Earache
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
An earache
can be caused by a problem within your ear. A problem or condition in another body area can also cause pain that travels to your ear. An earache can be caused by any of the following:
- Infection of the inner or outer ear
- Earwax buildup, or small objects put into your ear
- Ear injury caused by a cotton swab or by air pressure changes from a plane ride or scuba diving
- Other infections, such as tonsillitis or pharyngitis
- Jaw or dental problems such as cavities or TMJ
- Neck pain caused by problems such as arthritis in your upper spine
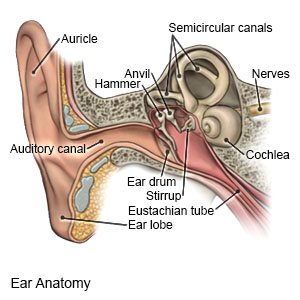 |
Call your doctor if:
- You have a severe earache.
- You have hearing loss, dizziness, a feeling of fullness in your ear, or ringing in your ears.
- Your ear pain worsens or does not go away with treatment.
- You have drainage from your ear.
- You have a fever.
- Your outer ear becomes red, swollen, and warm.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Treatment for an earache
may include any of the following:
- Acetaminophen decreases pain and fever. It is available without a doctor's order. Ask how much to take and how often to take it. Follow directions. Read the labels of all other medicines you are using to see if they also contain acetaminophen, or ask your doctor or pharmacist. Acetaminophen can cause liver damage if not taken correctly.
- NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen, help decrease swelling, pain, and fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Do not give aspirin to children younger than 18 years. Your child could develop Reye syndrome if he or she has the flu or a fever and takes aspirin. Reye syndrome can cause life-threatening brain and liver damage. Check your child's medicine labels for aspirin or salicylates.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
