Dilantin Toxicity
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
Dilantin, or phenytoin, toxicity happens when you have high levels of Dilantin in your body that become harmful. Dilantin is a medicine that is used to prevent and treat seizures. Dilantin toxicity can lead to a coma.
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Return to the emergency department if:
- You have fast, uncontrollable eye movements or double vision.
- You have a lack of coordination of fingers, hands, arms, legs, or other part of your body.
- You are dizzy, drowsy, or confused.
- Your speech is slurred.
- You have irregular or jerky movements.
- You cannot be awakened.
Call your doctor if:
- You missed a dose of Dilantin.
- You have nausea, or you are vomiting.
- You have a decreased appetite.
- Your abdomen is bloated.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Related medications
How to take Dilantin safely:
- Take this medicine exactly as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you miss a dose or you have any questions about how to take Dilantin.
- Do not stop taking Dilantin or change your dose. Your risk for seizures increases if you decrease your dose or stop taking Dilantin. Even a small increase in your dose can cause toxicity.
- Go to all your follow-up appointments. Your provider will need to monitor you closely while you are taking Dilantin. You will need regular blood and urine tests.
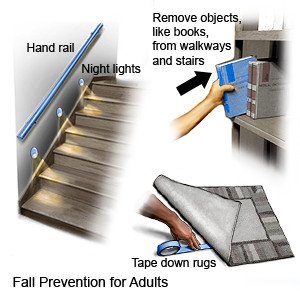
Prevent falls:
You may still be at risk for falling for a period of time after treatment. Follow your healthcare provider's recommendations for preventing falls.
 |
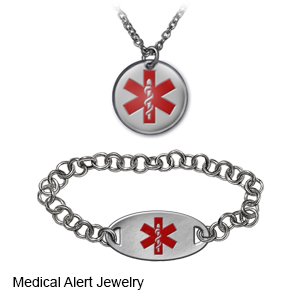
What else you should do while you are taking Dilantin:
Wear medical alert jewelry or carry a card that says you take Dilantin. Ask where to get these items.
 |
What to do if you think you or someone you know took too much Dilantin:
Call the Poison Control Center at 1-800-222-1222 immediately.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Dilantin Toxicity
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
