Apnea of Prematurity
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
Apnea of prematurity is an episode when a premature baby stops breathing for 15 to 20 seconds. Premature babies are born earlier than 37 weeks, before certain parts of the body have fully formed. Apnea may happen when the part of the brain that controls breathing is affected. It may also happen from weak airway and breathing muscles. Most premature babies outgrow apnea after a few weeks.
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You have to perform CPR on your baby.
- Your baby is not breathing or is gasping for breath.
- Your baby will not wake up.
Call your baby's pediatrician if:
- Your baby's skin, lips, or fingernails are pale or blue.
- You have questions about your baby's condition or care.
If your baby is not breathing:
Do not shake your baby to make him or her breathe.
- Gently tap the sole of your baby's foot.
- Rub his or her back.
- Change the position of his or her head and neck.
- Perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), if necessary. Then call your local emergency number. Keep emergency numbers near the phone.
Related medications
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Medicines:
- Medicines may be given to make blood flow and breathing go faster.
- Give your child's medicine as directed. Contact your child's healthcare provider if you think the medicine is not working as expected. Tell the provider if your child is allergic to any medicine. Keep a current list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs your child takes. Include the amounts, and when, how, and why they are taken. Bring the list or the medicines in their containers to follow-up visits. Carry your child's medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Use an apnea monitor if directed:
This device monitors how well your baby is breathing. The monitor alarm will sound if your baby stops breathing or takes shallow breaths. It will also sound if your baby's heart rate is lower or higher than it should be. Your baby's healthcare providers will teach you and other members of your household how to use it. Make sure someone is always available to respond to the apnea monitor's alarms.
Help your baby breathe easier:
- Remove mucus from your baby's nose with a bulb syringe. Squeeze the bulb and gently put the tip into one of your baby's nostrils. Do not put the stem of the syringe in your baby's nose. Release the bulb so that it sucks out the mucus. When the bulb has expanded, remove it from your baby's nose. Empty it into a tissue. Repeat the steps for the other nostril, if needed.
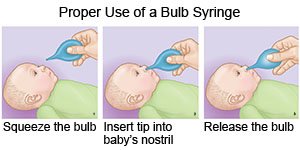
- Have your baby lie with his or her head and body in a straight line. Make sure your baby's head does not flop forward or bend to the side.
- Always put your baby on his or her back to sleep. Do this every time your baby sleeps (naps and at night). Do this even if he or she sleeps more soundly on his or her stomach or side.

- Take extra care when you feed your baby. Hold your baby so his or her head is higher than his or her stomach. Feed your baby in a place with enough light so you can see any changes in his or her skin color. Stop from time to time to allow your baby to take breaths between sucks on the bottle or breast. Stop the feeding if he or she looks tired.
- Use a cool mist humidifier to increase air moisture in your home. This may make it easier for your child to breathe and help decrease his or her cough.
- Do not let anyone smoke around your baby. Cigarette smoke can affect your baby's lungs and make it more difficult for him or her to breathe.
For support and more information:
- American Academy of Pediatrics
345 Park Boulevard
Itasca , IL 60143
Phone: 1- 800 - 433-9016
Web Address: http://www.aap.org
Follow up with your baby's pediatrician as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Apnea of Prematurity
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
