Post Concussion Syndrome
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is post-concussion syndrome (PCS)?
PCS is a group of symptoms that affect your body, thinking, and behavior. PCS develops 10 to 14 days after a concussion and can last for weeks to years.
What increases my risk for PCS?
- Older age
- Being female
- A substance use disorder, such as drugs or alcohol
- A past brain injury
- A current mood or anxiety disorder
- Health problems before your concussion
What are the signs and symptoms of PCS?
- Headaches or vision problems
- Dizziness or poor balance
- Forgetfulness or problems concentrating
- Problems with sleep
- Changes in your personality
- Seizures
- Depression or anxiety
How is PCS diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your injury. Tell him or her when it happened, what hit you, and the force of the blow. You, or someone close to you, should tell your provider about any confusion you have or changes in your behavior. You may need any of the following:
- A neurologic exam is used to test your memory and concentration. It will also show healthcare providers your eye, verbal, and muscle responses.
- Blood and urine tests will be done to check for any other cause of your symptoms. Infections and substances, such as alcohol, can affect your memory and behavior.
- CT scan or MRI pictures of your head may show an injury or bleeding. You may be given contrast liquid to help healthcare providers see the pictures better. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
How is PCS treated?
Treatment will focus on your symptoms:
- Acetaminophen decreases pain and fever. It is available without a doctor's order. Ask how much to take and how often to take it. Follow directions. Read the labels of all other medicines you are using to see if they also contain acetaminophen, or ask your doctor or pharmacist. Acetaminophen can cause liver damage if not taken correctly.
- NSAIDs help decrease swelling and pain or fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Antidepressants may be given for depression or sleep problems.
- Migraine medicines may be given for migraine headaches.
How can I prevent PCS?
- Follow your treatment plan after a concussion to help you heal. You will heal more quickly if you follow your healthcare provider's instructions.
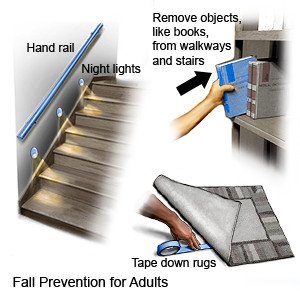
- Make your home safe. Home safety measures can help prevent head injuries that could lead to a concussion. Install handrails for every staircase. Put soft bumpers on furniture edges and corners. Secure furniture, such as dressers and bookcases so they do not fall over.
- Always wear a seatbelt in the car. A seatbelt helps decrease your risk for a head injury if you are in a car accident.
- Wear protective sports equipment that fits properly. Helmets help decrease your risk for a serious brain injury. Talk to your provider about other ways that you can decrease your risk for a concussion if you play sports. Ask for more information about sports concussions.
What can I do to manage my symptoms?
- Rest from physical and mental activities as directed. Mental activities need you to think, concentrate, and pay attention. Rest will help you recover from your concussion. Ask your healthcare provider when you can return to school and other daily activities.
- Go to therapy as directed. A cognitive behavioral therapist teaches you skills to help with any thinking and behavior problems you may have. An occupational therapist teaches you skills to help with daily activities.
- Do not participate in sports or physical activities until your provider says it is okay. These activities could make your symptoms worse or lead to another concussion. Your provider will tell you when it is okay to return to sports or physical activities.
Where can I find more information?
- Brain Injury Association
1608 Spring Hill Road
Vienna , VA 22182
Phone: 1- 703 - 761-0750
Phone: 1- 800 - 444-6443
Web Address: http://www.biausa.org
Have someone call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You have a seizure.
- You have trouble breathing.
- You are not responding, or you cannot be woken.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have a sudden headache that seems different or much worse than your usual headaches.
- You cannot stop vomiting.
- You have sudden changes in your vision, or your pupils are different sizes.
When should I call my doctor?
- You feel depressed.
- You have nausea or are vomiting.
- You have trouble concentrating.
- You have trouble speaking or thinking.
- Your symptoms get worse.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Post Concussion Syndrome
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
