Lyme Disease
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
Lyme disease is a bacterial infection caused by the bite of an infected tick.
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- Your heart is beating faster than usual and you feel dizzy.
- You have chest pain or trouble breathing.
- You suddenly cannot talk or see well, or you have trouble moving an area of your body.
Return to the emergency department if:
- You have a headache and a stiff neck.
- You have trouble concentrating or thinking clearly.
- You have numbness or tingling in your arms or legs, or you have trouble walking.
Call your doctor if:
- Your rash grows or spreads to other areas of your body.
- You suddenly have trouble falling or staying asleep.
- You have new or worsening pain and swelling in your joints.
- You have new or worsening weakness and muscle pain.
- You have a new tick bite.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Antibiotics treat a bacterial infection.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Prevent a tick bite:
Ticks live in areas covered by brush and grass. They may even be found in your lawn if you live in certain areas. Outdoor pets can carry ticks inside the house. Ticks can grab onto you or your clothes when you walk by grass or brush. If you go into areas that contain many trees, tall grasses, and underbrush, do the following:
 |
- Wear light colored pants and a long-sleeved shirt. Tuck your pants into your socks or boots. Tuck in your shirt. Wear sleeves that fit close to the skin at your wrists and neck. This will help prevent ticks from crawling through gaps in your clothing and onto your skin. Wear a hat in areas with trees.
- Apply insect repellant on your skin. The insect repellant should contain DEET. Do not put insect repellant on skin that is cut, scratched, or irritated. Always use soap and water to wash the insect repellant off as soon as possible once you are indoors. Do not apply insect repellant on your child's face or hands.
- Spray insect repellant onto your clothes. Use permethrin spray. This spray kills ticks that crawl on your clothing. Be sure to spray the tops of your boots, bottom of pant legs, and sleeve cuffs. As soon as possible, wash and dry clothing in hot water and high heat.
- Check your and your child's clothing, hair, and skin for ticks. Shower within 2 hours of coming indoors. Carefully check the hairline, armpits, neck, and waist.
- Decrease the risk for ticks in your yard. Ticks like to live in shady, moist areas. Mow your lawn regularly to keep the grass short. Trim the grass around birdbaths and fences. Cut branches that are overgrown and take them out of the yard. Clear out leaf piles. Stack firewood in a dry, sunny area.
- Treat pets with tick control products as directed. This will decrease your risk for a tick bite. Check your pets for ticks. Remove ticks from pets the same way as you remove them from people. Ask your pet's veterinarian about the best product to use on your pet.
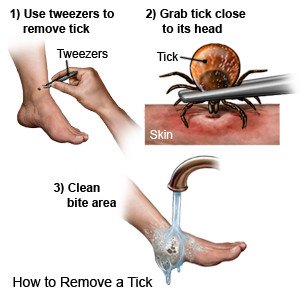
- Remove a tick with tweezers. Wear gloves. Grasp the tick as close to your skin as possible. Pull the tick straight up and out. Do not touch the tick with your bare hands. Check to make sure you removed the whole tick, including the head. Clean the area with soap and water or rubbing alcohol. Then wash your hands with soap and water.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Lyme Disease
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
