Gas and Bloating
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What do I need to know about gas and bloating?
Gas is air that collects in your digestive system (stomach or intestines). Bloating is the tight, full feeling you get from too much gas.
 |
What are common causes for gas and bloating?
- Swallowing air while you eat, drink, chew gum, or smoke cigarettes
- Certain foods such as pasta, beans, potatoes, or dairy products
- Carbonated drinks, such as soft drinks
- Medical conditions such as celiac disease, lactose intolerance, or irritable bowel syndrome
What are the symptoms of gas and bloating?
- Abdominal pain or cramping
- Bloating that is worse during the day and better at night
- Burping or passing gas more often than usual
- Gurgling noise coming from your abdomen
- Constipation
How is the cause of gas and bloating diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about what you eat and examine your abdomen. You may need any of the following tests:
- A blood test may show an underlying medical condition that may be causing your symptoms.
- A breath test may show a stomach infection or a problem with food digestion. You will breathe into a machine that can test your breath for signs of these or other problems.
- A bowel movement sample may be tested for infection.
- An x-ray, CT, MRI, or ultrasound may show a blockage in your bowels or other problems in your digestive system. Contrast liquid may be given to help the area show up better in pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal may cause serious injury. Tell the provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
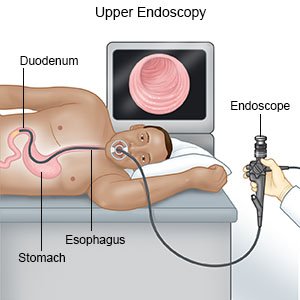
- An endoscopy may be done to check your digestive system. An endoscope is a long, flexible tube with a light and tiny camera on the end. The tube is put into your mouth and guided down into your digestive system. Tissue samples may be taken and sent to a lab for tests.
How is gas and bloating treated?
Treatment depends on the cause. Gas relief medicines may help decrease gas pain and bloating. These are available without a doctor's order. You may need other medicines to control a medical condition. Surgery may be needed if you have a tumor or a problem such as a bowel obstruction.
How can I manage or prevent gas and bloating?
- Keep a record. Write down what you eat and drink and how often you pass gas each day.
- Eat slowly and chew your food well. This will help you swallow less air. Foods such as meat, poultry, fish, and eggs do not cause gas. Avoid processed or salty foods. Avoid foods that you know make you feel gassy or bloated.
- Drink liquids as directed. You may need to drink more liquids than usual. Liquids such as water help your intestines move food through. Teas such as peppermint, chamomile, or fennel may help reduce gas. Do not drink beer, soda, or other carbonated drinks. Do not drink through a straw.
- Be physically active. Physical activity, such as walking, can help relieve gas and bloating. Your healthcare provider can help you create a physical activity plan.

- Do not smoke cigarettes or chew gum. These can cause you to swallow air. Avoid hard candy.
- Make sure your dentures fit properly. Have your dentures fixed if they are loose. Loose dentures can cause you to swallow too much air.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have severe abdominal pain.
- You have blood in your bowel movement.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have a fever.
- Your abdominal pain does not go away or gets worse
- You vomit or have diarrhea.
- You lose weight without trying.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
