Retractile Testicle
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
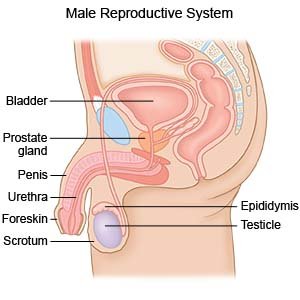
A retractile testicle
is a testicle that moves back and forth between the scrotum and groin. A muscle near the testes causes the testicle to move towards the body and out of the scrotum. The testicle usually returns to the scrotum on its own. One or both of your child's testicles may be affected.
 |
Common signs and symptoms:
- A scrotum that looks empty
- A testicle that moves from the scrotum and returns on its own
- A testicle that can easily be moved back to the scrotum and stay there for a period of time
Call your child's doctor if:
- Your child's testicle does not return to his scrotum on its own.
- Your child's testicle cannot be moved from his groin.
- Your child has pain or swelling in his groin or scrotum.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Treatment
is not usually needed. Most children grow out of this condition by puberty. Your child may need surgery if his testicle stays in his groin.
Manage your child's retractile testicle:
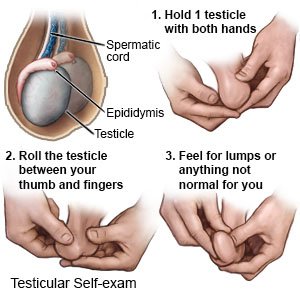
- Check your child's testicles or have your child self-check, as directed. Your child's healthcare provider will tell you how often to check your child's testicles. Feel your child's scrotum for both testicles while he is taking a bath. Encourage your older child to check his testicles. Healthcare providers can help teach your child how to do testicle checks.
Follow up with your child's doctor as directed:
Your child will need regular doctor visits until his testicles permanently stay in his scrotum. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
