Spermatocele
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is a spermatocele?
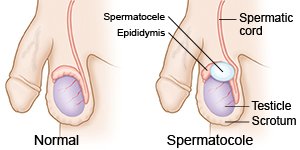
A spermatocele is a fluid collection or cyst that forms in the epididymis behind your testicles. The cyst contains a milky liquid that usually has sperm in it. The cyst will feel like a smooth mass near your testicles that you can move inside your scrotum. The mass is not cancer. A spermatocele is usually not painful, but you may feel heaviness in your scrotum. The area may also be swollen. The cause of your spermatocele may not be known. Trauma, blockage, infection, or inflammation in your scrotum may increase your risk.
 |
How is a spermatocele diagnosed?
Spermatoceles are sometimes found during a routine physical exam. Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms and when they began. Your provider may use the following to find the cause of your symptoms:
- A manual exam means your provider will feel your testicles and other parts of your scrotum. Your provider will check for lumps, pain, or other problems.
- An ultrasound may be used to check any lumps for a spermatocele.
How is a spermatocele treated?
Treatment may not be needed. You may need any of the following if the spermatocele becomes large or causes pain or other problems:
- Medicine may be used to relieve pain or swelling.
- Surgery may be used to remove the cyst. Talk to your provider about the risks of having a spermatocele removed. The procedure may cause infertility (problems fathering children).
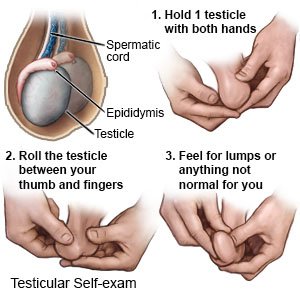
What is a testicular self-exam?
A testicular self-exam is a monthly check of your testicles and scrotum. Your provider may ask you to check for changes, lumps, or pain. Ask for more information on how to do a testicular self-exam.
 |
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have sudden, severe pain in your scrotum or testicle.
When should I call my doctor?
- The cyst does not go away or gets bigger.
- The cyst becomes painful or causes discomfort.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
