Endocarditis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
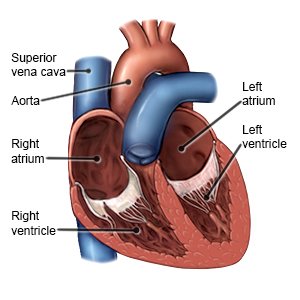
Endocarditis is an infection of the inner lining of your heart. It may also affect the valves of your heart. Endocarditis, and the health problems it may cause, can be serious and can become life-threatening.
 |
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
Activity:
You may need to rest in bed until your heart problem is under control. Your healthcare provider will tell you when it is okay to get out of bed. Call your healthcare provider before you get up for the first time. If you feel weak or dizzy, sit or lie down right away and call your healthcare provider.
Medicines:
- Antibiotics help treat a bacterial infection.
- Antifungals help treat a fungal infection.
- Heart medicine is given to strengthen your heart or decrease stress on your heart.
- Diuretics remove extra fluid from your body. You may urinate more often when you take this medicine.
- Acetaminophen or ibuprofen decrease pain and fever.
Monitoring:
- Telemetry is continuous monitoring of your heart rhythm. Sticky pads placed on your skin connect to an EKG machine that records your heart rhythm.
- Intake and output of the amount of liquids you are drinking and urinating may need to be tracked. Do not flush your urine down the toilet unless healthcare providers say it is okay.
- Pulse oximetry measures the amount of oxygen in your blood.
- You may be weighed each day. Healthcare providers compare your weight from day to day to make sure you do not lose or retain too much fluid.
Tests:
- Blood and urine tests may show if you have an infection or if another health condition is causing your symptoms.
- An EKG records your heart rhythm and how fast your heart beats. It is used to check for problems with your heart.
- An echocardiogram is a type of ultrasound. Sound waves are used to show the structure and function of your heart. You may need a transthoracic or transesophageal echocardiogram. Ask your healthcare provider about these types of echocardiogram.
- An x-ray, CT scan, or MRI scan may show problems in your heart. You may be given contrast liquid to help your heart show up better in the pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
Treatment:
- You may need extra oxygen if your blood oxygen level is lower than it should be. You may get oxygen through a mask placed over your nose and mouth or through small tubes placed in your nostrils. Ask your healthcare provider before you take off the mask or oxygen tubing.
- Surgery may be needed to repair or replace a damaged heart valve. Surgery may also be needed to remove an implanted device that has caused the infection. This may include removal of a pacemaker or defibrillator.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
RISKS:
The infection may spread to other areas of your heart and body. Endocarditis increases your risk for a blood clot, heart failure, and stroke. It also increases your risk for arthritis, kidney infection, brain infection, and abnormal heart beats. These may become life-threatening.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Endocarditis
Treatment options
- Medications for Endocarditis
- Medications for Infectious Endocarditis
- Medications for Valvular Heart Disease
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
