic reaction, such as trouble breathing, hives, or wheezing.
Seek care immediately if:
- Your child has a high fever or any symptoms that concern you.
Call your child's doctor if:
- You have questions or concerns about the hepatitis A vaccine.
Related medications
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
- measles virus vaccine/mumps virus vaccine/rubella virus vaccine/varicella virus vaccine
- ProQuad
- Rotarix
- RotaTeq
- rotavirus vaccine
The following increase the risk for hepatitis A:
- Exposure to hepatitis A within the past 2 weeks
- A scheduled trip or move to an area where hepatitis A is common or has an active outbreak
- Close contact with a child adopted from a country where hepatitis A is common or has an active outbreak
- A chronic liver disease, HIV, or a weak immune system
- Use of street drugs
- Being male and having sex with another male
Reasons your child should not get the hepatitis A vaccine or should wait to get it:
Your child should not get a second dose if the first caused a severe allergic reaction. Ask about ingredients in the vaccine that can trigger a reaction if your child has a severe allergy. Wait to get the vaccine if your child is sick or has a fever on the appointment day.
Risks of the hepatitis A vaccine:
The area where your child got the shot may be sore or tender. This is usually mild and goes away in a few hours. Your child may also have a headache or loss of appetite, or feel tired for up to 2 days. Your child may have an allergic reaction to the vaccine. This can be life-threatening.
Apply a warm compress
to the area where your child got the vaccine to relieve swelling and pain.
Follow up with your child's doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Hepatitis A Vaccine for Children
Treatment options
Care guides
- Hepatitis A Vaccine
- Hepatitis A Vaccine for Children
- Hepatitis B Vaccine
- Hepatitis B Vaccine for Children
- The Importance of Immunizations (Vaccines) for Adults
- The Importance of Immunizations (Vaccines) for Children
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
