Transverse Process Fracture
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
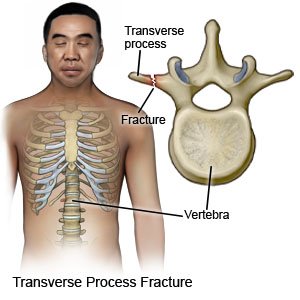
What is a transverse process fracture?
This fracture is a break or crack in one of the wing-like sides at the back of a vertebra. Muscles and ligaments are attached to this part of the vertebra. The fracture can be caused by trauma or by a severe muscle contraction. A high amount of force is needed to cause a transverse process fracture. Nerves are usually not damaged, but the force can cause internal injuries and bleeding. A transverse process fracture most commonly happens in the middle or lower back.
 |
What increases my risk for a transverse process fracture?
- Older age
- Osteoporosis or low muscle mass
- Not wearing a seatbelt in a car accident
- Playing a contact sport
- Playing a sport that causes you to twist or do 1 motion many times, such as rowing
What are the signs and symptoms of a transverse process fracture?
Signs and symptoms depend on where the fracture happened, and how severe it is:
- Pain that happens suddenly and is worse when you move
- Swollen, tender skin at the fracture site
- Trouble moving your back at the fracture site
How is a transverse process fracture diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will examine you and ask about your symptoms. Tell him or her how the injury happened. You may also need any of the following:
- X-rays may show a fracture and any injury to nearby muscles or tissues.
- MRI or CT scan pictures may be taken if a fracture seems likely but does not show up on x-rays. Contrast liquid may be used to help a fracture or injury show up better in the pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious damage. Tell the provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
How is a transverse process fracture treated?
- Medicine may be used to relieve pain or to relax your muscles.
- Surgery may be needed for the most serious fracture. Surgery is used to put pieces of bone back in place. The pieces may be held in place with screws or other medical hardware. Surgery may also be needed if you have internal bleeding or organ damage.
What can I do to manage my symptoms?
The fracture may take weeks or months to heal. The following can help manage your symptoms:
- Rest as directed. Rest will help the fracture heal. Avoid activities that can cause pain or more injury. Begin normal, slow movements as directed by your healthcare provider. Your provider will tell you when it is okay to drive and to return to your normal activities. He or she can also help you make a plan to return to sports, if needed.
- Apply ice to help decrease swelling and pain. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover it with a towel before you apply it to your skin. Apply ice for 15 to 20 minutes every hour or as directed.
- Wear a back brace, if directed. A back brace may help you feel more comfortable while the fracture heals. Your healthcare provider will tell you the kind of brace to use. He or she will tell you how long to wear it each day, and for how many days.
- Go to physical therapy, if directed. A physical therapist teaches you exercises to help improve movement and strength, and to decrease pain.
How can I prevent more injury?
- Strengthen your muscles and bones. Weight-bearing activities such as walking helps strengthen bones. Activities that help strengthen muscles, such as weightlifting, help protect your bones. Your healthcare provider can help you create a safe physical activity plan. He or she can also help you manage any condition that weakens your bones, such as osteoporosis.


- Reach or maintain a healthy weight. Extra weight puts more stress on your back. Your healthcare provider can help you create a safe weight loss plan, if needed.
- Get more calcium and vitamin D, as directed. Calcium and vitamin D work together to make bones stronger. Good sources of calcium are milk, cheese, broccoli, tofu, almonds, and canned salmon or sardines. Vitamin D is in fish oils, some vegetables, and fortified milk, cereal, or bread. Vitamin D is also formed in the skin when it is exposed to the sun.

- Lower your risk for injuries or accidents. Always wear a seatbelt when you are in a car or other vehicle. Keep walkways in your home clear so you will not trip as you walk. Use handrails when you go up or down stairs.
- Play sports safely. Wear proper protective gear. Take breaks when you practice if your sport involves repeating the same motion. Use proper body mechanics for your sport.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) or have someone else call if:
- You feel lightheaded, short of breath, or have chest pain.
- You cough up blood.
- You cannot move your arms or legs.
When should I seek immediate care?
- Your arm or leg feels warm, tender, and painful. It may look swollen and red.
- You have pain in your abdomen.
- You are dizzy, weak, pale, or faint.
- You are confused or have trouble thinking clearly.
- You see blood in your urine, or your urine is dark.
- You have new problems urinating or having bowel movements.
- You have severe pain.
When should I call my doctor?
- You cannot sleep or rest because of pain.
- You have pain or swelling that is getting worse or does not go away.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
