Cardiogen-82: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: rubidium chloride rb-82
Dosage form: injection, solution
Drug class: Diagnostic radiopharmaceuticals
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 31, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Use In Specific Populations
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
Highlights of Prescribing Information
CARDIOGEN-82® (rubidium Rb 82 generator) to produce rubidium chloride Rb 82 injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1989
WARNING: HIGH LEVEL RADIATION EXPOSURE WITH USE OF INCORRECT ELUENT and FAILURE TO FOLLOW THE ELUATE TESTING PROTOCOL
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
High Level Radiation Exposure with Use of Incorrect Eluent
Using the incorrect eluent can cause high Strontium (Sr) 82 and Sr 85 breakthrough levels.
- Use only additive-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection to elute CardioGen-82.
- If an incorrect solution is used to elute CardioGen-82:
Excess Radiation Exposure with Failure to Follow the Eluate Testing Protocol
Excess radiation exposure occurs when the levels of Sr 82 or Sr 85 in the Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection exceed limits.
Recent Major Changes
Indications and Usage for Cardiogen-82
CardioGen-82, used to produce Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection, is a radioactive diagnostic agent indicated for positron emission tomography (PET) of the myocardium under rest or pharmacologic stress conditions to evaluate regional myocardial perfusion in adult patients with suspected or existing coronary artery disease. (1)
Cardiogen-82 Dosage and Administration
- Dosing when using the Model 510 Infusion System: 1,480 MBq (40 mCi), with a range of 1,110 MBq to 2,220 MBq (30 mCi to 60 mCi) per rest or stress component of a procedure via intravenous infusion at 50 mL/min. (2.2)
- Dosing when using the Model 1700 Infusion System: 10 MBq/kg to 30 MBq/kg actual body weight (0.27 mCi/kg to 0.81 mCi/kg) per rest or stress component of a procedure via intravenous infusion at 50 mL/minute or 20 mL/minute. (2.2)
- Do not exceed a maximum dose of 2,220 MBq (60 mCi) or a maximum volume of 100 mL per rest or stress component of a procedure. (2.2)
- The minimum interval between the rest and stress doses is 10 minutes to allow sufficient Rb 82 decay. (2.2)
- Start image acquisition 60 seconds to 90 seconds after completion of the infusion; if a longer circulation time is anticipated, wait for 120 seconds. Image acquisition is 5 minutes long. (2.3)
- For radiation safety, infusion systems, elution instruction, eluate testing, dose delivery, and expiration limits of CardioGen-82, and radiation dosimetry see full prescribing information. (2.1, 2.5, 2.6,2.7, 2.8, 2.9, 2.10)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Rubidium Rb 82 generator used to produce Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection: 3,330 MBq to 5,550 MBq (90 mCi to 150 mCi) of strontium-82 (Sr 82) at calibration time, adsorbed on a hydrous stannic oxide column. (3)
Contraindications
None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
Risk Associated with Pharmacological Stress: Pharmacologic induction of cardiovascular stress may cause serious adverse reactions such as myocardial infarction, arrhythmia, hypotension, broncho-constriction, and cerebrovascular events. Perform testing only in setting where cardiac resuscitation equipment and trained staff are readily available. (5.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Bracco Diagnostics Inc. at 1-800-257-8151 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
Lactation: Do not resume breastfeeding until at least one hour after administration of Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 12/2024
Full Prescribing Information
WARNING: HIGH LEVEL RADIATION EXPOSURE WITH USE OF INCORRECT ELUENT and FAILURE TO FOLLOW THE ELUATE TESTING PROTOCOL
High Level Radiation Exposure with Use of Incorrect Eluent
Patients are exposed to high radiation levels when the CardioGen-82 generator is eluted with the incorrect eluent due to high strontium (Sr) 82 and Sr 85 breakthrough levels.
- Use only additive-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection to elute the generator.
- If an incorrect solution is used to elute the CardioGen-82 generator:
Excess Radiation Exposure with Failure to Follow the Eluate Testing Protocol
Excess radiation exposure occurs when the levels of Sr 82 or Sr 85 in the Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection exceed specified limits.
- Record each generator eluate volume, including waste and test volumes, and keep a record of the cumulative eluate volume.
- Strictly adhere to the generator eluate testing protocol, to minimize the risk of excess radiation exposure, including daily testing and additional testing at Alert Limits.
- Stop using the generator if it reaches any of its Expiration Limits:
1. Indications and Usage for Cardiogen-82
CardioGen-82, used to produce Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection, is indicated for positron emission tomography (PET) of the myocardium under rest or pharmacologic stress conditions to evaluate regional myocardial perfusion in adult patients with suspected or existing coronary artery disease.
2. Cardiogen-82 Dosage and Administration
2.1 Radiation Safety - Drug Handling
CardioGen-82, when eluted with additive-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, produces Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection. Handle CardioGen-82, Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection, and Infusion Systems with appropriate safety measures to minimize radiation exposure. Wear waterproof gloves and effective shielding throughout the entire preparation and handling [See Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Limit the use of radiopharmaceuticals to healthcare providers who are qualified by specific training and experience in the safe use and handling of radionuclides and whose experience and training have been approved by the appropriate government agency authorized to license the use of radionuclides.
2.2 Dosing and Administration of Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection
Important Dosing and Administration Instructions
- Observe aseptic techniques in all drug handling and administration.
- Use CardioGen-82 with the CardioGen-82 Infusion System to elute and administer Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection.
- There are two infusion systems that are different in dosing, elution, and eluate testing. Ensure use of the correct infusion system when following the instructions for dosing, elution, and eluate testing.
- Use the lowest dose necessary, consistent with the goal of as low as reasonably achievable (ALARA), to obtain adequate cardiac visualization based on patient body weight and the imaging equipment and acquisition methodology used to perform the procedure. For example, 3D image acquisition may require doses at the lower end of the recommended range, compared to 2D imaging.
- Administer two single doses to complete rest and stress myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- The minimum interval between the rest and stress doses is 10 minutes to allow sufficient Rb 82 decay.
- Instruct patients to void as soon as a study is completed and as often as possible thereafter for at least one hour [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Dosing When Using the CardioGen-82 Model 510 Infusion System
The recommended dose of Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection per rest or stress component of a PET MPI procedure in adults is 1,480 MBq (40 mCi), with a range of 1,110 MBq to 2,220 MBq (30 mCi to 60 mCi), administered by intravenous infusion at 50 mL/minute through a catheter inserted into a large peripheral vein.
Do not exceed a maximum dose of 2,220 MBq (60 mCi) or a maximum volume of 100 mL per rest or stress component of a procedure.
Dosing When Using the CardioGen-82 Model 1700 Infusion System
The recommended dose of Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection per rest or stress component of a PET MPI procedure in adults is 10 MBq/kg to 30 MBq/kg actual body weight (0.27 mCi/kg to 0.81 mCi/kg) administered by intravenous infusion at 50 mL/minute or 20 mL/minute through a catheter inserted into a large peripheral vein.
Do not exceed a maximum dose of 2,220 MBq (60 mCi) or a maximum volume of 100 mL per rest or stress component of a procedure.
2.3 Image Acquisition Instructions
- Administer a single dose of Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection.
- Start imaging 60 seconds to 90 seconds after completion of the first dose infusion and acquire images for 5 minutes.
- Begin the study at least 10 minutes after completion of the resting dose infusion, to allow for sufficient Rb 82 decay.
- Administer a pharmacologic stress agent in accordance with its prescribing information.
- After the administration of the pharmacologic stress agent, administer the second dose of Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection at the time interval according to the prescribing information of the pharmacologic stress agent.
- Start imaging 60 seconds to 90 seconds after completion of the second dose infusion and acquire images for 5 minutes.
- If a longer circulation time is anticipated (e.g., in a patient with severe left ventricular dysfunction), start imaging 120 seconds after the dose.
- Acquisition may be started immediately post-injection if dynamic imaging is needed.
2.4 Infusion System
- Use CardioGen-82 only with the CardioGen-82 Infusion System Model 510 or the CardioGen-82 Infusion System Model 1700, which are specifically designed for use with the generator and capable of accurate measurement and delivery of doses of Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection.
- Follow instructions in the CardioGen-82 Infusion System Model 510 or Model 1700 Operator’s Manual for the set up and administration of Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection.
- The CardioGen-82 Infusion System Model 510 provides ± 10% accuracy for measuring Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection doses of 1,110 MBq to 2,220 MBq (30 mCi to 60 mCi).
- The CardioGen-82 Infusion System Model 1700 provides ± 10% accuracy for measuring Rubidium Rb 82 Chloride Injection doses of 1,110 MBq to 2,220 MBq (30 mCi to 60 mCi), and ± 15% accuracy for doses of 370 MBq to 1,110 MBq (10 mCi to 30 mCi).
2.5 Directions for Eluting Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection
- Use only additive-free 0.9 % Sodium Chloride Injection to elute the generator [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Prepare the 0.9 % Sodium Chloride Injection for use with the Saline Tag
- Prepare the intravenous port in accordance with the approved prescribing information of the 0.9 % Sodium Chloride Injection.
- The intravenous administration port of the 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection container must be penetrated only one time.
- Strap the saline tag provided with the CardioGen-82 Infusion System on the additive-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection container and install on the CardioGen-82 Infusion System.
- Once the container port closure is penetrated, it should remain installed on the CardioGen-82 Infusion System for its entire period of use. A maximum of 12 hours from the initial port closure penetration is permitted, after which the bag must be replaced for the next patient.
- Allow at least 10 minutes between elutions for regeneration of Rb 82.
- If the CardioGen-82 Infusion System Model 510 is used:
- Discard the first 50 mL eluate each day the generator is eluted and employ proper safety precautions since the eluate contains radioactivity.
- Maintain an on-going record of all eluate volumes (washing, testing, dosing volumes), including a summary of the cumulative volume of eluate from the generator.
- Perform eluate testing according to the Eluate Testing Protocol for Infusion System Model 510 [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
- If the CardioGen-82 Infusion System Model 1700 is used:
- The system software automatically discards the first 50 mL of eluate each day the generator is eluted and records and saves all eluate volumes (all flushing, quality control (QC) testing, and patient infusions), representing the cumulative volume of eluate each day the generator is eluted.
- Perform eluate testing according to the Eluate Testing Protocol for Infusions System Model 1700 [see Dosage and Administration (2.7)].
- Stop using the generator when the expiration limits are reached [see Dosage and Administration (2.8)].
- The maximum available activity of Rb 82 (dose delivery limit) will decrease as the generator ages. See Table 3 for the estimated maximum available Rb 82 activity as a function of generator age [see Dosage and Administration (2.9)].
2.6 Eluate Testing Protocol for Infusion System Model 510
Use only additive-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection for all elutions[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Observe aseptic technique throughout.
Follow all instructions in the CardioGen-82 Infusion System Model 510 Operator’s Manual for performing all eluate testing as described.
Before administering Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection to the first patient each day, perform the following testing:
Strontium Alert Limits and Mandatory Eluate Testing:
- Use an ionization chamber-type dose calibrator for eluate testing.
- Daily, before administering Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection to any patient, perform an eluate testing to determine Rb 82, Sr 82, and Sr 85 levels
- Perform additional daily eluate tests after detecting any of the following Alert Limits:
- 14 L total elution volume has passed through the generator column, or
- Sr 82 level reaches 0.002 microCi per mCi Rb 82, or
- Sr 85 level reaches 0.02 microCi per mCi Rb 82.
- Perform the additional daily eluate tests at time points determined by the day’s elution volume; tests are performed every 750 mL.
- For example, if an Alert Limit were reached and the clinical site eluted less than 750 mL from the generator during the day, then no additional eluate tests would have been performed that day.
- If the same clinical site the next day eluted 1,500 mL from the generator, then the site would have performed three tests that day: 1) the required daily test that precedes any patient dosing, 2) a test at the 750 mL elution point, and 3) a test at the 1,500 mL elution points.
- If a generator’s Alert Limit is reached, the clinical site performs the additional daily tests (at intervals of 750 mL) each subsequent day the generator is used. The additional tests are necessary to promptly detect excessive Sr 82 and/or Sr 85 in eluates.
Rubidium Eluate Level Testing:
- Set a dose calibrator for Rb 82 as recommended by the manufacturer or use the Co-60 setting and divide the reading obtained by 0.548. Obtain the reading from the instrument in millicuries.
- Elute the generator with 50 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection and discard the eluate (first elution).
- Allow at least 10 minutes for the regeneration of Rb 82, then elute the generator with 50 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection at a rate of 50 mL/min and collect the eluate in a stoppered glass vial (plastic containers are not suitable). Note the exact time of end of elution (E.O.E.).
- Using the dose calibrator, determine the activity of Rb 82 and note the time of the reading. Correct the reading for decay to the E.O.E. using the appropriate decay factor for Rb 82 (see Table 1). Note: If the reading is taken 2 ½ minutes after end of elution, multiply the dose calibrator reading by 4 to correct for decay.
- Using the sample obtained for the Rb 82 activity determination, allow the sample to stand for at least one hour to allow for the complete decay of Rb 82.
- Measure the activity of the sample in a dose calibrator at the setting recommended by the manufacturer for Rb 82 and/or Sr 82. As an alternative, use the Co-60 setting and the reading obtained divided by 0.548. Set the instrument to read in microcuries and record in the display.
- Calculate the ratio (R) of Sr 85/Sr 82 on the day (post-calibration) of the measurement using the ratio of Sr 85/Sr 82 on the day of calibration provided on the generator label and the Sr 85/Sr 82 Ratio Factor from Table 2. Determine R using the following equation:
- Use a correction factor (F) of 0.478 to compensate for the contribution of Sr 85 to the reading.
- Calculate the amount of Sr 82 in the sample using the following equation:
Example: dose calibrator reading (microCi) = 0.8; Sr85/Sr82 ratio (R) = 1.48; correction factor (F) = 0.478.
- Determine if Sr 82 in the eluate exceeds an Alert or Expiration Limit by dividing the microCi of Sr 82 by the mCi of Rb 82 at End of Elution (see below for further instructions based on the Sr 82 level)
Example: 0.47 microCi or Sr 82; 50 mCi of Rb 82 E.O.E.
- Determine if Sr 85 in the eluate exceeds an Alert or Expiration Limit by multiplying the result obtained in step 10 by (R) as calculated in step 7 (above).
Example: 0.0094 x 1.48 = 0.014 microCi Sr 85/mCi Rb 82 (test result is below Alert and Expiration Limits)
Use Table 1 to calculate the decay factor for Rb 82; step 4 (above).
Use Table 2 to calculate the ratio (R) of Sr 85/Sr 82; step 7 (above).
2.7 Eluate Testing Protocol for Infusion System Model 1700
Use only additive-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection for all elutions[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Observe aseptic technique throughout.
Follow all instructions in the CardioGen-82 Infusion System Model 1700 Operator’s Manual for performing all eluate testing as described.
Perform Mandatory Eluate Testing to determine Rb 82, Sr 82, and Sr 85 levels:
- Daily – Before administering Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection to the first patient each day.
- Repeat as indicated after an Alert Limit has been detected.
- 14 L total elution volume has passed through the generator column, or
- Sr 82 level reaches 0.002 microCi per mCi Rb 82, or
- Sr 85 level reaches 0.02 microCi per mCi Rb 82.
- The CardioGen-82 Infusion System Model 1700 will automatically indicate when alert limits have been reached, and will require that additional tests be performed, to facilitate the prompt detection of excessive levels of Sr 82 and/or Sr 85 should they occur.
- These additional daily eluate tests will be performed at intervals determined by the day’s elution volume and will be enforced by the System software. Specifically, the infusion system will require the user to perform additional eluate testing after each 750 mL of elution volume when any Alert Limit parameter has been reached.
Infusion System Calibration: Before administering Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection to the first patient:
After installation of a new generator and / or installation of a new CardioGen-82 Accessory Package, Item # 001710, perform the Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection Dose Calibration (performed using an external dose calibrator).
- Set a dose calibrator for Rb 82 as recommended by the manufacturer. Obtain the reading from the instrument in millicuries.
- Following the prompts in the Graphical User Interface (GUI) for the CardioGen-82 Infusion System Model 1700, elute the generator with additive-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection at a rate of 50 mL/min and collect the eluate in the stoppered vial specifically provided for use with the CardioGen-82 Infusion System Model 1700 (alternative vials, glass or plastic are not suitable). Note the exact time of end of elution (EOE).
- Using the external dose calibrator, assay the eluate at exactly 2:30, 3:45, or 5:00 minutes after EOE.
- Following the prompts in the GUI for the CardioGen-82 Infusion System Model 1700, enter the Rb 82 reading from the dose calibrator and the time since EOE.
- The infusion system software will automatically calculate the Calibration Ratio.
- If the ratio is within +/- 2% (0.98 to 1.02), the infusion system will allow acceptance of the calibration factor that was used for the elution.
- If the ratio is not within +/- 2% (0.98 to 1.02), the system requires another calibration elution (steps 1 through 4).
- Repeat steps 1 through 4 for a flow rate of 20 mL/min.
Perform additional system calibration every 14 days.
Daily Quality Control: Eluate (Strontium Level) Testing and Dose Constancy
Each day, before administering Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection, perform the following test, including Mandatory Eluate Testing:
Daily Quality Control (performed on-board the CardioGen-82 Infusion System Model 1700, using the gamma (Sr) detector):
- Place the stoppered vial, which is specifically provided for use with the CardioGen-82 Infusion System, Model 1700 (alternative vials, glass or plastic are not suitable) in the Sr detector well on the CardioGen-82 Infusion System Model 1700 and, following the prompts in the GUI for the infusion system, initiate the Daily Quality Control workflow.
- The infusion system will automatically perform the Sr Detector Background Reading.
- The infusion system will automatically perform the Generator Column Wash.
- Strontium Level Test and Dose Constancy:
- The infusion system will elute the generator with 50 mL of additive-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection at a rate of 50 mL/min into the stoppered vial (which is specifically provided for use with the CardioGen-82 Infusion System Model 1700).
- The Sr detector measures the Rb 82 and strontium in the 50 mL elution.
- The infusion system software will automatically calculate the Sr 82 and Sr 85 levels on the day (post calibration) of the measurement using the ratio of Sr 85/Sr 82 on the day of calibration provided on the generator label, and using the full exponential decay calculation for each, accounting for the generator’s age.
- Using the Rb 82 and strontium measurements, the infusion system software will automatically calculate microCi Sr 82/mCi Rb 82 and microCi Sr 85/mCi Rb 82. The GUI will automatically indicate if the results exceed Alert or Expiration Limits.
- The infusion system software will automatically calculate Dose Constancy.
- Constancy Check of the Sr detector: The infusion system GUI will prompt the user to perform the constancy check of the Sr detector.
- Place the external constancy source in the detector well of the infusion system.
- The infusion system software will automatically calculate the constancy of the Sr detector versus the external constancy source when instructed.
2.8 Expiration Limits of CardioGen-82
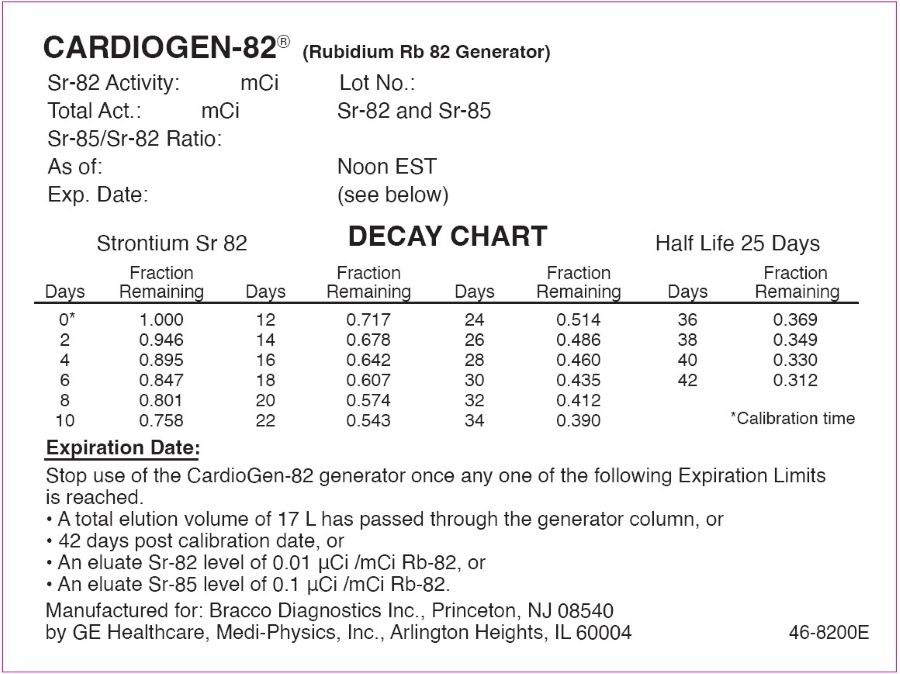
If using the Infusion System Model 510, stop use of CardioGen-82 once any one of the following Expiration Limits is reached:
- A total elution volume of 17 L has passed through the generator column
- 42 days post calibration date
- An eluate Sr 82 level of 0.01 microCi/mCi Rb 82
- An eluate Sr 85 level of 0.1 microCi/mCi Rb 82
If using the Infusion System Model 1700, the software will automatically indicate, and will stop use of CardioGen-82, once any one of the above Expiration Limits is reached.
2.9 Dose Delivery Limit of CardioGen-82
The maximum available Rb 82 activity per elution (dose delivery limit) will decrease as the generator ages. Table 3 provides an estimate of the maximum available activity of Rb 82 as a function of generator age.
2.10 Radiation Dosimetry
The estimated absorbed radiation doses for Rb 82, Sr 82, and Sr 85 from an intravenous injection of Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection are shown in Table 4.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Rubidium Rb 82 generator used to produce Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection: strontium-82 (Sr 82), with an activity of 3,330 MBq to 5,550 MBq (90 mCi to 150 mCi) at calibration time, adsorbed on a hydrous stannic oxide column.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 High Level Radiation Exposure with Use of Incorrect Eluent
Additives present in solutions (particularly calcium ions) used by mistake to elute CardioGen-82 expose patients to high levels of radiation by causing the release of large amounts of Sr 82 and Sr 85 into the eluate regardless of the generator’s age or prior use. When solutions containing calcium ions are used, high levels of radioactivity are present in any subsequent eluate even with the use of additive-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection.
Use only additive-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection to elute CardioGen-82. If an incorrect eluent is used, immediately stop the patient infusion, evaluate the patient’s radiation absorbed dose, and monitor for the effects of radiation to critical organs such as bone marrow. Permanently discontinue use of the affected CardioGen-82 generator [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
5.2 Excess Radiation Exposure with Failure to Follow the Eluate Testing Protocol
Excess radiation exposure occurs when the Sr 82 and Sr 85 levels in the Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection exceed the specified generator eluate limits.
Strictly adhere to the eluate testing protocol to minimize radiation exposure to the patient. Stop using the CardioGen-82 generator when the expiration limits are reached [see Dosage and Administration (2.6, 2.7, 2.8)].
5.3 Risks Associated with Pharmacologic Stress
Pharmacologic induction of cardiovascular stress may be associated with serious adverse reactions such as myocardial infarction, arrhythmia, hypotension, bronchoconstriction, and cerebrovascular events. Perform pharmacologic stress testing in accordance with the pharmacologic stress agent’s prescribing information and only in the setting where cardiac resuscitation equipment and trained staff are readily available.
5.4 Cumulative Radiation Exposure: Long-Term Risk of Cancer
Rubidium chloride Rb 82 contributes to a patient’s overall long-term cumulative radiation exposure. Long-term cumulative radiation exposure is associated with an increased risk of cancer. Use the lowest dose of Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection necessary for imaging and ensure safe handling to protect the patient and health care providers. Encourage patients to void as soon as a study is completed and as often as possible thereafter for a least one hour [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.2)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- High Level Radiation Exposure with Use of Incorrect Eluent [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Excess Radiation Exposure with Failure to Follow Eluate Testing Protocol [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
The following serious adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of CardioGen-82. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
High level radiation exposure to the bone marrow from using an incorrect eluent.
Excess radiation exposure due to insufficient eluate testing.
Related/similar drugs
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
There are no data available on the use of rubidium chloride Rb 82 in pregnant women. Animal reproductive studies have not been conducted with rubidium chloride Rb 82. However, all radiopharmaceuticals, including Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection generated by CardioGen-82, have the potential to cause fetal harm depending on the fetal stage of development and the magnitude of the radiation dose. If considering Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection administration to a pregnant woman, inform the patient about the potential for adverse pregnancy outcomes based on the radiation dose from rubidium-82 (Rb 82) and the gestational timing of exposure.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
There is no information regarding the presence of rubidium chloride Rb 82 in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant or the effects on milk production. Due to the short half-life of Rb 82 (75 seconds), exposure of a breastfed infant through breast milk can be minimized by temporary discontinuation of breastfeeding (see Clinical Considerations). The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection, any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from Rb 82 or from the underlying maternal condition.
Exposure to Rb 82 through breast milk can be minimized if breastfeeding is discontinued when Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection is administered. Do not resume breastfeeding until at least one hour after administration of Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of CardioGen-82, used to produce Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection, in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In elderly patients with a clinically important decrease in cardiac function, lengthen the delay between infusion and image acquisition [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Observe for the possibility of fluid overload.
11. Cardiogen-82 Description
11.1 Generator Characteristics
CardioGen-82 (rubidium Rb 82 generator) contains accelerator-produced Sr 82 adsorbed on stannic oxide in a lead-shielded column and provides a means to produce sterile nonpyrogenic Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection, a radioactive diagnostic agent, for intravenous use. The chemical form of Rb 82 is 82RbCl.
The amount (mCi) of Rb 82 obtained in each elution will depend on the potency of the generator. When eluted at a rate of 50 mL/minute, each generator eluate at the end of elution should not contain more than 0.02 microCi of Sr 82 and not more than 0.2 microCi of Sr 85 per mCi of Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection, and not more than 1 mcg of tin per mL of eluate.
11.2 Nuclear Physical Characteristics
Rb 82 decays by positron emission and associated gamma emission with a physical half-life of 75 seconds. Table 5 shows the annihilation photons released following positron emission which are useful for detection and imaging studies.
The decay modes of Rb 82 are: 95.5% by positron emission, resulting in the production of annihilation radiation, i.e., two 511 keV gamma rays; and 4.5% by electron capture, resulting in the emission of “prompt” gamma rays of predominantly 776.5 keV. Both decay modes lead directly to the formation of stable krypton 82 (Kr 82).
| Table 5. Principal Radiation Emission Data for Rb 82 | ||
The specific gamma ray constant for Rb 82 is 6.1 R/hour-mCi at 1 cm. The first half-value layer is 0.7 cm of lead (Pb). Table 6 shows a range of values for the relative attenuation of the radiation emitted by this radionuclide that results from interposition of various thicknesses of lead. For example, the use of a 7.0 cm thickness of Pb will attenuate the radiation emitted by a factor of about 1,000.
| Table 6. Radiation Attenuation by Lead Shielding | |
Sr 82 (half-life of 25 days (600 hrs.) decays to Rb 82. To correct for physical decay of Sr 82, Table 7 shows the fractions that remain at selected intervals after the time of calibration.
To correct for physical decay of Rb 82, Table 1 shows the fraction of Rb 82 remaining in all 15 second intervals up to 300 seconds after time of calibration [see Dosage and Administration (2.6, 2.7)].
12. Cardiogen-82 - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Rb 82 is analogous to potassium ion (K+) in its biochemical behavior and is extracted by the myocardium in proportion to the blood flow. Rb+ participates in the sodium-potassium (Na+/K+) ion exchange pumps that are present in cell membranes. The intracellular uptake of Rb 82 requires maintenance of ionic gradient across cell membranes. Rb 82 radioactivity is increased in viable myocardium reflecting intracellular retention, while the tracer is cleared from necrotic or infarcted tissue.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In human studies, myocardial activity was noted within the first minute after peripheral intravenous injection of rubidium chloride Rb 82. When areas of infarction or ischemia are present in the myocardium, they are visualized within 2 minutes to 7 minutes after injection as photon-deficient, or “cold”, areas on the myocardial scan. In patients with reduced cardiac function, transit of the injected dose from the peripheral infusion site to the myocardium may be delayed [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Blood flow brings Rb 82 to all areas of the body during the first pass of circulation. Accordingly, visible uptake is also observed in other highly vascularized organs, such as the kidneys, liver, spleen, and lungs.
14. Clinical Studies
In a descriptive, prospective, blinded image interpretation study of adult patients with known or suspected coronary artery disease, myocardial perfusion deficits in stress and rest PET images obtained with ammonia N 13 (n = 111) or rubidium chloride Rb 82 (n = 82) were compared to changes in stenosis flow reserve (SFR) as determined by coronary angiography. PET perfusion defects at rest and stress for seven cardiac regions (anterior, apical, anteroseptal, posterolateral, anterolateral, posterolateral, and inferior walls) were graded on a scale of 0 (normal) to 5 (severe). Values for stenosis flow reserve, defined as flow at maximum coronary vasodilatation relative to rest flow, ranged from 0 (total occlusion) to 5 (normal). With increasing impairment of flow reserve, the subjective PET defect severity increased. A PET defect score of 2 or higher was positively correlated with flow reserve impairment (SFR<3).
A systematic review of published literature was conducted using pre-defined inclusion/exclusion criteria which resulted in identification of 10 studies evaluating the use of Rb 82 PET myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) for the identification of coronary artery disease as defined by catheter-based angiography. In these studies, the patient was the unit of analysis and 50% stenosis was the threshold for clinically significant coronary artery disease (CAD). Of these 10 studies, 9 studies were included in a meta-analysis for sensitivity (excluding one study with 100% sensitivity) and 7 studies were included in a meta-analysis of specificity (excluding 3 studies with 100% specificity). A random effects model yielded overall estimates of sensitivity and specificity of 92% (95% CI: 89% to 95%) and 81% (95% CI: 76% to 86%), respectively. The use of meta-analysis in establishing performance characteristics is limited, particularly by the possibility of publication bias (positive results being more likely to be published than negative results) which is difficult to detect especially when based on a limited number of small studies.
16. How is Cardiogen-82 supplied
CardioGen-82 (rubidium Rb 82 generator), used to produce Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection, is supplied in a lead shield surrounded by a labeled plastic container with an activity at calibration time of 3,330 MBq to 5,550 MBq (90 mCi to 150 mCi) of Sr 82 adsorbed on a hydrous stannic oxide column (NDC 0270-0091-01).
The container label provides complete assay data for each generator.
Store the generator at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
- Receipt, transfer, possession, storage, disposal or use of this product is subject to the radioactive material regulations and licensing requirements of the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC), Agreement States or Licensing States as appropriate. Do not dispose of the generator in regular refuse systems. This generator is approved for use by persons licensed by the Illinois Emergency Management Agency pursuant to Section 330.260(a), (b) or (c) and 32 Ill. Adm. Code 335.4010 or under equivalent licenses of NRC or an Agreement State.
For questions about the disposal of the CardioGen-82 generator, contact Bracco Diagnostics Inc. at 1-800-447-6883, option 3.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Instruct patients to void after completion of each image acquisition session and as often as possible for one hour after completion of the PET scan [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Advise a pregnant woman of the potential risk to a fetus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Advise lactating women that exposure to Rb 82 through breast milk can be minimized if breastfeeding is discontinued when Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection is administered. Advise lactating women not to resume breastfeeding for at least one hour after administration of Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Manufactured for
Bracco Diagnostics Inc.
Princeton, NJ 08540
Manufactured By
GE Healthcare, Medi-Physics, Inc.
Arlington Heights, IL 60004
CardioGen-82® Rubidium 82 Generators, Infusion Systems, and Accessories contain proprietary technology covered by one or more patents listed at www.braccoimaging.com/us-en/patents.
| CARDIOGEN-82
rubidium chloride rb-82 injection, solution |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Bracco Diagnostics Inc (849234661) |
| Registrant - Bracco Diagnostics Inc (849234661) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| GE HEALTHCARE INC. | 095263729 | MANUFACTURE(0270-0091) , LABEL(0270-0091) , PACK(0270-0091) , ANALYSIS(0270-0091) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| BWXT ITG Canada, Inc. | 203794193 | API MANUFACTURE(0270-0091) | |
More about Cardiogen-82 (rubidium chloride rb-82)
- Compare alternatives
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: diagnostic radiopharmaceuticals