Abscess
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
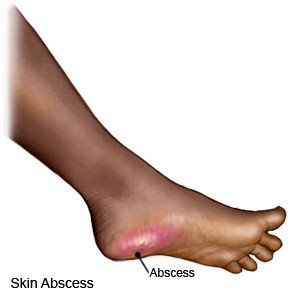
An abscess
is an area under the skin where pus (infected fluid) collects. An abscess is often caused by bacteria, fungi or other germs that get into an open wound. You can get an abscess anywhere on your body.
 |
Common signs and symptoms of an abscess:
You may have a swollen mass that is red and painful. Pus may leak out of the mass. The pus will be white or yellow and may smell bad. You may have redness and pain days before the mass appears. You may have a fever and chills if the infection spreads.
Seek immediate care if:
- The area around your abscess becomes very painful, warm, or has red streaks.
- You have a fever and chills.
- Your heart is beating faster than usual.
- You feel faint or confused.
Call your doctor if:
- Your abscess gets bigger or does not get better.
- Your abscess returns.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Treatment for an abscess:
Your healthcare provider may need to make a cut in the abscess to allow the pus to drain. You may need surgery to remove your abscess. You may need any of the following:
- Antibiotics help treat a bacterial infection.
- Acetaminophen decreases pain and fever. It is available without a doctor's order. Ask how much to take and how often to take it. Follow directions. Read the labels of all other medicines you are using to see if they also contain acetaminophen, or ask your doctor or pharmacist. Acetaminophen can cause liver damage if not taken correctly.
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Self-care:
- Apply a warm compress to your abscess. This will help it open and drain. Wet a washcloth in warm, but not hot, water. Apply the compress for 10 minutes. Repeat this 4 times each day. Do not press on an abscess or try to open it with a needle. You may push the bacteria deeper or into your blood.
- Do not share your clothes, towels, or sheets with anyone. This can spread the infection to others.
- Wash your hands often. This can help prevent the spread of germs. Use soap and water or an alcohol-based hand rub.

Care for your wound after it is drained:
- Care for your wound as directed. If your healthcare provider says it is okay, carefully remove the bandage and gauze packing. You may need to soak the gauze to get it out of your wound. Clean your wound and the area around it as directed. Dry the area and put on new, clean bandages. Change your bandages when they get wet or dirty.
- Ask your healthcare provider how to change the gauze in your wound. Keep track of how many pieces of gauze are placed inside the wound. Do not put too much packing in the wound. Do not pack the gauze too tightly in your wound.
Follow up with your healthcare provider in 1 to 3 days:
You may need to have your packing removed or your bandage changed. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Abscess
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
