Benoquin: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: Monobenzone
Dosage form: cream, USP
Drug class: Topical depigmenting agents
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Mar 24, 2025.
On This Page
Benoquin Description
Monobenzone is the monobenzyl ether of hydroquinone. Monobenzone occurs as a white, almost tasteless crystalline powder, soluble in alcohol and practically insoluble in water.
Chemically, monobenzone is designated as p-(benzyloxy) phenol; the empirical formula is C13H12O2; molecular weight 200.24. The structural formula is:
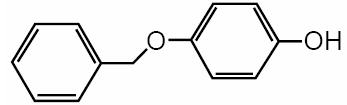
C13H12O2 200.24
Each gram of Benoquin Cream contains 200 mg of monobenzone USP, in a water-washable base consisting of purified water USP, cetyl alcohol NF, propylene glycol USP, sodium lauryl sulfate NF and white wax NF.
Benoquin - Clinical Pharmacology
Benoquin Cream 20% is a depigmenting agent whose mechanism of action is not fully understood.
The topical application of monobenzone in animals, increases the excretion of melanin from the melanocytes. The same action is thought to be responsible for the depigmenting effect of the drug in humans. Monobenzone may cause destruction of melanocytes and permanent depigmentation. This effect is erratic and may take one to four months to occur while existing melanin is lost with normal sloughing of the stratum corneum. Hyperpigmented skin appears to fade more rapidly than does normal skin, and exposure to sunlight reduces the depigmenting effect of the drug. The histology of the skin after depigmentation with topical monobenzone is the same as that seen in vitiligo; the epidermis is normal except for the absence of identifiable melanocytes.
Indications and Usage for Benoquin
Benoquin Cream 20% is indicated for final depigmentation in extensive Vitiligo.
Benoquin Cream 20% is applied topically to permanently depigment normal skin surrounding vitiliginous lesions in patients with disseminated (greater than 50 percent of body surface area) idiopathic vitiligo.
Benoquin Cream 20% is not recommended in freckling; hyperpigmentation caused by photosensitization following the use of certain perfumes (berlock dermatitis); melasma (chloasma) of pregnancy; or hyperpigmentation resulting from inflammation of the skin. Benoquin Cream 20% is not effective for the treatment of cafe-au-lait spots, pigmented nevi, malignant melanoma or pigmentation resulting from pigments other than melanin (e.g.: bile, silver, or artificial pigments).
Contraindications
Benoquin Cream 20% contains a potent depigmenting agent and is not a cosmetic skin bleach. Use of Benoquin Cream 20% is contraindicated in any conditions other than disseminated vitiligo. Benoquin Cream 20% frequently produces irreversible depigmentation, and it must not be used as a substitute for hydroquinone.
Benoquin Cream 20% is also contraindicated in individuals with a history of sensitivity or allergic reactions to this product, or any of its ingredients.
Warnings
Benoquin Cream 20% is a potent depigmenting agent, not a mild cosmetic bleach. Do not use except for final depigmentation in extensive vitiligo.
Keep this, and all medications out of the reach of children. In case of accidental ingestion, call a physician or a Poison Control Center immediately.
Precautions
(See Warnings):
General
Benoquin Cream 20% is for External Use Only. Following therapy with Benoquin Cream 20%, the skin will be sensitive for the rest of the patient’s life. He/she must use sunscreens during exposure to the sun.
Information for the Patient
Benoquin Cream 20% contains a potent depigmenting agent and is not a cosmetic skin bleach. Use of Benoquin Cream 20% is contraindicated in any conditions other than disseminated vitiligo. Use only for final depigmentation in extensive vitiligo. Areas of normal skin distant to the site of Benoquin Cream 20% application may become depigmented, and irregular, excessive, unsightly, and frequently permanent depigmentation may occur.
Carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, impairment of fertility
No long term studies have been performed to evaluate carcinogenic potential.
Pregnancy: Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Benoquin Cream 20%. It is also not known whether Benoquin Cream 20% can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman, or can affect reproduction capacity. Benoquin Cream 20% should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Mild, transient skin irritation and sensitization, including erythematous and eczematous reactions have occurred following topical application of Benoquin Cream 20%. Although those reactions are usually transient, treatment with Benoquin Cream 20% should be discontinued if irritation, a burning sensation, or dermatitis occur. Areas of normal skin distant to the site of Benoquin Cream 20% application frequently have become depigmented, and irregular, excessive, unsightly, and frequently permanent depigmentation has occurred.
Related/similar drugs
Benoquin Dosage and Administration
A thin layer of Benoquin Cream 20% should be applied and rubbed into the pigmented area two or three times daily, or as directed by physician. Prolonged exposure to sunlight should be avoided during treatment with Benoquin Cream 20%, or a sunscreen should be used.
Depigmentation is usually accomplished after one to four months of Benoquin Cream 20% treatment. If satisfactory results are not obtained after four months of Benoquin Cream 20% treatment, the drug should be discontinued. When the desired degree of depigmentation is obtained, Benoquin Cream 20% should be applied only as often as needed to maintain depigmentation (usually only two times weekly).
| BENOQUIN
monobenzone cream |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Labeler - ICN Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
More about Benoquin (monobenzone topical)
- Compare alternatives
- Reviews (2)
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- Drug class: topical depigmenting agents
