Chronic Liver Disease
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Sep 23, 2025.
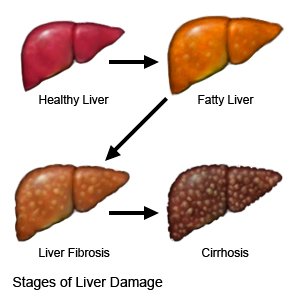
CLD is the gradual worsening of the liver for more than 6 months. The liver makes enzymes and bile that help digest food and gives your body energy. It also removes harmful material from your body, such as alcohol and other chemicals. Repeated swelling and damage to your liver over time causes scar tissue to form. Scar tissue starts to replace healthy liver tissue. The scar tissue prevents the liver from working properly.
 |
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
Medicines:
- Blood pressure medicine lowers high blood pressure in the portal vein (the blood vessel that goes to your liver).
- Diuretics decrease fluid that collects in a part of your body, such as your legs and abdomen. Diuretics can also decrease your blood pressure. You will urinate more often when you take this medicine.
- Antibiotics prevent or treat a bacterial infection.
Monitoring:
- Abdomen measuring may be done every 4 to 8 hours. A sudden increase in the size of your abdomen may mean you are retaining fluid.
- Intake and output means healthcare providers will keep track of the amount of liquid you are getting. They also may need to know how much you are urinating. Ask how much liquid you should drink each day. Ask healthcare providers if they need to measure or collect your urine.
- Neuro signs , or neuro checks show healthcare providers your brain function. They will check how your pupils react to light. They may check your memory and how easily you wake up. Your strength, balance, vision, and other brain functions may also be tested.
Tests:
- Blood tests may be used to check your liver enzymes. This test shows how well your liver is working.
- An ultrasound may be used to check for damage to your liver or other tissues or organs.
- CT or MRI pictures may be taken of your liver. You may be given contrast liquid to help your liver show up better in the pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. The MRI machine uses a powerful magnet. Do not enter the MRI room with anything made of metal. Metal can cause serious injury from the magnet. Tell the healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
- A liver biopsy is a procedure used to take a small piece of your liver to be tested for damage.
- An endoscopy may show swollen veins in the esophagus or stomach. An endoscope is a bendable tube with a light and camera on the end. It is placed through the mouth and down the throat.
Treatment:
- Surgery may be used to create a channel inside your liver to increase blood flow. This will help decrease swelling in your abdomen and lower blood pressure in the portal vein. Your risk for bleeding in your esophagus and stomach will also be decreased.
- A liver transplant may be needed if your liver fails.
RISKS:
Without treatment, scar tissue will continue to replace healthy tissue. This can cause severe liver damage, and your liver can fail. You may develop swollen blood vessels in your esophagus and stomach. The vessels may burst and bleed over time. You could go into a coma, or bleed heavily. This can be life-threatening.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
