Umbilical Hernia
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is an umbilical hernia?
An umbilical hernia is a bulge through the abdominal wall near your umbilicus (belly button). The hernia may contain tissue from the abdomen, part of an organ (such as the intestine), or fluid.
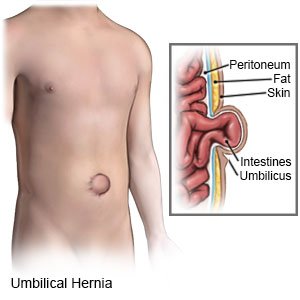 |
What increases my risk for an umbilical hernia?
An umbilical hernia may develop because you have a hole or weak area in your abdominal muscles. The following may increase your risk for an umbilical hernia:
- High body weight or pregnancy
- Being female or age older than 60
- A medical condition such as liver cirrhosis
- A large growth in your abdomen
- Chronic constipation, chronic cough, or straining to have bowel movements
- Surgery or trauma to the abdomen, such as from a motor vehicle accident
- Intense exercise or lifting heavy objects often
What are the signs and symptoms of an umbilical hernia?
Umbilical hernias usually do not cause pain. Your hernia may disappear when you lay flat. You may have any of the following:
- A soft bulge or swelling in or near your belly button
- A bulge that gets bigger when you cough, strain to have a bowel movement, or sit up
- Nausea or vomiting
- Constipation
How is an umbilical hernia diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms and when they started. Tell your provider about other medical conditions you have and your activities. You may also need:
- An ultrasound, MRI, or CT scan may show if tissue, fluid, or an organ is trapped inside the hernia. The imaging tests will also help your provider plan your treatment. You may be given contrast liquid to help organs show up better in the pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
How is an umbilical hernia treated?
- Watchful waiting may be recommended if your hernia is small and not painful. This means you do not need immediate treatment, but you have regular exams to check for changes. If your hernia becomes larger or painful during watchful waiting, your provider may recommend surgery.
- Manual reduction of your hernia may be needed. Manual reduction means your healthcare provider uses his or her hands to put firm, steady pressure on your hernia. Pressure is applied until the hernia disappears inside your abdominal wall.
- Surgery is usually done to place the hernia back inside the abdominal wall. You may need surgery if the hernia stops blood flow to any of your organs. You may also need surgery if your intestines or an organ get trapped inside the hernia.
How can I manage my umbilical hernia?
- Drink liquids as directed. Liquids may prevent constipation and straining during a bowel movement. Ask how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you.
- Do not lift heavy objects. This can increase pressure on your abdominal muscles and make your hernia bigger or cause another hernia.
- Eat foods high in fiber. Fiber may prevent constipation and straining during a bowel movement. Foods that contain fiber include fruits, vegetables, beans, lentils, and whole grains.

- Do not put pressure on your hernia. Do not push on the hernia or place tape or a coin over it.
- Maintain a healthy weight. If your body weight is higher than recommended, weight loss may help relieve your symptoms. Your healthcare provider will tell you what a healthy weight is for you. Your provider can help you create a safe weight loss plan, if needed.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can weaken the abdominal wall. This may increase your risk for another hernia. Ask your provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your provider before you use these products.
When should I seek immediate care?
- Your hernia gets bigger, feels firm, or turns blue or purple.
- You have severe abdominal pain with nausea or vomiting.
- Your abdomen is larger than usual.
- You are unable to have a bowel movement or pass gas.
- You see blood in your bowel movement.
When should I call my doctor or gastroenterologist?
- You have a fever.
- You have nausea or are vomiting.
- You are constipated.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Umbilical Hernia
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
