Epilepsy in Older Adults
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Epilepsy in older adults
develops often, but the signs are not always easy to recognize. Seizure activity may be mistaken for effects of aging, such as memory problems, confusion, falls, dizziness, and numbness.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- The person stops breathing or you cannot feel a pulse.
- The person's seizure lasts longer than 5 minutes.
- The person has a second seizure within 24 hours of the first.
- The person injures himself or herself during a seizure.
Call the person's doctor if:
- He or she does not take his or her medicine.
- You have questions or concerns about his or her condition, safety, or care.
Signs and symptoms of epilepsy
depend on the type of seizures a person is having. Contact the person's healthcare provider if you notice any of the following happening more than once or in the same pattern:
- Falling to the ground shaking
- Confusion
- Staring into space
- Wandering
- Unusual movements such as muscle jerking or lip smacking
- Not able to answer questions or talk
Treatment may include
medicines to help control seizures. Medicine may be needed daily to prevent seizures or during a seizure to stop it. Do not let the person stop taking seizure medicine unless directed by his or her healthcare provider.
Help an older adult with epilepsy:
Older adults with epilepsy can continue to live alone if they remain healthy and mentally capable. Here are some things to help an older adult remain independent:
- Reduce injuries:
- Live in a single level house or apartment
- Carpet can help by providing cushion for falls
- Put padding around corners of tables and rails of a bed if seizures are frequent
- Make people aware:
- Set up with neighbors the time every day that the curtains or blinds will be opened. Neighbors will check to make sure there are no problems if the curtains or blinds remain closed.
- Get a device that can alert others when a seizure is happening. Talk to the person's healthcare provider about available devices.
- Remind the person to carry medical alert identification. He or she should wear medical alert jewelry or carry a card that says he or she has epilepsy. Ask the person's healthcare provider where to get these items.
Seizure prevention:
The person may not be able to prevent every seizure. The following can help manage triggers that may make a seizure start:
- Take medicine every day at the same time. This will also help prevent medicine side effects. Set an alarm to help remind the person to take his or her medicine every day. A medicine organizer can also help the person keep track of medicine taken each day.
- Set a regular sleep schedule. A lack of sleep can trigger a seizure. Encourage the person to try to go to sleep and wake up at the same times every day. Keep his or her bedroom quiet and dark. Talk to the person's healthcare provider if he or she is having trouble sleeping.
- Limit or do not drink alcohol as directed. Alcohol can trigger a seizure, especially if the person drinks a large amount at one time. A drink of alcohol is 12 ounces of beer, 1½ ounces of liquor, or 5 ounces of wine. Ask the person's healthcare provider how much alcohol is okay for him or her. The provider may recommend that the person does not drink any alcohol. Tell the provider if help is needed to quit drinking.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Keep an older adult safe during a seizure:
Give the following instructions to the person's family, friends, and coworkers:
- Do not panic.
- Do not hold him or her down or put anything in his or her mouth.
- Gently guide him or her to the floor or a soft surface.
- Place him or her on his or her side to help prevent swallowing saliva or vomit.
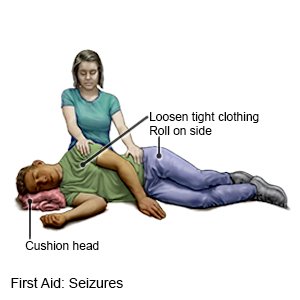
- Protect him or her from injury. Remove sharp or hard objects from the area surrounding him or her, or cushion his or her head.
- Loosen the clothing around his or her head and neck.
- Time how long the seizure lasts. Call 911 if the seizure lasts longer than 5 minutes or if there is a second seizure within 24 hours of the first.
- Stay with him or her until the seizure ends. Let him or her rest until fully awake and aware.
- If possible, perform CPR if he or she stops breathing or you cannot feel a pulse.
- Do not give him or her anything to eat or drink until he or she is fully awake and aware.
Follow up with the person's doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Epilepsy
Treatment options
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
