Cervical Fracture
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
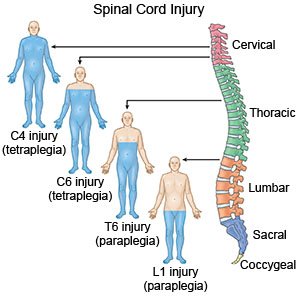
A cervical fracture is a break in a vertebra (bone) in your neck. The 7 cervical vertebrae are called C1 through C7. Cervical vertebrae support your head and allow your neck to bend and twist. The vertebrae enclose and protect the spinal cord. Nerves in the spinal cord control your ability to move.
 |
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
A Foley catheter
is a tube put into your bladder to drain urine into a bag. Keep the bag below your waist. This will prevent urine from flowing back into your bladder and causing an infection or other problems. Also, keep the tube free of kinks so the urine will drain properly. Do not pull on the catheter. This can cause pain and bleeding, and may cause the catheter to come out.
A ventilator
is a machine that gives you oxygen and breathes for you when you cannot breathe well on your own. An endotracheal (ET) tube is put into your mouth or nose and attached to the ventilator. You may need a trach if an ET tube cannot be placed. A trach is a tube put through an incision and into your windpipe.
Medicines:
- Pain medicine may be needed. Do not wait until the pain is severe before you ask for more medicine.
- Blood thinners help prevent blood clots. Clots can cause life-threatening conditions such as a stroke or heart attack. Blood thinners make it more likely for you to bleed or bruise. Use an electric razor and soft toothbrush to help prevent bleeding.
Tests:
- A neurologic exam is also called neuro signs, neuro checks, or neuro status. A neurologic exam can show healthcare providers how well your brain works after an injury or illness. A provider will check how your pupils react to light. He or she may check your memory and how easily you wake up. Your hand grasp and balance may also be tested.
- X-rays may be used to check for broken bones or other neck problems.
- A CT scan or MRI may show pressure on or damage to your spinal cord. You may be given contrast liquid to help your spinal cord show up better in pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Tell the provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
Treatment:
- Immobilization is used to keep your head and neck from moving as your cervical fracture heals. You may need the following:
- A halo brace and vest prevent most head and neck movements. The halo brace is attached to your head with pins placed in your skull. It cannot be removed during treatment. Ask your healthcare provider for more information about halo brace placement and care.
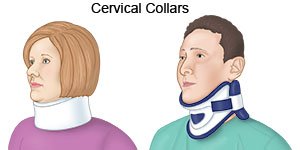
- A semirigid collar uses plastic plates to stop side-to-side or up-and-down motion in your neck.
- A soft collar is a flexible brace placed around the neck. It is often used after a more rigid collar has been worn.
- Traction uses weights to pull your bones back into place and to straighten the cervical spine.
- Surgery may be needed to repair your cervical fracture. You may also have surgery after immobilization if your fracture has not healed.
- Internal fixation means the broken pieces of bone and ligaments are moved back to their correct places. Bone pieces and ligaments may be secured using screws, wires, or rods.
- Cervical discectomy is done to remove one or more damaged discs in your neck.
- Cervical fusion is used to place a bone graft between your vertebrae after a damaged disc is removed. A bone graft is a piece of bone taken from another area of your body. Over time, the vertebrae and the bone graft grow and fuse (lock) together.
- Therapy may be recommended. A physical therapist and an occupational therapist may exercise your arms, legs, and hands. They may also teach you new ways to do things around the house. A speech therapist may work with you to help you talk or swallow.
RISKS:
After treatment, you may still have pain or problems turning your head. Your cervical fracture may not completely heal. You may get an infection. You may get a blood clot in your leg or arm. This can cause pain and swelling, and it can stop blood from flowing where it needs to go in your body. The blood clot can break loose and travel to your lungs. A blood clot in your lungs can cause chest pain and trouble breathing. These problems can be life-threatening.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
