Gastroenteritis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
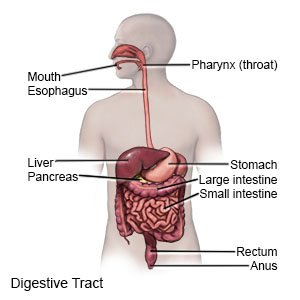
Gastroenteritis, or stomach flu, is an infection of the stomach and intestines. Causes may include bacteria, parasites, viruses, chemicals, or reactions to medicines.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Return to the emergency department if:
- You see blood in your vomit or diarrhea.
- You cannot stop vomiting.
- You have severe abdominal pain, or your abdomen is swollen.
- You have not urinated for 12 hours.
- You feel like you are going to faint.
Call your doctor if:
- You have a fever that does not go away.
- You continue to vomit or have diarrhea, even after treatment.
- You see worms in your diarrhea.
- Your mouth or eyes are dry. You are not urinating as much or as often.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
- Medicines may be given to stop vomiting or diarrhea, decrease abdominal cramps, or treat an infection.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Manage your symptoms:
- Drink liquids as directed. Ask your healthcare provider how much liquid to drink each day, and which liquids are best for you. You may also need to drink an oral rehydration solution (ORS). An ORS has the right amounts of sugar, salt, and minerals in water to replace body fluids.
- Eat bland foods. When you feel hungry, begin eating soft, bland foods. Examples are bananas, clear soup, potatoes, and applesauce. Do not have dairy products, alcohol, sugary drinks, or drinks with caffeine until you feel better. Avoid eating high-fat or fast foods.
- Eat small, frequent meals throughout the day. Your stomach may tolerate small meals every 2 to 3 hours instead of 3 large meals.
- Rest as much as possible. Slowly start to do more each day when you begin to feel better.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Prevent the spread of gastroenteritis:
Gastroenteritis can spread easily. Keep yourself, your family, and your surroundings clean to help prevent the spread of gastroenteritis:
- Wash your hands often. Use soap and water. Wash your hands after you use the bathroom, change a child's diapers, or sneeze. Wash your hands before you prepare or eat food.

- Clean surfaces and do laundry often. Wash your clothes and towels separately from the rest of the laundry. Clean surfaces in your home with antibacterial cleaner or bleach.
- Clean food thoroughly and cook safely. Wash raw vegetables before you cook. Cook meat, fish, and eggs fully. Do not use the same dishes for raw meat as you do for other foods. Refrigerate any leftover food immediately.
- Be aware when you camp or travel. Drink only clean water. Do not drink from rivers or lakes unless you purify or boil the water first. When you travel, drink bottled water and do not add ice. Do not eat fruit that has not been peeled. Do not eat raw fish or meat that is not fully cooked.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Gastroenteritis
Treatment options
- Medications for Allergic Colitis
- Medications for Gastroenteritis
- Medications for Infection
- Medications for Infectious Gastroenteritis
- Medications for Noninfectious Colitis
Care guides
- Enteritis
- Food Poisoning
- Gastroenteritis
- Giardiasis
- Infectious Colitis
- Salmonella Infection
- Traveler's Diarrhea
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
