Hiatal Hernia in Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
A hiatal hernia is a condition that causes part of your child's stomach to bulge through the hiatus (small opening) in the diaphragm. This part of the stomach may move up and down, or it may get trapped above the diaphragm. Your child may have been born with a large or weak hiatus, or with the hiatal hernia.
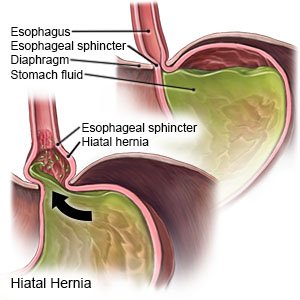 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- Your child has severe chest pain and sudden trouble breathing.
Return to the emergency department if:
- Your child has severe abdominal pain.
- Your child's bowel movements are black or bloody.
- Your child's vomit looks like coffee grounds or has blood in it.
- Your child cannot swallow food or liquids.
Call your child's doctor if:
- Your child's symptoms are getting worse.
- Your child has nausea and is vomiting.
- Your child is losing weight.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Medicines:
- Medicines may be given to relieve heartburn symptoms. These medicines help to decrease or block stomach acid.
- Give your child's medicine as directed. Contact your child's healthcare provider if you think the medicine is not working as expected. Tell the provider if your child is allergic to any medicine. Keep a current list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs your child takes. Include the amounts, and when, how, and why they are taken. Bring the list or the medicines in their containers to follow-up visits. Carry your child's medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Care for your child:
The following nutrition and lifestyle changes may be recommended to relieve symptoms of heartburn:
 |
- Do not give your child foods or drinks that may increase heartburn. These include chocolate, peppermint, spicy, fatty, or fried foods, drinks that contain caffeine, or carbonated drinks (soda). Do not give your child citrus fruits, tomatoes, and juices.
- Give your child several small meals during the day. Your child's stomach will make more acid to digest large amounts of food. Remind your child to eat 6 small meals a day and to eat slowly.
- Tell your child not to lie down after eating. Do not allow your child to eat meals 2 to 3 hours before bedtime.
- Help your child avoid abdominal pressure. Tell your child to wear clothes that are loose around the waist. Tell your child not to bend forward after meals.
- Help your child achieve or maintain a healthy weight. If your child has excess weight, weight loss may help relieve some symptoms.
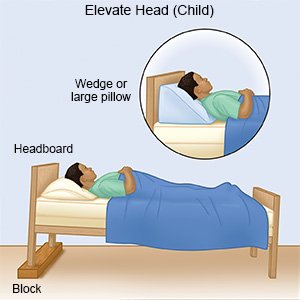
- Keep your child's head and upper body elevated at least 6 inches during sleep. Ask your child's healthcare provider how to do this safely. Do not put pillows under a young child's head.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
- omeprazole
- famotidine
- lansoprazole
- aluminum hydroxide/magnesium hydroxide/simethicone
- aluminum hydroxide/magnesium trisilicate
Follow up with your child's doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Hiatal Hernia
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
