Pancytopenia in Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 6, 2024.
What is pancytopenia?
Pancytopenia is low levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Red blood cells carry oxygen to all the organs and tissues in your child's body. White blood cells help your child's body fight infection by attacking and killing germs. Platelets stop the bleeding when your child is cut or injured. Pancytopenia increases your child's risk for infection and bleeding. Without treatment, these problems can become life-threatening.
What causes pancytopenia?
There are many causes of pancytopenia in children. Any of the following may cause pancytopenia:
- A genetic condition that causes low blood cell levels
- An autoimmune condition that attacks the bone marrow
- A viral or bacterial infection
- Cancer, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy
- Exposure to toxins such as benzene, arsenic, or insecticides
- Not enough folic acid or vitamin B12 in the foods your child eats
- Some medicines, such as antiseizure medicine, antibiotics, or medicines to treat autoimmune diseases
What are the signs and symptoms of pancytopenia?
- Feeling tired, weak, dizzy, or short of breath
- Frequent fevers or infections
- Pale skin or purple or red dots on the skin
- Bleeding from the gums or nose, blood in bowel movements or urine, or heavy bleeding from a cut
- Bruising easily, or getting bruises without an injury
- Heavy menstruation in females
How is pancytopenia diagnosed?
Your child's healthcare provider will examine him or her. Tell the provider about any symptoms your child has. Your child may need any of the following:
- Blood tests are used to check your child's blood cell levels. Other blood tests are used to find the cause of pancytopenia.
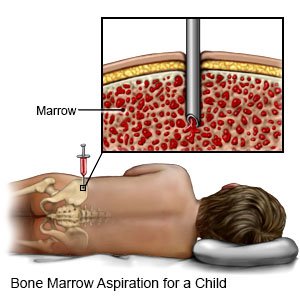
- A bone marrow biopsy is a procedure to remove a small sample of bone marrow from your child's bone. This procedure is used to check how well your child's bone marrow is making blood cells. The bone marrow sample is also checked for tumors or anything that prevents the bone marrow from making healthy cells.
How is pancytopenia treated?
The treatment of pancytopenia depends on the cause. Your child may need any of the following:
- A blood transfusion can help increase red blood cell, white blood cell, and platelet levels. This may prevent bleeding or organ damage. This does not treat pancytopenia. Instead, a blood transfusion may keep your child safe until the cause of pancytopenia is known.
- A stem cell transplant is a procedure to replace unhealthy stem cells with healthy cells. Stem cells are able to become all of the blood cells. Stem cells can also travel to your child's bone marrow and can become new bone marrow cells.
How should I balance my child's activity with rest?
- Have your child rest when needed. Rest will help your child save energy for other activities.
- Your child should do activities when his or her energy levels are the highest. Do not plan too many activities for your child in one day.
How do I prevent or control bleeding?
- Do not give your child aspirin or NSAIDs. These medicines can cause your child to bleed and bruise more easily.
- Use caution with skin and mouth care. Have your child use a soft washcloth and a soft toothbrush. This can keep your child's skin and gums from bleeding. Keep your child's nails trimmed to prevent scratches.
- Apply firm, steady pressure to stop bleeding from a wound. Apply pressure with a clean gauze or towel for 5 to 10 minutes. Call 911 if bleeding becomes heavy or does not stop.
- Do not let your child play contact sports or do activities that can cause bleeding. Ask your healthcare provider what activities are safe for your child to do.
What can I do to prevent infections?
- Wash your hands and your child's hands often. Use an alcohol-based hand rub if soap and water are not available.

- Keep your child away from crowds and anyone who may be sick. Do not let your child return to school or daycare until his or her healthcare provider says it is okay. Ask your child's healthcare provider if he or she needs to wear a mask in public places.
- Offer your child low-bacteria foods as directed. This will help decrease your child's risk for an infection. You will need to choose, prepare, and cook foods that contain a low amount of bacteria. Examples include pasteurized milk, well-cooked meats, and cooked pasta. Ask your child's healthcare provider for more information on a low-bacteria diet.
Call 911 for any of the following:
- Your child cannot be woken.
- Your child has a seizure.
- Your child has trouble breathing.
- You cannot stop the bleeding from your child's wound even after you hold firm pressure for 10 minutes.
When should I seek immediate care?
- Your child has a fever or chills.
- Your child has blood in his or her urine or bowel movement.
- Your child feels dizzy or he or she faints.
- Your child's heart is beating faster than usual.
When should I contact my child's healthcare provider?
- Your child has a rash or red or purple dots on his or her skin.
- Your child feels more tired than usual.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your child's care. Learn about your child's health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your child's healthcare providers to decide what care you want for your child. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2024 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Pancytopenia
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
