Basal Cell Carcinoma
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is basal cell carcinoma (BCC)?
BCC is a common skin cancer that begins in the top layer of the skin. BCC grows slowly and rarely spreads.
What increases my risk for BCC?
- Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays in sunlight or tanning beds
- Multiple sunburns, or a lot of UV exposure when you were a child
- Light skin that burns instead of tans
- Age over 40 years
- Other skin cancers or radiation treatments
What are the signs of BCC?
BCC usually forms on skin that has been exposed to the sun. Tumors on the head, ears, nose, and neck are common. Most tumors are not painful. The following are common signs of a BCC:
- Shiny, waxy, pale or pink bumps or growths that may have blood vessels on the surface
- Red, scaly patches
- Open sores that may bleed and do not heal
 |
How is BCC diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask when you first saw the growth. He or she will ask if the size, color, or shape have changed since you first saw it. He or she will look over the rest of your skin for other growths. Tell your provider if you have a family history of skin cancer, or you had sunburns or have used tanning beds. A skin biopsy is used to remove a sample of the growth to be tested for cancer.
How is BCC treated?
Treatment depends on your cancer, the area affected, and any other health conditions you may have:
- Surgery is the most common treatment. Your healthcare provider will remove the tumor. He or she may look at the tissue pieces with a microscope to make sure all of the cancer cells are removed. He or she may use an electric needle to burn off cancer cells or freeze the tumor with a chemical.
- Skin medicines may be used to help remove the cancer. This includes medicines that kill the cancer cells directly or help your immune system to attack the cancer cells.
- Radiation may be used to kill the cancer cell if you cannot have surgery, are older, or have a large tumor.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
What can I do to help prevent another BCC?
 |
- Follow up with your healthcare provider as directed. You may need to see your healthcare provider every few months. Ask how often you need to be checked.
- Do a body check 1 time each month. Look for new growths or sores. Check for changes in the size, shape, or color of your moles and freckles. Look for sores that do not heal. Use a mirror to check places that are hard to see. Ask family members or friends to help.
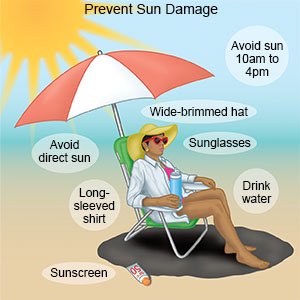
- Protect your skin from UV light. Avoid the sun between 10 am and 4 pm, when the rays are strongest. If you are outside, apply sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of 30 or more every 2 hours. Do this even on cloudy days. Wear pants and long sleeves to cover your body. Hats with a wide brim can protect your face, head, and neck. Wear sunglasses that block 99% of UV rays. Avoid tanning beds.
Where can I find support and information?
- American Cancer Society
250 Williams Street
Atlanta , GA 30303
Phone: 1- 800 - 227-2345
Web Address: http://www.cancer.org
- The Skin Cancer Foundation
149 Madison Avenue, Suite 901
New York , NY 10016
Phone: 1- 212 - 725-5176
Web Address: www.skincancer.org
When should I call my doctor?
- You have a fever.
- You have a sore that has not healed within 2 months.
- You see new growths on your skin.
- The size, shape, or color of a mole or freckle has changed.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Basal Cell Carcinoma
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
