Spermatocelectomy
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
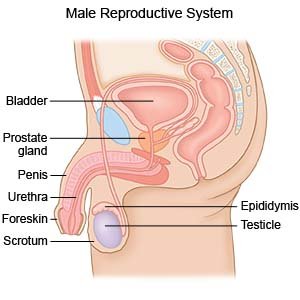
A spermatocelectomy is surgery to remove a spermatocele. A spermatocele is a cyst (sac of fluid) that contains sperm. It forms inside your scrotum on the outside of your testicle. The cyst is most often attached to the epididymis. The epididymis is a tube that stores sperm.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Seek care immediately if:
- Blood soaks through your bandage.
- You have severe, sudden pain in your scrotum or testicle.
Call your surgeon or urologist if:
- You have a fever or chills.
- Your wound is red, swollen, or draining pus.
- You have swelling in your testicle that is getting worse.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Antibiotics prevent or fight an infection caused by bacteria.
- Acetaminophen decreases pain and fever. It is available without a doctor's order. Ask how much to take and how often to take it. Follow directions. Read the labels of all other medicines you are using to see if they also contain acetaminophen, or ask your doctor or pharmacist. Acetaminophen can cause liver damage if not taken correctly.
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Self-care:
- Wear an athletic supporter as directed. This device helps decrease swelling and pain, and holds bandages on your scrotum.
- Apply ice on your scrotum for 15 to 20 minutes every hour or as directed. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover it with a towel. Ice helps prevent tissue damage and decreases swelling and pain.
- Ask about activities that are okay while you heal. Ask your healthcare provider when it is okay to have sex. Limit heavy activity for 2 weeks after your surgery, or for as long as directed. Heavy activity includes lifting heavy objects and strenuous exercise.
Follow up with your surgeon or urologist as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
