Testicular Cancer
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
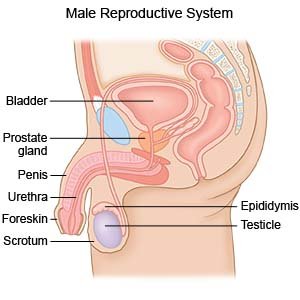
Most testicular cancer starts in the sperm-making cells of the testicles. Testicular cancer occurs most commonly in males aged 15 to 39 years.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Seek care immediately if:
- Your leg feels warm, tender, and painful. It may look swollen and red.
- You suddenly feel lightheaded and short of breath.
- You have chest pain when you take a deep breath or cough.
- You cough up blood.
- You are confused or cannot think clearly.
Call your doctor or oncologist if:
- You have a fever.
- You are vomiting and cannot keep any food or liquids down.
- You feel lumps or other changes in your testicle.
- You are depressed and feel you cannot cope with your illness.
- You have pain that does not decrease or go away after you take your pain medicine.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
- Antibiotics help treat or prevent an infection caused by bacteria.
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Do not wait until the pain is severe before you take this medicine.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
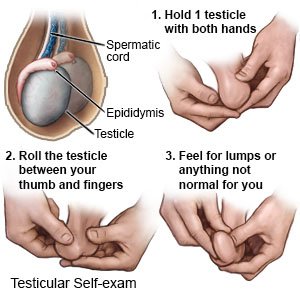
Do testicular self-exams:
A testicular self-exam (TSE) can help you learn how your testicles normally look and feel. Ask your healthcare provider or oncologist for more information about a TSE and how often to do one.
- Stand in front of a mirror and look at your scrotum. Look for changes in its shape, size, and color. It may be normal for one side of your scrotum to be larger or to hang lower than the other.
- Examine one testicle at a time. Put the thumbs of both hands in front of the testicle. Put the second (pointer) fingers behind the testicle. Gently roll each testicle between the thumbs and fingers of both hands. Feel for any lumps or changes in the testicle. It may be normal for one of your testicles to feel slightly larger than the other. Find a long, cord-like tube on top and in back of each testicle. This is the epididymis. Feel for any changes in the epididymis.
 |
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Do not smoke:
Nicotine can damage blood vessels and make it more difficult to manage your testicular cancer. Smoking also increases your risk for new or returning cancer and delays healing after treatment. Do not use e-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco in place of cigarettes or to help you quit. They still contain nicotine. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help quitting.
Drink liquids as directed:
Ask how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you. Drink extra liquids to prevent dehydration. You will also need to replace fluid if you are vomiting or have diarrhea from cancer treatments.
Eat healthy foods:
Healthy foods include fruits, vegetables, whole-grain breads, low-fat dairy products, beans, lean meats, and fish. Ask if you need to be on a special diet.
 |
Limit or do not drink alcohol as directed:
Limit alcohol to 2 drinks per day. A drink of alcohol is 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1½ ounces of liquor.
Be physically active as directed:
Physical activity can help increase your energy level. Ask your healthcare provider about the best activity plan for you.
 |
Follow up with your oncologist as directed:
You will need to see your oncologist for ongoing treatment. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Testicular Cancer
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
