Mastoiditis in Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
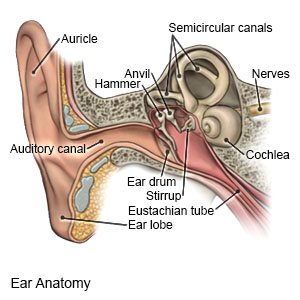
Mastoiditis is an infection in the air cells and mastoid bone of your child's skull. The mastoid bone is located behind your child's ear. Mastoiditis is most common in children younger than 2 years who have a history of ear infections. Mastoiditis is often caused by an ear infection that spreads. Your child's ear canal swells and traps fluid inside his or her ear. Trapped fluid causes bacteria to grow and spread to the mastoid bone.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- Your child has a seizure or loses consciousness.
- You cannot wake your child.
Seek care immediately if:
- Your child's symptoms, such as pain, redness, swelling, ear drainage, or hearing loss get worse.
- Your child's fever gets worse, or does not go away with treatment.
- Your child has a headache that does not go away with treatment.
- Your child has weakness in his or her face.
- Your child has a mass behind his or her ear that is red and swollen.
- Your child has a headache, fever, and a stiff neck.
Call your child's doctor if:
- You think your child's medicine is not working.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Medicines:
Your child may need any of the following:
- Antibiotics help treat or prevent a bacterial infection. They may be given as pills or eardrops.
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If your child takes blood thinner medicine, always ask if NSAIDs are safe for him or her. Always read the medicine label and follow directions. Do not give these medicines to children younger than 6 months without direction from a healthcare provider.
- Acetaminophen decreases pain and fever. It is available without a doctor's order. Ask how much your child should take and how often he or she should take it. Follow directions. Acetaminophen can cause liver damage if not taken correctly.
- Do not give aspirin to children younger than 18 years. Your child could develop Reye syndrome if he or she has the flu or a fever and takes aspirin. Reye syndrome can cause life-threatening brain and liver damage. Check your child's medicine labels for aspirin or salicylates.
- Give your child's medicine as directed. Contact your child's healthcare provider if you think the medicine is not working as expected. Tell the provider if your child is allergic to any medicine. Keep a current list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs your child takes. Include the amounts, and when, how, and why they are taken. Bring the list or the medicines in their containers to follow-up visits. Carry your child's medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Care for your child's ears:
Keep your child's ears dry. Have your child use earplugs as directed when he or she bathes or swims. Fluid in your child's ears may slow healing and cause discomfort.
Help prevent ear infections that may lead to mastoiditis:
- Keep your child away from cigarette smoke, or areas that smell like cigarette smoke.
- Get early treatment for ear infections.
- Continue to breastfeed your child if you already are. This may reduce the risk of ear infections and mastoiditis.
- Vaccines may help prevent ear infections and mastoiditis. Ask your child's healthcare provider which vaccines are right for your child.
Follow up with your child's doctor or ear, nose, and throat specialist as directed:
Your child may need to have his or her hearing checked after he or she heals from mastoiditis. Your child may also need to have his or her ears cleaned frequently by the healthcare provider. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Mastoiditis
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
