Bradycardia
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
Bradycardia is a slow heart rate, usually fewer than 60 beats per minute. A slow heart rate is normal for some people, such as athletes, and needs no treatment. Bradycardia may also be caused by health conditions that do need treatment. Your healthcare provider will tell you what heart rate is too low for you.
 |
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
An IV
is a small tube placed in your vein that is used to give you medicine or liquids.
Oxygen:
You may need extra oxygen if your blood oxygen level is lower than it should be. You may get oxygen through a mask placed over your nose and mouth or through small tubes placed in your nostrils.
Medicines:
- Heart medicines may be given to increase your heart rate. These medicines are given through an IV.
- Other medicines may be given for any medical problems that are causing your bradycardia. These health problems may include an infection, or a blood sugar, electrolyte, or thyroid imbalance. Talk to your healthcare provider about these medicines.
Tests:
- Blood tests may be done to see if you have any heart damage. They may also be used to find the cause of your bradycardia.
- An EKG records the electrical activity of your heart. It may be used to check for heart damage from a heart attack or problems with the way electrical signals travel through your heart. You may be asked to walk on a treadmill during this test to check if exercise triggers symptoms.
Monitoring:
- Vital signs include a check of your heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rate, and temperature. Your vital signs may be checked several times while you are in the hospital.
- A pulse oximeter monitors the oxygen in your blood. Your body may not get enough oxygen if your heart pumps too slowly. A cord with a clip or sticky strip will be placed on your finger, ear, or toe. The other end of the cord is hooked to a machine.
- A heart monitor called telemetry, will be used to track your heart rate and rhythm while you are in the hospital.
Treatment:
Your healthcare provider will talk with you about the benefits and risks of treatment that may be right for you:
- A temporary pacemaker is a short-term treatment in the hospital. The pacemaker is applied to your skin with sticky pads or placed into a vein in your neck or chest. A small pacing device helps keep your heartbeat stable.
- A permanent pacemaker is implanted under the skin of your chest or abdomen during surgery. A tiny battery creates electrical impulses that keep your heart rate regular.
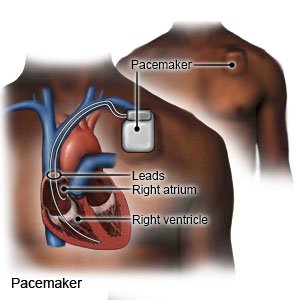
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
RISKS:
You may faint when your heart rate gets too low. You may develop seizures, high blood pressure, chest pain, or heart failure. Your heart may stop beating.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Bradycardia
Treatment options
- Medications for Bradyarrhythmia
- Medications for Sinus Node Dysfunction
- Medications for Tachyarrhythmia
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
