Arteriovenous Malformation
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
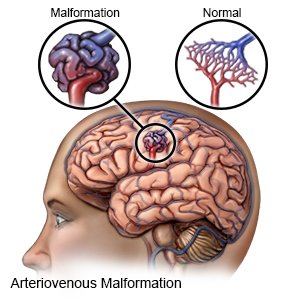
An arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is an abnormal connection between arteries and veins. The connection becomes tangled. Blood flows too quickly from the arteries and pushes on the walls of the veins. The walls weaken and become narrow. The artery walls also become weak. They begin to bulge from blood that is not able to go into the narrow veins. An AVM that has not burst usually causes no symptoms, or may cause headaches or seizures. A burst AVM may cause blood to leak into surrounding tissue, and may lead to a stroke. The leaked blood can also cause your brain to swell.
 |
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
You may need extra oxygen
if your blood oxygen level is lower than it should be. You may get oxygen through a mask placed over your nose and mouth or through small tubes placed in your nostrils. Ask your healthcare provider before you take off the mask or oxygen tubing.
Medicines:
- Anticonvulsant medicine is given to prevent or control seizures.
- Blood pressure medicine lowers your blood pressure to help prevent the blood vessels in your brain from bursting and bleeding.
- Diuretics help decrease swelling in your brain. This may help your brain get better blood flow.
- Steroid medicine decreases swelling in your brain.
Related medications
Tests:
- Blood tests may be used to check your overall health. Your blood's ability to clot will also be tested. The tests may include a check for diabetes. Diabetes increases your risk for a stroke.
- An angiogram is used to check for problems with blood flow in your brain. X-rays are taken as contrast liquid goes into blood vessels in your brain. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid.
- CT or MRI pictures may be used to check blood vessels and tissues in your brain. You may be given contrast liquid to help arteries and veins show up better in the pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
- A neurologic exam can show healthcare providers how well your brain is working. Healthcare providers may check your memory and how easily you wake up. Your hand grasp and balance may also be tested.
Treatment:
- Surgery may be needed to repair or remove your AVM. If the AVM has already bled, surgery may be needed to repair burst blood vessels, or remove blood from your brain. Your healthcare provider will use the size, location, and depth of the AVM to decide whether surgery is right for you. Surgery can also be used to treat the abnormal blood vessels to prevent them from rupturing or bleeding.
- Endovascular embolization is sometimes done before surgery or radiation to make the AVM smaller and easier to treat. A catheter (tube) is put into a large blood vessel in your groin, and guided up to the AVM in your brain. Dye and an x-ray machine may be used to find the AVM. Healthcare providers use the catheter to put chemicals, metal coils, or plastic beads in the AVM to stop the blood flow to it.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
RISKS:
An AVM may get bigger or more tangled. You are at risk of a stroke if the AVM bursts. Treatment may not remove the AVM, or another AVM may develop. You may develop brain damage. AVM treatment during pregnancy puts both the mother and the unborn baby at risk. The increased blood pressure that occurs with pushing the baby out during delivery can affect the AVM.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Arteriovenous Malformation
Treatment options
- Medications for Cardiovascular Conditions and Disorders
- Medications for Cerebral Vascular Disorder
- Medications for Cerebrovascular Insufficiency
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
