Imovax Rabies: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: rabies vaccine
Dosage form: intramuscular injection kit
Drug class: Viral vaccines
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 17, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Use In Specific Populations
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- References
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
Highlights of Prescribing Information
IMOVAX® RABIES (Rabies Vaccine) for injectable suspension, for intramuscular use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1980
Recent Major Changes
| Dosage and Administration, Pre-exposure Prophylaxis Dose and Schedule (2.1) | 7/2025 |
Indications and Usage for Imovax Rabies
IMOVAX RABIES is a vaccine indicated for the prevention of rabies in all age groups. IMOVAX RABIES is approved for pre-exposure prophylaxis and post-exposure prophylaxis to prevent rabies. (1)
Imovax Rabies Dosage and Administration
For intramuscular use. Each dose of IMOVAX RABIES is 1 mL. The vaccination schedule differs depending on whether IMOVAX RABIES is administered for pre-exposure prophylaxis or post-exposure prophylaxis. (2.1, 2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Contraindications
Warnings and Precautions
- Individuals with altered immunocompetence may have reduced immune response to IMOVAX RABIES. (5.1)
- In individuals who have experienced an anaphylactic reaction following a dose of IMOVAX RABIES, the risk of developing rabies must be carefully considered in decisions regarding the discontinuation of post-exposure vaccination. (5.2)
- Do not inject the vaccine into the gluteal area. (5.4)
- Do not inject the vaccine intradermally. (5.4)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most commonly reported adverse reactions were:
- Five-dose regimen for post-exposure prophylaxis: the commonly reported local adverse reactions (≥25%) were pain, erythema, swelling, and itching; the commonly reported systemic adverse reactions (≥20%) were headache, nausea, abdominal pain, muscle aches, and dizziness.
- Three-dose regimen for pre-exposure prophylaxis: the most commonly reported solicited adverse reactions (≥10%) were injection site pain (30.4% and 43.5%), headache (27.5% and 19.6%), malaise (23.2% and 17.4%) and myalgia (18.8% and 10.9%) (in participants 18 years of age and older and participants 2 years through 17 years of age, respectively); and fever (17.4%) (in participants 2 years through 17 years of age).
- Two-dose regimen for pre-exposure prophylaxis: the most commonly reported solicited adverse reactions (≥10%) were injection site pain (35.4% and 25.7%) and headache (21.3% and 13.9%) (in participants 18 years of age and older and participants 2 years through 17 years of age, respectively); malaise (26.0%) and myalgia (22.8%) (in participants 18 years of age and older). (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Sanofi Pasteur Inc. at 1-800-822-2463 (1-800-VACCINE) or VAERS at 1-800-822-7967 and http://vaers.hhs.gov.
Drug Interactions
Immunosuppressive agents should not be administered during post-exposure prophylaxis unless essential for the treatment of other conditions. (7.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 7/2025
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Imovax Rabies
IMOVAX RABIES is a vaccine indicated for the prevention of rabies in all age groups.
- IMOVAX RABIES is approved for pre-exposure prophylaxis to prevent rabies.
- IMOVAX RABIES is approved for post-exposure prophylaxis to prevent rabies.
2. Imovax Rabies Dosage and Administration
For intramuscular use
2.1 Pre-exposure Prophylaxis Dose and Schedule
Each dose of IMOVAX RABIES is 1 mL.
Primary Vaccination series:
-
Three-dose schedule: Administer a dose at Day 0, 7, and 21 or 28
OR - Two-dose schedule: Administer a dose at Day 0 and 7
Booster:
Administer a single dose of IMOVAX RABIES.
The United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has published clinical guidance on administration of booster doses of rabies vaccine depending on rabies exposure risk and for vaccination of individuals who are immunocompromised or who are receiving chloroquine or drugs related to chloroquine. (1) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Drug Interactions (7.1)]
2.2 Post-exposure Prophylaxis Dose and Schedule
Each dose of IMOVAX RABIES is 1 mL.
The IMOVAX RABIES post-exposure prophylaxis schedule depends on whether or not the individual has been previously vaccinated and/or immunized against rabies. The CDC considers individuals to be previously vaccinated if they received one of the recommended cell-culture vaccines either in a pre-exposure or post-exposure prophylaxis regimen, or they received another vaccine regimen (or vaccines other than cell-culture vaccine) and had a documented adequate rabies virus neutralizing antibody (RVNA) response (defined as ≥ 0.5 IU/mL by Rapid Fluorescent Focus Inhibition Test [RFFIT]). (2)
Previously Vaccinated Individuals
In previously vaccinated individuals (see definition above),
- Administer a dose of IMOVAX RABIES immediately after exposure (at Day 0) and at Day 3.
Unvaccinated or Immunosuppressed (irrespective of previous vaccination status) Individuals
For individuals who have not previously received rabies vaccine, or who are immunosuppressed,
- Administer a dose of IMOVAX RABIES immediately after exposure (at Day 0) and at Day 3, 7, 14, and 28. Administer each dose of IMOVAX RABIES at an anatomical site distant from the Human Rabies Immunoglobulin (HRIG) administration site(s).
- Administer HRIG at Day 0 according to its Prescribing Information.
- Post-vaccination serologic testing is indicated when the individual is known to be immunosuppressed. (3) Contact local or state health department or CDC for recommendations for serologic testing. (3)
Individuals with Uncertain Immune Status
In individuals whose RVNA status is not known and who 1) have not received the full recommended regimen of a cell culture vaccine either in a pre-exposure or post-exposure prophylaxis regimen OR 2) received another (non-cell culture) rabies vaccine regimen,
- Administer a dose of IMOVAX RABIES immediately after exposure (at Day 0) and at Day 3, 7, 14, and 28. Administer each dose of IMOVAX RABIES at an anatomical site distant from the HRIG administration site(s).
- Administer HRIG at Day 0 according to its Prescribing Information.
- If antibody levels ≥ 0.5 IU/mL by RFFIT can be demonstrated in a serum sample collected before vaccine is given, vaccinations may be discontinued after at least two doses of IMOVAX RABIES. (1) (2)
2.3 Preparation
IMOVAX RABIES is supplied in a package containing a vial of lyophilized vaccine, a Luer-Lok prefilled syringe containing 1 mL of Sterile Water diluent with a plunger rod either inserted into the syringe or provided separately, and a sterile reconstitution needle. Reconstitute the lyophilized vaccine with the Sterile Water diluent to form IMOVAX RABIES, as described in the instructions below.
Instructions for vaccine reconstitution
Step 1: Screw the plunger rod into the syringe containing Sterile Water diluent if the plunger rod is provided separately.
| Step 2: Hold the syringe cap (avoid holding the plunger rod or syringe barrel) and unscrew the tip cap by twisting it counterclockwise. | 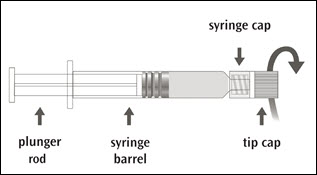 |
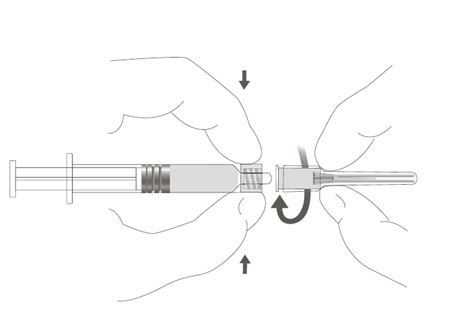
| Step 3: Attach the reconstitution needle to the syringe, by gently twisting the needle clockwise into the syringe until slight resistance is felt. | 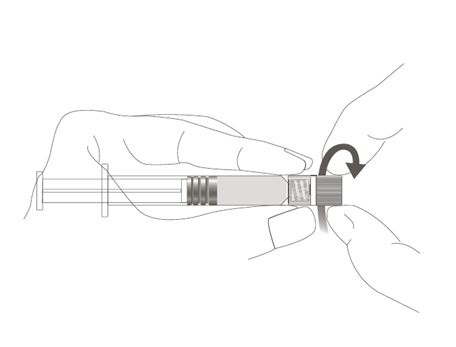 |
Step 4: Transfer the entire content of the syringe containing Sterile Water diluent into the vial containing lyophilized vaccine.
Step 5: Gently swirl the vial until completely dissolved. After reconstitution, IMOVAX RABIES is pink to red.
Step 6: Unscrew the syringe from the reconstitution needle to eliminate negative pressure.
Reattach the syringe to the reconstitution needle which has remained in the vial.
Step 7: Withdraw the total content of the vial (approximately 1 mL) containing reconstituted vaccine. Remove the reconstitution needle and discard it.
Step 8: Attach a new sterile needle (as per Step 3) of a proper length and gauge suitable for intramuscular administration.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. If either of these conditions exist, IMOVAX RABIES should not be administered.
2.4 Administration
Administer IMOVAX RABIES intramuscularly immediately after reconstitution.
For adults and older children, the vaccine should be injected into the deltoid muscle. (4) (5) (6) In infants and small children, the anterolateral aspect of the thigh may be preferable, depending on age and body mass.
Do not administer in the gluteal area [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Do not administer intradermally [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
For injectable suspension. A single dose after reconstitution is 1 mL.
4. Contraindications
Pre-exposure Prophylaxis
Do not administer to anyone with a known life-threatening systemic hypersensitivity reaction to any component of the vaccine [See Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Description (11)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Altered Immunocompetence
Individuals with altered immunocompetence, including those receiving immunosuppressant therapy, may have reduced immune response to IMOVAX RABIES [See Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.2) and Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.2 Management of Allergic Reactions
Appropriate medical treatment must be immediately available to manage potential anaphylactic reactions following administration of IMOVAX RABIES.
In individuals who have experienced an anaphylactic reaction following a dose of IMOVAX RABIES, the risk of developing rabies must be carefully considered in decisions regarding the discontinuation of post-exposure prophylaxis vaccination.
5.3 Other Adverse Reactions
- Once initiated, rabies prophylaxis should not be interrupted or discontinued because of local or mild systemic adverse reactions to rabies vaccine [See Adverse Reactions (6)].
- Serious neuroparalytic reactions occurring during the administration of rabies vaccines pose a dilemma for the attending physician. An individual's risk of developing rabies must be carefully considered before deciding to discontinue vaccination. Moreover, the use of corticosteroids to treat life-threatening neuroparalytic reactions carries the risk of inhibiting the development of active immunity to rabies. It is especially important in these cases that the serum of the patient be tested for RVNA titers. Advice and assistance on the management of serious adverse reactions in individuals receiving rabies vaccines may be sought from the local or state health department. (7)
- Individuals who have experienced "immune complex-like" hypersensitivity reactions should receive no further doses of IMOVAX RABIES unless they are exposed to rabies or they are truly likely to be inapparently and/or unavoidably exposed to rabies virus and have unsatifactory RVNA titers.
5.4 Administration Precautions
- Do not inject the vaccine into the gluteal area as administration in this area may result in lower RVNA titers. (3) There have been reports of possible vaccine failure when the vaccine has been administered in this area. Presumably, subcutaneous fat in the gluteal area may interfere with the immune response to IMOVAX RABIES. (4) (8)
- Do not inject the vaccine intradermally.
- The product is provided in a single-dose vial. Because the single-dose vial contains no preservative, it is not to be used as a multi-dose vial for intradermal injection. In both pre-exposure and post-exposure immunization, the full 1 mL dose should be given intramuscularly.
5.5 Serum Sickness Type Reactions
Serum sickness type reactions have been reported in individuals receiving booster doses of rabies vaccine for pre-exposure prophylaxis. The reaction is characterized by onset approximately 2 to 21 days post-booster, presents with a generalized urticaria, and may also include arthralgia, arthritis, angioedema, nausea, vomiting, fever, and malaise. None of the reported reactions were life-threatening. This has been reported in up to 7% of individuals receiving booster vaccination. (9)
5.6 Guillain-Barré Syndrome
Rare cases of neurologic illness resembling Guillain-Barré syndrome, (10) (11) a transient neuroparalytic illness, that resolved without sequelae in 12 weeks and a focal subacute central nervous system disorder temporally associated with IMOVAX RABIES, have been reported. (12)
5.7 Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
This product contains albumin, a derivative of human blood. Based on effective donor screening and product manufacturing processes, it carries an extremely remote risk for transmission of viral diseases and variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD). There is a theoretical risk for transmission of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD), but if that risk actually exists, the risk of transmission would also be considered extremely remote. No cases of transmission of viral diseases, CJD, or vCJD have ever been identified for licensed albumin or albumin contained in other licensed products.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
In a clinical trial evaluating a five-dose regimen for post-exposure prophylaxis, the commonly reported local adverse reactions (≥25%) were pain, erythema, swelling, and itching; the commonly reported systemic adverse reactions (≥20%) were headache, nausea, abdominal pain, muscle aches, and dizziness.
In a clinical trial evaluating the three-dose regimen for pre-exposure prophylaxis, the most commonly reported adverse reactions (≥10%) were injection site pain (30.4% and 43.5%), headache (27.5% and 19.6%), malaise (23.2% and 17.4%) and myalgia (18.8% and 10.9%) (percentages reflect rates in participants 18 years of age and older and participants 2 years through 17 years of age, respectively), fever (17.4%) (in participants 2 years through 17 years of age).
In a clinical trial evaluating the two-dose regimen for pre-exposure prophylaxis, the most commonly reported adverse reactions (≥10%) were injection site pain (35.4% and 25.7%) and headache (21.3% and 13.9%) (percentages reflect rates in participants 18 years of age and older and participants 2 years through 17 years of age, respectively), malaise (26.0%) and myalgia (22.8%) (in participants 18 years of age and older).
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a vaccine cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another vaccine and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Post-exposure Prophylaxis
Reactions after vaccination with IMOVAX RABIES have been observed. (9) In a study using five doses of IMOVAX RABIES, local reactions such as pain, erythema, swelling or itching at the injection site were reported in about 25% of recipients of IMOVAX RABIES, and mild systemic reactions such as headache, nausea, abdominal pain, muscle aches, and dizziness were reported in about 20% of recipients. (7)
Pre-exposure Prophylaxis
The 2-dose and 3-dose pre-exposure prophylaxis regimens of IMOVAX RABIES were evaluated in two clinical trials.
Study 1 (NCT03700242), a randomized, open-label, controlled multicenter study included healthy participants 2 years of age and older. In this study, the safety analysis set included 228 participants who received a 2-dose pre-exposure prophylaxis regimen (on Day 0 and Day 7) and 115 participants who received a 3-dose pre-exposure prophylaxis regimen (on Day 0, Day 7 and Day 21). Of these participants, 101 were 2 years through 11 years of age (66 received 2-dose regimen, 35 received 3-dose regimen), 46 were 12 years through 17 years of age (35 received 2-dose regimen, 11 received 3-dose regimen), and 196 were 18 years through 59 years of age (127 received 2-dose regimen, 69 received 3-dose regimen).
Study 2 (NCT04127786), an observer blind, randomized, controlled multicenter study included healthy participants 1 year of age and older. In this study, the safety analysis set included 139 participants who received a 2-dose pre-exposure prophylaxis regimen (on Day 0, and Day 7) and 200 participants who received a 3-dose pre-exposure prophylaxis regimen (on Day 0, Day 7, and Day 28). Of those who received the 3-dose pre-exposure prophylaxis regimen, 100 participants were 1 year through 17 years of age (70 from 1 year through 11 years of age and 30 from 12 years through 17 years of age) and 100 participants were 18 years of age and older, including 2 participants 65 years of age and older. Per study design, no participants 1 year through 17 years of age were included in the 2-dose pre-exposure prophylaxis regimen group.
In both Study 1 and 2, solicited local (injection site) and systemic adverse reactions were recorded by participants or by parents/guardians in a diary card daily for 7 days after any dose. At subsequent visits, approximately 7 to 21 days post-vaccination, participants or parents/guardians reviewed diary cards with study investigators and when necessary, made corrections or clarifications. Unsolicited non-serious adverse events were recorded through 28 days after any dose, and serious adverse events were recorded for at least 6 months following the last vaccination.
The solicited adverse reactions that occurred within 7 days following any dose of IMOVAX RABIES in participants 18 years and older and participants 2 years through 17 years of age in Study 1 are presented in Table 1.
| ≥ 18 years of age | 2 years through 17 years of age | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solicited Adverse Reactions | IMOVAX RABIES 2-dose Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (N=127) | IMOVAX RABIES 3-dose Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (N=69) | IMOVAX RABIES 2-dose Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (N=101) | IMOVAX RABIES 3-dose Pre-exposure prophylaxis (N=46) |
| N = Number of participants who received at least one dose | ||||
|
||||
| Local (injection site) | ||||
| Pain, any* | 35.4 | 30.4 | 25.7 | 43.5 |
| Pain, Grade 3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Erythema, any† | 0.0 | 2.9 | 1.0 | 2.2 |
| Erythema, Grade 3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Swelling, any† | 0.0 | 1.4 | 2.0 | 6.5 |
| Swelling, Grade 3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Systemic | ||||
| Fever, any‡ | 4.7 | 7.2 | 4.0 | 17.4 |
| Fever, Grade 3 | 0.8 | 1.4 | 2.0 | 2.2 |
| Headache, any§ | 21.3 | 27.5 | 13.9 | 19.6 |
| Headache, Grade 3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Malaise, any§ | 26.0 | 23.2 | 9.9 | 17.4 |
| Malaise, Grade 3 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Myalgia, any§ | 22.8 | 18.8 | 5.9 | 10.9 |
| Myalgia, Grade 3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
In Study 2 participants, the commonly reported adverse reactions were generally consistent with those reported in Study 1 participants. In the two participants 1 year to less than 2 years of age in Study 2, the only reported systemic adverse reactions were vomiting and abnormal crying, both occurring in the same participant.
In both Study 1 and Study 2, most solicited adverse reactions resolved within 3 days. No related serious adverse events or deaths were reported in either study.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following additional adverse events have been identified during postmarketing use of IMOVAX RABIES. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to IMOVAX RABIES exposure.
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders
Lymphadenopathy
Immune System Disorders
Anaphylactic reaction, serum sickness type reaction, dermatitis allergic, pruritus (itching), edema
Nervous System Disorders
Paresthesia, neuropathy, convulsion, encephalitis, syncope
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Vomiting, diarrhea
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders
Arthralgia
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions
Asthenia, malaise, fever and chills (shivering), injection site hematoma
Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal Disorders
Wheezing, dyspnea
Related/similar drugs
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Immunosuppressive Treatments
Corticosteroids, other immunosuppressive agents or treatments, and immunosuppressive illnesses can interfere with the development of active immunity and predispose the patient to developing rabies [See Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.2)]. Immunosuppressive agents should not be administered during post-exposure prophylaxis, unless essential for the treatment of other conditions. When rabies post-exposure prophylaxis is administered to individuals receiving steroids or other immunosuppressive therapy, it is especially important that serum be tested for an RVNA titer to ensure that an adequate response has developed. (3)
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
All pregnancies have a risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the US general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of IMOVAX RABIES in pregnant women. Data on IMOVAX RABIES administered to pregnant women are insufficient to inform vaccine-associated risks in pregnancy.
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with IMOVAX RABIES.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known whether IMOVAX RABIES is excreted in human milk. Data are not available to assess the effects of IMOVAX RABIES on the breastfed infant or on milk production/excretion.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for IMOVAX RABIES and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from IMOVAX RABIES or from the underlying maternal condition. For preventive vaccines, the underlying maternal condition is susceptibility to the disease prevented by the vaccine.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy have been established in all pediatric age groups [See Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of IMOVAX RABIES did not include sufficient numbers of participants aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger participants [See Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14)].
11. Imovax Rabies Description
IMOVAX RABIES (Rabies Vaccine) is a sterile, injectable suspension for intramuscular use. IMOVAX RABIES is supplied as a vial of lyophilized vaccine which must be reconstituted with the accompanying Sterile Water diluent. The vaccine is prepared from rabies vaccine virus strain PM-1503-3M.
The vaccine virus is harvested from infected human diploid cells, MRC-5 cell line, concentrated by ultrafiltration and is inactivated by beta-propiolactone. One dose of reconstituted vaccine contains less than 100 mg human albumin, less than 150 mcg neomycin sulfate and 20 mcg of phenol red indicator. Beta-propiolactone, a residual component of the manufacturing process, is present in less than 50 parts per million. IMOVAX RABIES contains no preservative.
The potency of one dose (1 mL) of IMOVAX RABIES is equal to or greater than 2.5 international units (IU) of rabies antigen.
The vial stopper, the plunger rod and the tip cap of the syringe are not made with natural rubber latex.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Pre-exposure Prophylaxis
Three-dose regimen for pre-exposure prophylaxis
Antibody responses to IMOVAX RABIES have been demonstrated in trials conducted in England (13), Germany (14) (15), France (16) and Belgium. (17) In the US, IMOVAX RABIES resulted in geometric mean titers (GMT) of 12.9 IU/mL at Day 49 and 5.1 IU/mL at Day 90 when three doses were given intramuscularly during the course of one month. The range of RVNA responses was 2.8 to 55.0 IU/mL at Day 49 and 1.8 to 12.4 IU/mL at Day 90. (18) The definition of a minimally accepted RVNA titer varies among laboratories and is influenced by the type of test conducted. The thresholds for an adequate immune response used in these trials were either 1:5 or 0.5 IU/mL depending on the trials.
Two-dose regimen for pre-exposure prophylaxis
The two-dose regimen (on Day 0, and Day 7) was assessed in two phase 3 studies.
In one observer-blind, randomized, controlled, multicenter study conducted in Thailand (Study 2), RVNA responses after 2 doses of IMOVAX RABIES were compared to RVNA responses after 3 doses of IMOVAX RABIES. In this study, 100 healthy participants 18 years of age and older (including 2 participants 65 years of age and older), and 100 participants 1 year through 17 years of age received a 3-dose pre-exposure prophylaxis regimen of IMOVAX RABIES. A key secondary objective of the study was to demonstrate in the pooled participants (from 1 year through 17 years of age and 18 years of age and older), the noninferiority of a 2-dose pre-exposure prophylaxis regimen of IMOVAX RABIES (on Day 0, and Day 7) at Day 28 compared to the 3-dose pre-exposure prophylaxis regimen of IMOVAX RABIES (on Day 0, Day 7, and Day 28) at Day 42 in terms of the percentage of participants with an RVNA titer ≥ 0.5 IU/mL. The analysis was done in the per protocol analysis set (PPAS) with data from Day 28 and Day 42 contributed from the same participants, and with the prespecified noninferiority margins of -10% and -5%.
At Day 28 (after 2 doses of IMOVAX RABIES), 98.8% of participants had an RVNA titer ≥ 0.5 IU/mL. At Day 42 (after 3 doses of IMOVAX RABIES), 100% participants had an RVNA titer ≥ 0.5 IU/mL. The difference in the percentage of participants who achieved an RVNA titer ≥ 0.5 IU/mL was -1.3% [95% confidence interval (CI): -4.4; 1.3]. As the lower bound of the 95% CI of this difference (-4.4%) was greater than the prespecified noninferiority margins of -10% and -5%, noninferiority of the 2-dose pre-exposure prophylaxis regimen at Day 28 to the 3-dose pre-exposure prophylaxis regimen at Day 42 was demonstrated.
In an open-label, randomized, controlled, multicenter study (Study 1) conducted in the Philippines, 228 healthy participants (including 101 participants from 2 years through 17 years of age and 127 participants 18 years through 52 years of age) were randomized to receive the 2-dose pre-exposure prophylaxis regimen of IMOVAX RABIES and 115 healthy participants (including 46 participants from 2 years through 17 years of age and 69 participants 18 years through 59 years of age) were randomized to receive a 3-dose pre-exposure prophylaxis regimen of IMOVAX RABIES. One year later, 200 participants from the 2-dose pre-exposure prophylaxis group and 107 participants from the 3-dose pre-exposure prophylaxis group received two doses of IMOVAX RABIES 3 days apart (on Day 0 and Day 3) to mimic a post-exposure prophylaxis regimen without actual rabies exposure (simulated post-exposure prophylaxis).
The primary objective of the study was to demonstrate noninferiority of a 2-dose pre-exposure prophylaxis regimen of IMOVAX RABIES (on Day 0 and Day 7) at Day 21 compared with the 3-dose pre-exposure prophylaxis regimen of IMOVAX RABIES (on Day 0, Day 7 and Day 28) at Day 35, in terms of the percentage of participants with an RVNA titer ≥ 0.5 IU/mL. The analysis was done in the PPAS with the prespecified noninferiority margin of -5%.
At Day 21, 96.7% of participants who received the 2-dose pre-exposure prophylaxis regimen of IMOVAX RABIES had an RVNA titer ≥ 0.5 IU/mL. At Day 35, 100% participants who received the 3-dose pre-exposure prophylaxis regimen of IMOVAX RABIES had an RVNA titer ≥ 0.5 IU/mL. Noninferiority was not demonstrated as the difference in the percentage of participants who had an RVNA titer ≥ 0.5 IU/mL threshold was ‑3.3% (95% CI: -6.8; 0.5) and the lower bound of the 95% CI was below the prespecified noninferiority margin (‑5%). All participants 2 years through 17 years of age who received the 2-dose pre-exposure prophylaxis regimen of IMOVAX RABIES had an RVNA titer ≥ 0.5 IU/mL at Day 21.
One year later, following the simulated post-exposure prophylaxis, 100% of participants primed with either a 2-dose or 3-dose pre-exposure prophylaxis regimen of IMOVAX RABIES had an RVNA titer ≥ 0.5 IU/mL at 7 and 14 days after the first simulated post-exposure prophylaxis injection, which demonstrated an anamnestic response.
14.2 Post-exposure Prophylaxis
Post-exposure efficacy of IMOVAX RABIES was demonstrated during clinical experience in Iran in which six 1 mL doses were given on Days 0, 3, 7, 14, 30, and 90, in conjunction with antirabies serum. Forty-five individuals severely bitten by rabid dogs and wolves received IMOVAX RABIES within hours of and up to 14 days after the bites. All individuals were fully protected against rabies. (19)
Studies conducted by the CDC have shown that a regimen of 1 dose of Rabies Immune Globulin (RIG) and 5 doses of IMOVAX RABIES induced a sufficient antibody response in all recipients. Of 511 individuals bitten by proven rabid animals and so treated, none developed rabies. (7)
15. References
- 1
- Rao AK, Briggs D, Moore SM, et al. Use of a Modified Preexposure Prophylaxis Vaccination Schedule to Prevent Human Rabies: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices - United States, 2022. MMWR. 2022;71(18):619–627.
- 2
- Rupprecht CE, Briggs D, Brown CM, et al. Use of a Reduced (4-Dose) Vaccine Schedule for Postexposure Prophylaxis to Prevent Human Rabies: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. MMWR. 2010;59(RR-2):1–9.
- 3
- Manning SE, Rupprecht CE, Fishbein D, et al. Human rabies prevention - United States, 2008: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. MMWR. 2008;57(RR-3):1–28.
- 4
- CDC. Human rabies despite treatment with rabies immune globulin and human diploid cell rabies vaccine - Thailand. MMWR. 1987;36(46):759–760, 765.
- 5
- Cockshott WP, Thompson GT, Howlett LJ, et al. Intramuscular or intralipomatous injections? N Engl J Med. 1982;307(6):356–358.
- 6
- Baer GM, Fishbein DB. Rabies postexposure prophylaxis. N Engl J Med. 1987;316:1270–1272.
- 7
- CDC. Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. Rabies Prevention--United States, 1984. MMWR. 1984;33(28):393–402, 407–408.
- 8
- Shill M, Baynes RD, Miller SD. Fatal rabies encephalitis despite appropriate post-exposure prophylaxis. N Engl J Med. 1987;316(20):1257–1258.
- 9
- CDC. Systemic allergic reactions following immunization with human diploid cell rabies vaccine. MMWR. 1984;33(14):185–187.
- 10
- Boe E, Nyland H. Guillain-Barré syndrome after vaccination with human diploid cell rabies vaccine. Scand J Infect Dis. 1980;12(3):231–232.
- 11
- CDC. Adverse reactions to human diploid cell rabies vaccine. MMWR. 1980;29:609–610.
- 12
- Bernard KW, Smith PW, Kader FJ, et al. Neuroparalytic illness and human diploid cell rabies vaccine. JAMA. 1982;248(23):3136–3138.
- 13
- Aoki FY, Tyrrell DAJ, Hill LE. Immunogenicity and acceptability of a human diploid-cell culture rabies vaccine in volunteers. Lancet. 1975;1(7908):660–662.
- 14
- Cox JH, Schneider LG. Prophylactic immunization of humans against rabies by intradermal inoculation of human diploid cell culture vaccine. J Clin Microbiol. 1976;3(2):96–101.
- 15
- Kuwert EK, Marcus I, Werner J, et al. Some experiences with human diploid cell strain (HDCS) rabies vaccine in pre- and post-exposure vaccinated humans. Dev Biol Stand. 1978;40:79–88.
- 16
- Ajjan N, Soulebot JP, Stellmann C, et al. Résultats de la vaccination antirabique préventive par le vaccin inactivé concentré souche rabies PM/W138-1503-3M cultivés sur cellules diploïdes humaines. [Results of preventive rabies vaccination with a concentrated vaccine of the PM/WI38-1503-3M rabies strain cultured on human diploid cells. Preparation of mixed antirabies-antitetanus hyperimmune immunoglobulin by plasmapheresis of blood taken from vaccinated veterinary students]. Dev Biol Stand. 1978;40:89–100.
- 17
- Costy-Berger F. Vaccination antirabique préventive par du vaccin préparé sur cellules diploïdes humaines [Preventive rabies vaccination using vaccine prepared from human diploid cells]. Dev Biol Stand. 1978;40:101–104.
- 18
- Bernard KW, Roberts MA, Sumner J, et al. Human diploid cell rabies vaccine. JAMA. 1982;247(8):1138–1142.
- 19
- Bahmanyar M, Fayaz A, Nour-Salehi S, et al. Successful protection of humans exposed to rabies infection. JAMA. 1976;236(24):2751–2754.
16. How is Imovax Rabies supplied
16.1 How Supplied
IMOVAX RABIES is supplied in a box (NDC 49281-252-51) with:
- One vial containing lyophilized vaccine (NDC 49281-246-58).
- One syringe containing Sterile Water diluent (NDC 49281-263-58). If not already inserted into the syringe, a separate plunger rod is provided.
- One sterile disposable needle for reconstitution.
Reconstitute one vial of the lyophilized vaccine with Sterile Water diluent in the accompanying syringe to form IMOVAX RABIES. A single dose after reconstitution is 1 mL.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the vaccine recipient or caregiver to read the FDA-approved labeling.
Inform the vaccine recipient or caregiver about:
- Potential benefits and risks with IMOVAX RABIES.
- Potential side effects that have been reported with administration of IMOVAX RABIES.
- Reporting any side effects to their healthcare provider, the vaccine manufacturer at 1-800-822-2463 (1-800-VACCINE) (or online at https://ae.reporting.sanofi), or to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) at 1-800-822-7967 or online at https://vaers.hhs.gov.
- Requesting medical advice before taking corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive agents as they can interfere with the immune response to the vaccine.
IMOVAX is a registered trademark of Sanofi Pasteur.
Luer-Lok is a registered trademark of Becton Dickinson and Company.
© 2025 Sanofi Pasteur Inc. – All rights reserved
Manufactured by:
Sanofi Pasteur SA
Lyon France
Distributed by:
Sanofi Pasteur Inc.
Swiftwater, PA 18370 USA
1-800-VACCINE (1-800-822-2463)
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1 mL Vial Label
Rabies
Vaccine
IMOVAX® RABIES
RABIES
(HDCV)
single-dose
vial
(1 mL)
IM only
Rx only
Mfd by: Sanofi Pasteur SA
Lyon France US Govt Lic #1724
Dist by: Sanofi Pasteur Inc.
Swiftwater PA 18370 USA
1-800-VACCINE (1-800-822-2463)
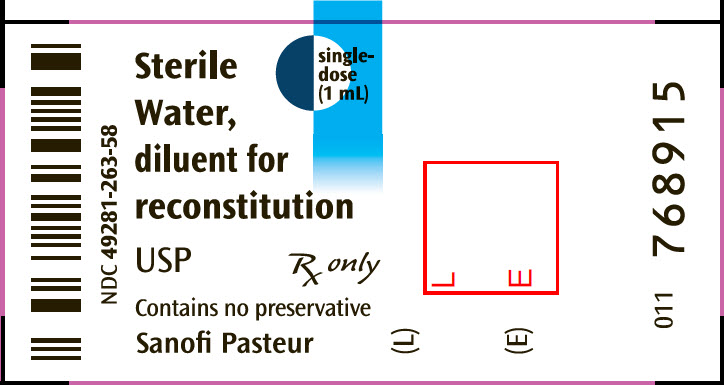
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1 mL Syringe Label
Sterile
Water,
diluent for
reconstitution
USP
single-
dose
(1 mL)
Rx only
Contains no preservative
Sanofi Pasteur
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Kit Carton
NDC 49281-252-51
List No 2501
RABIES
(HDCV)
Rabies Vaccine
IMOVAX® RABIES
PRE- AND POSTEXPOSURE
INTRAMUSCULAR IMMUNIZATION ONLY
single-dose
(1 mL)
NOT FOR INTRADERMAL USE
Wistar Rabies Virus Strain PM-1503-3M-Grown in Human Diploid Cell
Cultures-Single Dose-Lyophilized Vaccine, Luer Syringe with Sterile water, diluent for reconstitution
USP, one needle for reconstitution.
Rx only
FOR INTRAMUSCULAR INJECTION
SANOFI PASTEUR
| IMOVAX RABIES
rabies virus strain pm-1503-3m antigen (propiolactone inactivated) and water kit |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Sanofi Pasteur Inc. (086723285) |
| Registrant - Sanofi Pasteur (578763542) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sanofi Winthrop Industrie | 281659436 | MANUFACTURE(49281-252) | |
More about Imovax Rabies (rabies vaccine, human diploid cell)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: viral vaccines
- En español
