Netspot: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: 68ga-dotatate
Dosage form: kit
Drug class: Radiologic conjugating agents
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jul 20, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Use In Specific Populations
- Overdosage
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
Highlights of Prescribing Information
NETSPOT® (kit for the preparation of gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection), for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2016
Recent Major Changes
| Dosage and Administration (2.3) | 10/2023 |
Indications and Usage for Netspot
NETSPOT, after radiolabeling with gallium-68, is a radioactive diagnostic agent indicated for use with positron emission tomography (PET) for localization of somatostatin receptor positive neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) in adult and pediatric patients. (1)
Netspot Dosage and Administration
- After radiolabeling, handle gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection with appropriate safety measures to minimize radiation exposure. (2.1)
- Instruct patients to drink a sufficient amount of water before administration, during the first hours following administration and to void frequently. (2.1)
- Recommended dose is 2 MBq/kg (0.054 mCi/kg) of body weight up to 200 MBq (5.4 mCi) administered as intravenous bolus injection. (2.2)
- See the Full Prescribing Information for detailed instructions on how to prepare gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection (e.g., radiolabeling). (2.3)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
NETSPOT is supplied as a multiple-dose kit containing:
- Vial 1 (reaction vial with lyophilized powder) containing 40 mcg of dotatate. (3)
- Vial 2 (buffer vial) containing 1 mL of reaction buffer solution. (3)
After radiolabeling with gallium-68 and pH adjustment with Reaction Buffer, Vial 1 contains a sterile solution of gallium Ga 68 dotatate at a strength up to 218 MBq/mL (5.89 mCi/mL). (3)
Contraindications
None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Radiation Risk: Gallium Ga 68 dotatate contributes to a patient’s overall long-term cumulative radiation exposure. Ensure safe handling and preparation procedures to protect patients and health care workers from unintentional radiation exposure. Restrict close contact with infants and pregnant women during the first 12 hours after administration of gallium Ga 68 dotatate. (5.1)
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Most reported reactions were rash and pruritus and reversible either spontaneously or with routine symptomatic management. (5.2)
- Risk for Image Misinterpretation: The uptake of gallium Ga 68 dotatate can be seen in a variety of tumor types other than NETs (e.g., those derived from neural crest tissue), in sites of splenosis or other pathologic conditions, and as a normal physiologic variant (e.g., uncinate process of the pancreas). (5.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Nausea, vomiting, and injection site pain and burning sensation were all reported during post-approval use. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation at 1-888-669-6682 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
Somatostatin Analogs: Somatostatin analogs competitively bind to the same somatostatin receptors as gallium Ga 68 dotatate and may affect imaging – image just prior to dosing with long-acting somatostatin analogs. (7.1)
Glucocorticoids: Repeated administration of high doses of glucocorticoids prior to gallium Ga 68 dotatate administration may affect imaging. (7.2)
Use In Specific Populations
Lactation: Breast milk should be pumped and discarded for 12 hours after administration. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 10/2023
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Netspot
NETSPOT, after radiolabeling with gallium-68, is indicated for use with positron emission tomography (PET) for localization of somatostatin receptor positive neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) in adult and pediatric patients.
2. Netspot Dosage and Administration
2.1 Radiation Safety
Drug Handling
After radiolabeling, handle the gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection with appropriate safety measures to minimize radiation exposure
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Use waterproof gloves, effective radiation shielding and appropriate safety measures when preparing and handling gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection.
Radiopharmaceuticals should be used by or under the control of physicians who are qualified by specific training and experience in the safe use and handling of radionuclides, and whose experience and training have been approved by the appropriate governmental agency authorized to license the use of radionuclides.
Patient Preparation
Instruct patients to drink a sufficient amount of water to ensure adequate hydration prior to administration of gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection. Drink and void frequently during the first hours following administration to reduce radiation exposure.
2.2 Recommended Dosage and Administration Instructions
In adults and pediatric patients, the recommended amount of radioactivity to be administered for PET imaging is 2 MBq/kg (0.054 mCi/kg) of body weight up to 200 MBq (5.4 mCi) by intravenous injection (bolus).
Verify the injected radioactivity by measuring the radioactivity of the syringe containing the gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection with a dose calibrator before administration to the patient [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. Ensure that the injected radioactivity is within ± 10% of the recommended activity.
2.3 Drug Preparation
The NETSPOT kit is supplied as 2 vials [see Dosage Forms and Strengths (3)] which allows for direct preparation of gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection with the eluate from one of the following generators (see below for specific instructions for use with each generator):
- Eckert & Ziegler GalliaPharm germanium-68/gallium-68 (68Ge/68Ga) generator
- IRE ELiT Galli Eo germanium-68/gallium-68 (68Ge/68Ga) generator
The 68Ge/68Ga generators are not supplied with the NETSPOT kit.
Components of the kit:
- Vial 1 (reaction vial with lyophilized powder) contains: 40 mcg dotatate, 5 mcg 1,10-phenanthroline; 6 mcg gentisic acid; 20 mg mannitol.
- Vial 2 (buffer vial) contains: 60 mg formic acid; 56.5 mg sodium hydroxide and water for injection.
Ancillary supplies (not included in the kit):
- Ancillary supplies needed (not supplied in kit): 1 mL sterile plastic syringe, 5 mL sterile plastic syringe, non-metallic or silicone coated sterile needles (size 21 to 23G), 0.2 micron sterile vented filter.
Prepare gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection according to the following aseptic procedure:
a. Use suitable shielding to reduce radiation exposure.
b. Wear waterproof gloves.
c. Test periodically (weekly) the gallium-68 chloride eluate for germanium-68 breakthrough by suitable method. Germanium-68 breakthrough and other gamma emitting radionuclides should be ≤ 0.001%.
d. Set the temperature of the shielded dry bath to 95°C (203°F) and wait for the temperature to reach the set point and stabilize.
e. Prepare syringes for elution and radiolabeling steps per Table 1 below.
f. Use non-metallic or silicone coated needles to minimize trace metal impurity levels. Radiolabeling of carrier molecules with gallium-68 chloride is very sensitive to the presence of trace metal impurities.
g. Use 1 mL low dead space plastic syringe to precisely measure the adequate volume of reaction buffer to be added during preparation. Do not use glass syringe.
h. Prior to piercing vial septums, flip the cap off and swab the top of the vial closure with alcohol to disinfect the surface, and allow the stopper to dry.
| Solutions for use with Eckert & Ziegler GalliaPharm generator | ||
| Syringe | Solution | Purpose |
|
5 mL sterile plastic syringe | 5 mL of 0.1 N sterile HCl supplied by the generator manufacturer |
For elution of the generator |
| 1 mL sterile plastic syringe |
Vial 2 buffer Calculate the volume (in mL) by multiplying the volume of HCl used for the elution of the generator in mL by its molarity: Reaction buffer volume in mL = HCl volume in mL x HCl molarity (5 mL x 0.1 N = 0.5 mL of reaction buffer). |
For radiolabeling reaction |
| Solutions for use with IRE Galli Eo generator | ||
| 5 mL sterile plastic syringe |
3.9 mL sterile water for injection |
For preliminary dilution of Vial 1 |
| 1 mL sterile plastic syringe |
Vial 2 buffer Calculate the volume (in mL) by multiplying the volume of HCl used for the elution of the generator in mL by its molarity: Reaction buffer volume in mL = HCl volume in mL x HCl molarity (1.1 mL x 0.1 N = 0.11 mL of reaction buffer). |
For radiolabeling reaction |
i. Pierce the Vial 1 septum with a sterile needle connected to a 0.2 micron sterile vented filter (not supplied) to maintain atmospheric pressure within the vial during the radiolabeling process.
j. Follow the generator specific radiolabeling procedures below. Then continue with the incubation step k.
Radiolabeling with Eckert & Ziegler GalliaPharm generator
- Connect the male luer of the outlet line of the GalliaPharm generator to a sterile needle (size 21G to 23G).
- Connect Vial 1 directly to the outlet line of the GalliaPharm generator by pushing the needle through the rubber septum and place the vial in a lead shield container.
- Elute the generator directly into the Vial 1 according to the instructions for use of the GalliaPharm generator that are supplied by Eckert & Ziegler, in order to reconstitute the lyophilized powder with 5 mL of eluate. Perform the elution manually or by means of a pump.
- At the end of the elution, disconnect the generator from Vial 1 by removing the needle from the rubber septum, and immediately (do not delay buffer addition more than 10 min) add the kit reaction buffer in the 1 mL sterile syringe (size 21G to 23G; the amount of reaction buffer was determined in Table 1).
- Withdraw the syringe and the 0.2 micron sterile air venting filter.
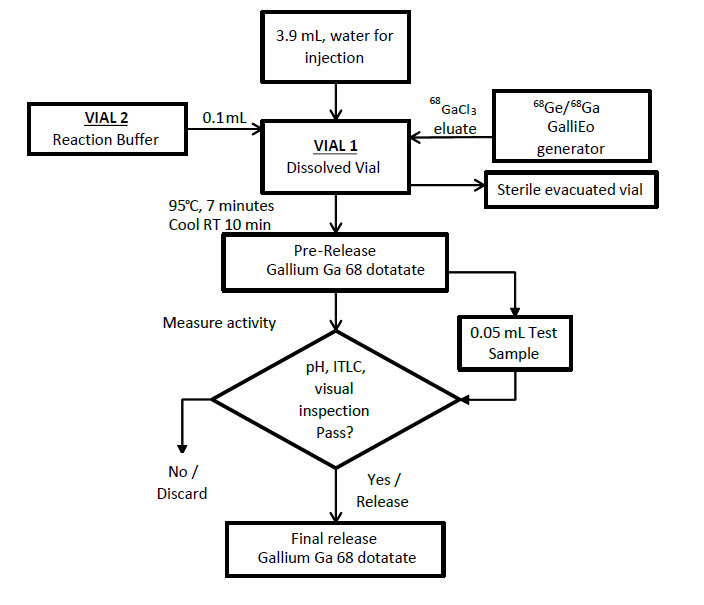
Radiolabeling with IRE Galli Eo generator
- Set the Galli Eo generator for the elution according to manufacturer instructions. Connect a sterile needle (size 21G to 23G) to the outlet tube of the generator, turn the button by 90° to loading position then wait 10 seconds before turning the button back to the initial position.
- Reconstitute Vial 1 with 3.9 mL of sterile water for injection as prepared in Table 1.
- Add the 0.1 mL reaction buffer to Vial 1 as prepared in Table 1.
- Connect Vial 1 to the outlet line of the Galli Eo generator by pushing the needle through the rubber septum.
- Connect one end of the two male luer ends of a sterile extension line to the 0.2 micron sterile vent filter inserted into Vial 1.
- Assemble a sterile needle on the second male luer end of the sterile extension line and connect it to a sterile evacuated vial (17 mL minimum volume) by pushing the needle through the rubber septum. The generator elution will start.
- Wait for the elution to be completed (minimum 3 minutes, according to the Galli Eo generator manufacturer instructions for use).
- At the end of the elution, first withdraw the needle from the evacuated vial in order to establish atmospheric pressure into Vial 1, then disconnect Vial 1 from the generator by removing the needle from the rubber septum and remove the 0.2 micron sterile vent filter from Vial 1.
Incubation
k. Using a tong, move Vial 1 to the heating hole of the dry bath, and leave the vial at 95°C (203°F), not to exceed 98°C (208°F), for at least 7 minutes (do not exceed 10 minutes heating) without agitation or stirring.
l. After 7 minutes, remove the vial from the dry bath, place it in an appropriate lead shield and let it cool down to room temperature for approximately 10 minutes.
m. Assay the whole vial containing the gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection for total radioactivity concentration using a dose calibrator and record the result.
n. Perform the quality controls according to the recommended methods in order to check the compliance with the specifications [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
o. Prior to use, visually inspect the solution behind a shielded screen for radioprotection purposes. Only use solutions that are clear without visible particles.
p. Keep the vial containing the gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection upright in a radio-protective shield container at a temperature below 25°C (77°F) until use.
q. After addition of gallium-68 chloride to the reaction vial, use gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection within 4 hours. After radiolabeling, do not perform further dilutions.
Figure 1. Radiolabeling Procedure for Eckert & Ziegler GalliaPharm Generator
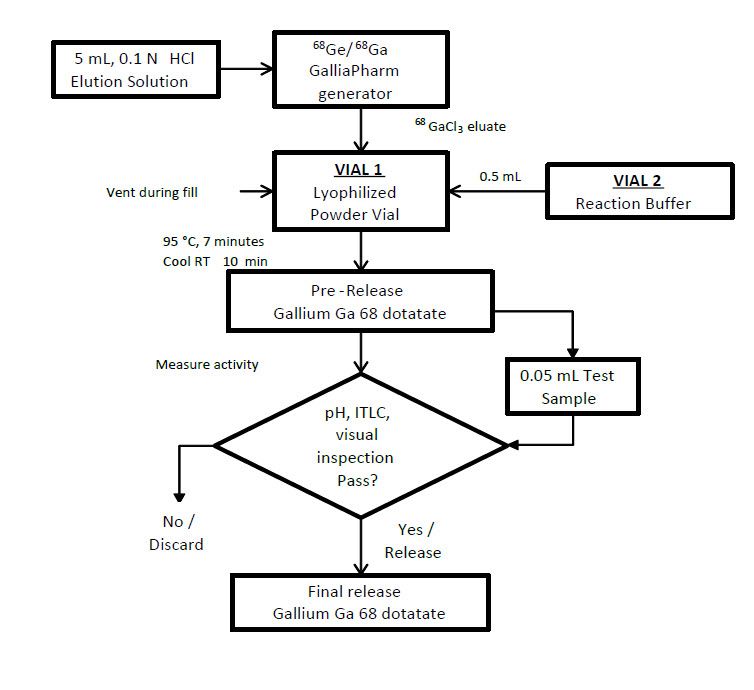
Figure 2. Radiolabeling Procedure for IRE Galli Eo Generator
2.4 Administration
Prior to use, visually inspect the prepared gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection behind a lead glass shield for radioprotection purposes. Only use solutions that are clear without visible particles. Using a single-dose syringe fitted with a sterile needle (size 21G to 23G) and protective shielding, aseptically withdraw the prepared gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection prior to administration. Measure the total radioactivity in the syringe by a dose calibrator immediately prior to administration. The dose calibrator must be calibrated with National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) traceable standards.
Accidental extravasation may cause local irritation due to the acidic pH of the gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection. In case of extravasation, the injection must be stopped, the site of injection must be changed and the affected area should be irrigated with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
Handle and dispose radioactive material in accordance with applicable regulations.
2.5 Specifications and Quality Control
Perform the quality controls in Table 2 behind a lead glass shield for radioprotection purposes.
| Test | Acceptance criteria | Method |
| Appearance | Colorless and particulate free | Visual inspection |
| pH | 3.2 to 3.8 | pH-indicator strips |
| Labeling efficiency | Gallium Ga 68 dotatate ≥ 95% and other gallium-68 species ≤ 5% | Thin layer chromatography (ITLC, see details below) |
Determine labeling efficiency of gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection applying one of the following recommended methods:
Obtain the following materials:
- ITLC SA or ITLC SG
- Ammonium acetate 1M: Methanol (1:1 V/V)
- Developing tank
- Radiometric TLC scanner
ITLC methods 1 and 2 (longer development length)
Perform the following:
- Pour ammonium acetate 1M: Methanol (1:1 V/V) solution to a depth of 3 mm to 4 mm in the developing tank, cover the tank, and allow it to equilibrate.
- Apply a drop of the gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection on a pencil line 1 cm from the bottom of the ITLC strip.
- Place the ITLC strip in the developing tank and allow it to develop for a distance of 10 cm from the point of application (i.e., to the top pencil mark).
- Scan the ITLC with a radiometric TLC scanner.
- Calculate radiochemical purity (RCP) by integration of the peaks on the chromatogram. Do not use the reconstituted product if the RCP is less than 95%.
- The retention factor (Rf) specifications are as follows for ITLC SA or ITLC SG:
ITLC SA: Non-complexed gallium-68 species, Rf = 0 to 0.1; gallium Ga 68 dotatate, Rf = 0.6 to 0.8
ITLC SG: Non-complexed gallium-68 species, Rf = 0 to 0.1; gallium Ga 68 dotatate, Rf = 0.8 to 1
ITLC method 3 (shorter development length)
Perform the following:
a) Pour ammonium acetate 1M: Methanol (1:1 V/V) solution to a depth of 3 mm to 4 mm in the developing tank, cover the tank, and allow it to equilibrate.
b) Apply a drop of the gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection on a pencil line 1 cm from the bottom of an ITLC SG strip.
c) Place the ITLC SG strip in the developing tank and allow it to develop for a distance of 6 cm from the point of application (i.e., to 7 cm from the bottom of the ITLC strip).
d) Scan the ITLC SG with a radiometric TLC scanner.
e) Calculate radiochemical purity (RCP) by integration of the peaks on the chromatogram. Do not use the reconstituted product if the RCP is less than 95%.
f) The retention factor (Rf) specifications are as follows:
Non-complexed gallium-68 species, Rf = 0 to 0.1; gallium Ga 68 dotatate, Rf = 0.8 to 1
2.6 Image Acquisition
For gallium Ga 68 dotatate PET imaging, the acquisition must include a whole body acquisition from skull to mid-thigh. Images can be acquired 40 minutes to 90 minutes after the intravenous administration of the gallium Ga 68 dotatate. Adapt imaging acquisition delay and duration according to the equipment used, and the patient and tumor characteristics, in order to obtain the best image quality possible.
2.7 Image Interpretation
Gallium Ga 68 dotatate binds to somatostatin receptors. Based upon the intensity of the signals, PET images obtained using gallium Ga 68 dotatate indicate the presence and density of somatostatin receptors in tissues. Tumors that do not bear somatostatin receptors will not be visualized. Increased uptake in tumors is not specific for NET [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
2.8 Radiation Dosimetry
Estimated radiation absorbed doses per injection activity for organs and tissues of adult patients following an intravenous bolus of gallium Ga 68 dotatate are shown in Table 3. Estimated radiation effective doses per injection activity for adult and pediatric patients following an intravenous bolus of gallium Ga 68 dotatate are shown in Table 4.
Gallium-68 decays with a half-life of 68 minutes to stable zinc-68:
- 89% through positron emission with a mean energy of 836 keV followed by photonic annihilation radiations of 511 keV (178%),
- 10% through orbital electron capture (X-ray or Auger emissions), and
- 3% through 13 gamma transitions from 5 exited levels.
The radiation effective dose resulting from the administration of 150 MBq (4.05 mCi) [within the range of the recommended gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection dose] to an adult weighing 75 kg, is about 3.15 mSv. For an administered activity of 150 MBq (4.05 mCi) the typical radiation absorbed dose to the critical organs, which are the urinary bladder wall, the spleen, the kidneys and the adrenals, are about 15 mGy, 16 mGy, 14 mGy and 13 mGy, respectively. Because the spleen has one of the highest physiological uptakes, higher uptake and radiation dose to other organs or pathologic tissues may occur in patients with spleen disorders (e.g., splenectomy and/or splenosis) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Physical data
Gamma constant: 0.67 mrem/hr per mCi at 1 meter [1.8E-4 mSv/hr per MBq at 1 meter]
Specific Activity: 4.1E7 Ci/g [1.51E18 Bq/g] max
| Organ/Tissue | Absorbed dose per administered activity (mGy/MBq) |
|
| Mean | SD | |
| Adrenals | 0.086 | 0.052 |
| Brain | 0.01 | 0.002 |
| Breasts | 0.01 | 0.002 |
| Gallbladder wall | 0.016 | 0.002 |
| Lower large intestine wall | 0.015 | 0.002 |
| Small intestine | 0.025 | 0.004 |
| Stomach wall | 0.013 | 0.002 |
| Upper large intestine wall | 0.021 | 0.003 |
| Heart wall | 0.018 | 0.003 |
| Kidneys | 0.093 | 0.016 |
| Liver | 0.05 | 0.015 |
| Lungs | 0.006 | 0.001 |
| Muscle | 0.012 | 0.002 |
| Ovaries | 0.016 | 0.001 |
| Pancreas | 0.015 | 0.002 |
| Red marrow | 0.015 | 0.003 |
| Osteogenic cells | 0.021 | 0.005 |
| Skin | 0.01 | 0.002 |
| Spleen | 0.109 | 0.058 |
| Testes | 0.01 | 0.001 |
| Thymus | 0.012 | 0.002 |
| Thyroid | 0.011 | 0.002 |
| Urinary bladder wall | 0.098 | 0.048 |
| Uterus | 0.015 | 0.002 |
| Total body | 0.014 | 0.002 |
| Effective dose per injection activity | mSv/MBq | |
| 0.021 | 0.003 | |
| Age | Effective dose per injection activity (mSv/MBq) |
| Adult | 0.021 |
| 15 years | 0.025 |
| 10 years | 0.04 |
| 5 years | 0.064 |
| 1 year | 0.13 |
| Newborn | 0.35 |
Table 4 indicates how effective dose per injection activity scales with body habitus in computational models of adult and pediatric patients.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
NETSPOT is supplied as a multiple-dose kit, containing two vials for preparation of gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection:
- Vial 1 (reaction vial with lyophilized powder): 40 mcg of dotatate, 5 mcg of 1,10-phenanthroline, 6 mcg gentisic acid and 20 mg D-mannitol for injection as a white lyophilized powder in a 10 mL glass vial with light-blue flip-off cap
- Vial 2 (buffer vial): clear, and colorless reaction buffer solution (60 mg formic acid, 56.5 mg sodium hydroxide in approximately 1 mL volume) in a 10 mL olefin polymer vial with a yellow flip-off cap
Gallium-68 is obtained from one of the following generators:
- Eckert & Ziegler GalliaPharm (68Ge/68Ga) generator
- IRE ELiT Galli Eo (68Ge/68Ga) generator
After radiolabeling with gallium-68 and pH adjustment with Reaction Buffer, Vial 1 contains a sterile solution of gallium Ga 68 dotatate at a strength of up to 218 MBq/mL (5.89 mCi/mL).
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Radiation Risk
Gallium Ga 68 dotatate contributes to a patient’s overall long-term cumulative radiation exposure. Long-term cumulative radiation exposure is associated with an increased risk of cancer. Ensure safe handling and preparation radiolabeling procedures to protect patients and health care workers from unintentional radiation exposure [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Avoid close contact with infants and pregnant women during the first 12 hours after administration of gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection.
5.2 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions following administration of somatostatin receptor imaging agents predominantly consisted of cutaneous reactions, such as rash and pruritus. Reactions reversed either spontaneously or with routine symptomatic management. Less frequently hypersensitivity reactions included angioedema or cases with features of anaphylaxis.
5.3 Risk for Image Misinterpretation
The uptake of gallium Ga 68 dotatate reflects the level of somatostatin receptor density in NETs. However, uptake can also be seen in a variety of other tumor types (e.g., those derived from neural crest tissue). Increased uptake might also be seen in sites of splenosis or other pathologic conditions (e.g., thyroid disease or subacute inflammation) or might occur as a normal physiologic variant (e.g., uncinate process of the pancreas). PET images with gallium Ga 68 dotatate should be interpreted visually and the uptake may need to be confirmed by histopathology or other assessments [see Dosage and Administration (2.7)].
A negative scan after the administration of gallium Ga 68 dotatate in patients who do not have a history of NETs, including in patients suspected of ectopic ACTH-secreting tumors, does not rule out the presence of NETs.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
The safety of gallium Ga 68 dotatate was evaluated in three single center studies [see Clinical Studies (14)] and in a survey of the scientific literature. No serious adverse reactions were identified.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of NETSPOT or other somatostatin receptor imaging agents. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to the drug.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Nausea and vomiting
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: Injection site pain and burning sensation
Immune System Disorders: Hypersensitivity reactions, predominantly rash, pruritus, less frequently angioedema or features of anaphylaxis.
Related/similar drugs
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Somatostatin analogs
Non-radioactive somatostatin analogs competitively bind to the same somatostatin receptors as gallium Ga 68 dotatate. Image patients with gallium Ga 68 dotatate PET just prior to dosing with long-acting analogs of somatostatin. Short-acting analogs of somatostatin can be used up to 24 hours before imaging with gallium Ga 68 dotatate.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no studies with gallium Ga 68 dotatate in pregnant women to inform any drug-associated risks; however, radioactive emissions, including those from gallium Ga 68 dotatate, can cause fetal harm. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with gallium Ga 68 dotatate.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risks of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies are 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information on the presence of gallium Ga 68 dotatate in human milk, the effect on the breastfed child, or the effect on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection or from the underlying maternal condition.
Clinical Considerations
Advise a lactating woman to interrupt breastfeeding and pump and discard breast milk for 12 hours after gallium Ga 68 dotatate administration in order to minimize radiation exposure to a breastfed child.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The efficacy of gallium Ga 68 dotatate PET imaging in pediatric patients with neuroendocrine tumors is based on extrapolation from adult studies, from studies demonstrating the ability of gallium Ga 68 dotatate to bind to somatostatin receptors [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], and from a published study of gallium Ga 68 dotatate PET imaging in pediatric patients with somatostatin receptor positive tumors. The safety profile of gallium Ga 68 dotatate is similar in adult and pediatric patients with somatostatin receptor positive tumors. The recommended gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection dose in pediatric patients is weight based as in adults [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over, to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients.
10. Overdosage
In the event of a radiation overdose, the absorbed dose to the patient should be reduced where possible by increasing the elimination of the radionuclide from the body by reinforced hydration and frequent bladder voiding. A diuretic might also be considered. If possible, an estimate of the radioactive dose given to the patient should be performed.
11. Netspot Description
NETSPOT is supplied as a sterile, multiple-dose kit for preparation of gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection for intravenous use.
Dotatate, also known as DOTA-0-Tyr3-Octreotate, is a cyclic 8 amino acid peptide with a covalently bound chelator (dota). The peptide has the amino acid sequence: H-D-Phe-Cys-Tyr-D-Trp-Lys-Thr-Cys-Thr-OH, and contains one disulfide bond. Dotatate has a molecular weight of 1435.6 Daltons and its chemical structure is shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3. Chemical Structure of Dotatate
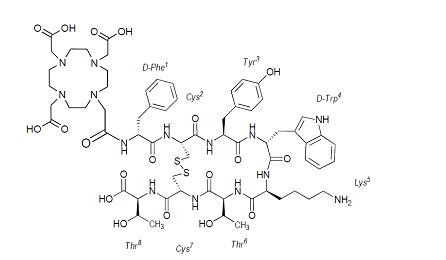
[(4,7,10-Tricarboxymethyl-1,4,7,10-tetrazacyclododec-1-yl)acetyl]-(D)-Phenylalanyl-(L)Cysteinyl-(L)-Tyrosyl-(D)-Tryptophanyl-(L)-Lysyl-(L)-Threoninyl-(L)-Cysteinyl-(L)-Threonine-cyclic(2-7)disulfide
NETSPOT is a kit with the following components:
- Vial 1 (reaction vial with lyophilized powder) contains: 40 mcg dotatate, 5 mcg 1,10-phenanthroline; 6 mcg gentisic acid; 20 mg mannitol.
- Vial 2 (buffer vial) contains: 60 mg formic acid; 56.5 mg sodium hydroxide and water for injection.
After radiolabeling, [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)], gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection also contains hydrochloric acid as an excipient derived from the generator eluate. The prepared gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection for intravenous use, is a sterile, pyrogen free, clear, colorless, buffered solution, with a pH between 3.2 and 3.8. Table 5, Table 6, and Table 7 display the principal radiation emission data, radiation attenuation by lead shielding, and physical decay of gallium-68.
| Radiation/Emission | % Disintegration | Mean energy (MeV) |
| beta+ | 88% | 0.8360 |
| beta+ | 1.1% | 0.3526 |
| gamma | 178% | 0.5110 |
| gamma | 3% | 1.0770 |
| X-ray | 2.8% | 0.0086 |
| X-ray | 1.4% | 0.0086 |
| Shield thickness (Pb) mm | Coefficient of attenuation |
| 6 | 0.5 |
| 12 | 0.25 |
| 17 | 0.1 |
| 34 | 0.01 |
| 51 | 0.001 |
| Minutes | Fraction remaining |
| 0 | 1.000 |
| 15 | 0.858 |
| 30 | 0.736 |
| 60 | 0.541 |
| 90 | 0.398 |
| 120 | 0.293 |
| 180 | 0.158 |
| 360 | 0.025 |
12. Netspot - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Gallium Ga 68 dotatate binds to somatostatin receptors, with highest affinity for subtype 2 receptors (SSTR2). It binds to cells that express somatostatin receptors, including malignant cells, which overexpress SSTR2. Gallium-68 is a β+ emitting radionuclide with an emission yield that allows PET imaging.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The relationship between gallium Ga 68 dotatate plasma concentrations and successful imaging was not explored in clinical trials.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Distribution
Gallium Ga 68 dotatate distributes to all SSTR2-expressing organs, such as pituitary, thyroid, spleen, adrenals, kidneys, pancreas, prostate, liver, and salivary glands. There is no uptake in the cerebral cortex or in the heart, and usually thymus and lung uptakes are low.
Elimination
A total of 12% of the injected dose is excreted in urine in the first four hours post-injection.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No animal studies on fertility, embryology, mutagenic potential, or carcinogenic potential have been conducted with gallium Ga 68 dotatate. However, genotoxicity studies conducted with a very similar molecule (mixture lutetium Lu 175 dotatate/dotatate) show that these non-radioactive compounds do not induce mutation at the TK locus of L5178Y mouse lymphoma cells in vitro, nor reverse mutation in Salmonella Typhimurium, or Escherichia coli (both in the absence or presence of S9 metabolic activation).
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of NETSPOT was established in three open label single center studies (Study A-C).
In Study A, 97 adult patients (mean age 54; 41 men and 56 women) with known or suspected neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) were evaluated with gallium Ga 68 dotatate PET. The gallium Ga 68 dotatate images were read by two independent readers blinded to clinical information. The reads were compared to CT and/or MR images and to indium In 111 pentetreotide images obtained with Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) within previous 3 years. Among 78 patients in whom CT and/or MR images and indium In 111 pentetreotide images were available, gallium Ga 68 dotatate PET was in agreement with the CT and/or MR images in 74 patients. Out of 50 patients with NETs localized by CT and/or MR imaging, gallium Ga 68 dotatate was positive in 48 patients, including 13 patients in whom indium In 111 pentetreotide was negative. Gallium Ga 68 dotatate was negative in 26 out of 28 patients in whom CT and/or MR imaging was negative.
Study B was a published study which involved 104 patients (mean age 58; 52 men and 52 women) with suspected NETs due to clinical symptoms, elevated levels of tumor markers, or indeterminate tumors suggestive of NET. Diagnostic performance of gallium Ga 68 dotatate PET in localizing tumor sites was retrospectively assessed using a reference standard: histopathology (n = 49) or clinical follow up of up to 5-month duration (n = 55). Images were interpreted by consensus between two on-site readers who were not blinded to clinical information. NET sites were localized by reference standard in 36 patients (all by histopathology). Out of these, gallium Ga 68 dotatate was positive, correctly identifying an NET site, in 29 patients and was falsely negative in seven. In 68 patients with no NET identified by a reference standard, the images were negative in 61 and falsely positive in seven patients.
Study C was a published study which involved 63 patients (mean age 58; 34 men and 29 women) evaluated for NET recurrence using a reference standard as described for Study B. Gallium Ga 68 dotatate images were interpreted independently by two central readers blinded to clinical information. Reader 1 correctly localized NETs in 23 out of 29 reference standard-positive patients and reader 2 correctly localized NETs in 22 such patients. In 34 patients with no NET identified by a reference standard, reader 1 was correct in 29 patients and reader 2 in 32.
16. How is Netspot supplied
16.1 How Supplied
NETSPOT is supplied as a multiple-dose kit (NDC# 69488-001-40) for preparing multiple doses of gallium-68 radiolabeled dotatate injection.
The kit contains:
- Vial 1 (10-mL Ultra inert Type I Plus glass vial, light-blue flip-off cap): 40 mcg of dotatate, 5 mcg 1,10-phenanthroline, 6 mcg gentisic acid, 20 mg mannitol as lyophilized powder (NDC# 69488-001-04)
- Vial 2 (10-mL cyclic olefin polymer vial, with a yellow flip-off cap): reaction buffer solution (approximately 1 mL volume), 60 mg formic acid, 56.5 mg sodium hydroxide and water for injection (NDC# 69488-001-01)
The radionuclide is not part of the kit. Before radiolabeling with gallium-68, the contents of this kit are not radioactive.
Expiry date is indicated on the original outer packaging, and on the vials. This medicinal product must not be used beyond the date indicated on the packaging.
16.2 Storage and Handling
For prolonged storage, store NETSPOT in its original packaging at room temperature below 25°C (77°F) (do not freeze). After radiolabeling [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] with activities of up to 1,110 MBq (30 mCi), keep gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection upright with an appropriate shielding to protect from radiation, at a temperature below 25°C (77°F) (do not freeze), and use within 4 hours. The storage of the radiolabeled product must comply with regulatory requirements for radioactive materials.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Adequate Hydration
Advise patients to drink a sufficient amount of water to ensure adequate hydration before their PET study and urge them to drink and urinate as often as possible during the first hours following the administration of gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection, in order to reduce radiation exposure [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Lactation
Advise a lactating woman to interrupt breastfeeding and pump and discard breast milk for 12 hours after gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection administration in order to minimize radiation exposure to a breastfed infant [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Close Contact
Advise patients to avoid close contact with infants and pregnant women during the first 12 hours after administration of gallium Ga 68 dotatate.
Distributed by:
Advanced Accelerator Applications USA, Inc. Millburn, NJ 07041
©2023 Advanced Accelerator Applications USA, Inc.
NETSPOT® is a registered trademark of Novartis AG and/or its affiliates.
T2023-68
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 69488-001-40
Rx Only
NETSPOT®
(kit for the preparation of
Gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection)
40 mcg dotatate
For Intravenous Use Only

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NETSPOT®
(kit for the preparation of
Gallium Ga 68 dotatate)
40 mcg dotatate per vial
Vial 1 (Reaction vial with
lyophilized powder)
NDC 69488-001-04
Rx Only
Multiple-dose vial
For Intravenous Use Only


PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NETSPOT®
For adjusting pH of Gallium Ga 68 dotatate injection
For pH adjustment of radiolabeled Netspot only
1 mL in 10 mL Vial
Vial 2 (Buffer)
NDC 69488-001-01
Rx Only
Each vial of buffer is
intended for use in the production of
one vial of Gallium Ga 68 dotatate



| NETSPOT
68ga-dotatate kit |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Advanced Accelerator Applications USA, Inc (051714355) |
| Registrant - Advanced Accelerator Applications USA, Inc (051714355) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Accelerator Applications (Italy) S.r.l. | 441182729 | MANUFACTURE(69488-001) , ANALYSIS(69488-001) , PACK(69488-001) , LABEL(69488-001) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baxter Oncology GmbH | 344276063 | MANUFACTURE(69488-001) , ANALYSIS(69488-001) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| LabAnalysis Life Science srl | 338466205 | ANALYSIS(69488-001) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| piCHEM Forschungs-und Entwicklungs GmbH | 303575690 | API MANUFACTURE(69488-001) | |
More about Netspot (gallium ga 68 dotatate)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- FDA approval history
- Drug class: radiologic conjugating agents
- Breastfeeding