Dsuvia FDA Approval History
FDA Approved: Yes (First approved November 2, 2018)
Brand name: Dsuvia
Generic name: sufentanil
Dosage form: Sublingual Tablets
Company: AcelRx Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Treatment for: Pain
Last updated by Judith Stewart, BPharm on Jan 7, 2021.
Dsuvia (sufentanil) is a synthetic opioid analgesic formulation for the management of acute pain that is severe enough to require an opioid analgesic, and for which alternative treatments are inadequate.
Because of the potential for life-threatening respiratory depression due to accidental exposure, Dsuvia is available only through a restricted program called the Dsuvia REMS Program. Dsuvia must only be administered by a healthcare provider in a certified medically supervised healthcare setting.
Limitations of Use:
- Not for home use or for use in children. Discontinue treatment with Dsuvia before patients leave the certified medically supervised healthcare setting.
- Not for use for more than 72 hours. The use of Dsuvia beyond 72 hours has not been studied.
- Only to be administered by a healthcare provider.
- Because of the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse with opioids, even at recommended doses, reserve Dsuvia for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options [e.g., non-opioid analgesics or opioid combination products]:
- Have not been tolerated, or are not expected to be tolerated,
- Have not provided adequate analgesia, or are not expected to provide adequate analgesia.
Directions for Use
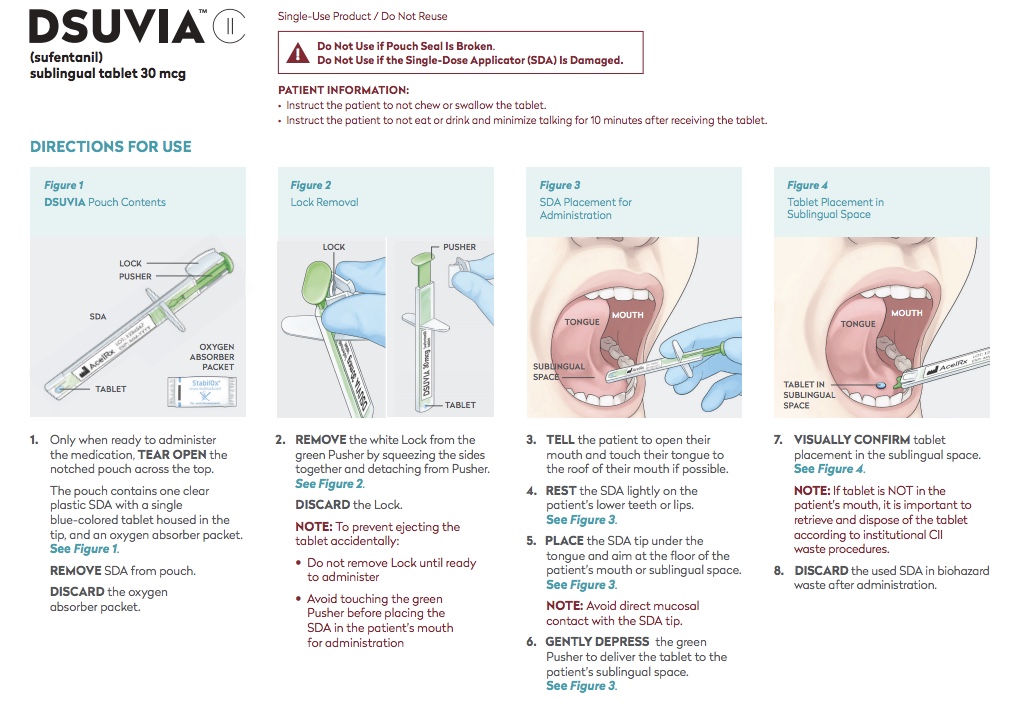
Contraindications
Use of Dsuvia is contraindicated in patients with:
- Significant respiratory depression
- Acute or severe bronchial asthma in an unmonitored setting or in the absence of resuscitative equipment
- Known or suspected gastrointestinal obstruction, including paralytic ileus
- Known hypersensitivity to sufentanil or components of Dsuvia.
Warnings and Precautions
- Accidental ingestion or exposure to even one dose of Dsuvia, especially in children, can result in respiratory depression and death due to an overdose of sufentanil.
- Dsuvia is for use in adult patients only in a certified medically supervised healthcare setting. Use of Dsuvia outside of this setting can increase the risk of accidental exposure in others for whom it is not prescribed, causing fatal respiratory depression. Discontinue use of Dsuvia prior to discharge or transfer from the certified medically supervised healthcare setting. Dsuvia is not for home or pediatric use.
- Dsuvia contains sufentanil, a Schedule II controlled substance. As an opioid, Dsuvia exposes users to the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse.
- Profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death may result from the concomitant use of Dsuvia with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants (e.g., non-benzodiazepine sedatives/hypnotics, anxiolytics, tranquilizers, muscle relaxants, general anesthetics, antipsychotics, other opioids, alcohol). Because of these risks, reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate.
- Life-threatening respiratory depression in patients with chronic pulmonary disease or in elderly, cachectic and debilitated patients: monitor patients closely, particularly when initiating Dsuvia therapy and when Dsuvia is used with other drugs that depress respiration. Management of respiratory depression may include close observation, supportive measures, and use of opioid antagonists, depending on the patient’s clinical status.
- A potentially life-threatening condition could result from concomitant serotonergic drug administration. Discontinue Dsuvia if serotonin syndrome is suspected. Cases of adrenal insufficiency have been reported with opioid use (usually > 1 month). Presentation and symptoms are non-specific and include nausea, vomiting, anorexia, fatigue, weakness, dizziness and low blood pressure. Confirm diagnosis with testing as soon as possible and, if confirmed, treat with physiologic replacement of corticosteroids and wean patient from opioid.
- As with all opioids, sufentanil may produce bradycardia or hypotension in some patients. Therefore Dsuvia should be used with caution in patients with bradyarrhythmias or hypovolemia.
- Dsuvia should not be used in patients who may be particularly susceptible to the intracranial effects of CO2 retention, such as those with evidence of increased intracranial pressure, impaired consciousness or coma.
- Prolonged use of Dsuvia during pregnancy can result in withdrawal in the neonate, which can be life-threatening. Observe newborns for signs of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and manage accordingly. Advise pregnant women using opioids for a prolonged period of this risk and ensure that appropriate treatment will be available.
- Insufficient data are available on the use of Dsuvia in patients with severe liver or kidney impairment. Dsuvia should be used with caution in such patients due to the importance of these organs in the metabolism and excretion of sufentanil.
Adverse Reactions
- Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression
- Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse
- Adrenal Insufficiency
- Severe hypotension
- Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
- Seizures
- Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome
The most commonly reported adverse reactions (≥ 2% and higher than placebo) were nausea, headache, vomiting, dizziness, and hypotension.
Development timeline for Dsuvia
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.

