Shoulder Bursitis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
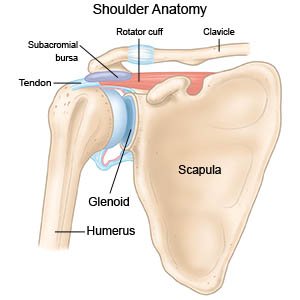
Shoulder bursitis is inflammation of the bursa in your shoulder. The bursa is a fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion between a bone and a tendon. A tendon is a cord of strong tissue that connects muscles to bones.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your doctor if:
- You have increased redness, pain, and swelling.
- Your symptoms do not improve with treatment.
- You have a fever.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions. Do not give these medicines to children younger than 6 months without direction from a healthcare provider.
- Aspirin helps relieve pain and swelling. Take aspirin exactly as directed by your healthcare provider.
- Antibiotics help treat or prevent a bacterial infection.
- Steroids help relieve pain and swelling. Steroids may be given for a short time for acute pain.
- Do not give aspirin to children younger than 18 years. Your child could develop Reye syndrome if he or she has the flu or a fever and takes aspirin. Reye syndrome can cause life-threatening brain and liver damage. Check your child's medicine labels for aspirin or salicylates.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Manage shoulder bursitis:
- Rest your shoulder as much as possible to decrease pain and swelling. Slowly start to do more each day. Return to your daily activities as directed.
- Apply ice to help decrease swelling and pain. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover the bag with a towel before you place it on your shoulder. Apply ice for 15 to 20 minutes, 3 to 4 times each day, as directed.
- Find a comfortable sleep position. Sleep on the side that is not injured. You may be more comfortable if you sleep on your stomach or back.
- Go to physical therapy, if directed. A physical therapist teaches you exercises to help improve movement and strength, and to decrease pain.
Prevent shoulder bursitis:
- Do not overuse your shoulders. Shorten the time you spend swimming, playing tennis, or doing other overhead arm movements. Take breaks as you do these activities. Try not to do the same activities each day. For example, swim every other day or every 3 days instead of daily.
- Always warm up and stretch before you exercise. This will help loosen your muscles and decrease stress on your shoulder. Cool down after you exercise.
- Prevent injury to your shoulders. Wear shoulder pads or protectors when you play sports.
- Try to keep pressure off your shoulders. If you need to sleep on your side, do not lie on same side each night.
- Manage health conditions that can lead to shoulder bursitis. Your healthcare provider may recommend you to a specialist, such as an arthritis specialist.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Shoulder Bursitis
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
