Inguinal Hernia
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
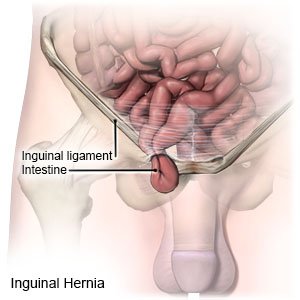
An inguinal hernia happens when abdominal organs or tissue push through a weak spot in the abdominal wall. The abdominal wall is made of fat and muscle. It holds the intestines in place. The hernia may contain fluid, tissue from the abdomen, or part of an organ (such as an intestine).
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Seek care immediately if:
- You have severe abdominal pain with nausea and vomiting.
- Your abdomen is larger than usual.
- Your hernia gets bigger or is purple or blue.
- You see blood in your bowel movements.
- You are unable to have a bowel movement or pass gas.
- You feel weak, dizzy, or faint.
Call your doctor or gastroenterologist if:
- You have a fever.
- You have pain even after you take medicine.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
You may need the following:
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Acetaminophen decreases pain and fever. It is available without a doctor's order. Ask how much to take and how often to take it. Follow directions. Read the labels of all other medicines you are using to see if they also contain acetaminophen, or ask your doctor or pharmacist. Acetaminophen can cause liver damage if not taken correctly.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Manage your symptoms and prevent another hernia:
- Do not lift heavy objects. This can increase pressure on your abdominal muscles and make your hernia worse or cause another hernia.
- Drink liquids as directed. Liquids may prevent constipation and straining during a bowel movement. Ask how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you.
- Apply ice as directed. Ice helps decrease swelling and pain. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover the bag with a towel before you place it on your hernia. Apply ice for 15 to 20 minutes every hour or as directed.
- Eat foods high in fiber. Fiber may prevent constipation and straining during a bowel movement. Foods that contain fiber include fruits, vegetables, beans, lentils, and whole grains.
- Maintain a healthy weight. If your body weight is higher than recommended, weight loss may help relieve your symptoms. Your healthcare provider will tell you what a healthy weight is for you. Your provider can help you create a safe weight loss plan, if needed.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can weaken the abdominal wall. This may increase your risk for another hernia. Ask your provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your provider before you use these products.
Follow up with your doctor or gastroenterologist as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Inguinal Hernia
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
