Hypomineralization of the Tooth
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
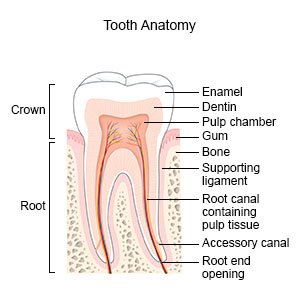
Hypomineralization
is a softening and discoloration of the enamel on your teeth. It is most common on the permanent first molars and incisor teeth. This softening may lead to tooth decay, cavities, or other damage to your teeth. The cause of hypomineralization is not clear.
 |
Common symptoms include the following:
- Tooth surface is white or chalky, or easy to see through, with yellow or brown areas
- Tooth sensitivity to hot and cold
Contact your dentist if:
- You have tooth pain.
- You have tooth sensitivity when you eat or drink.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Treatment for hypomineralization:
You may need a fluoride treatment, varnish, or sealant. These treatments help protect your teeth, decrease sensitivity, and prevent decay. Your dentist may recommend microdermabrasion or bleaching to improve the discoloration. Your teeth may need to be repaired with bonding, crowns, or other filling materials if your tooth becomes decayed or damaged. Ask your dentist about these and other treatments you may need.
Manage your symptoms:
- Brush your teeth at least 2 times a day. Your dentist may recommend a fluoride or remineralizing toothpaste. These help prevent tooth decay and decrease sensitivity.
- Floss between your teeth at least 1 time each day.
- Rinse your mouth with fluoride mouthwash after meals and snacks.
- Chew sugarless gum after meals and snacks.
- Visit your dentist every 6 months for dental cleanings and oral exams. Follow the treatment recommended by your dentist.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
