Periodontal Disease
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
Periodontal disease is also called gum disease. It can be mild and cause problems such as bad breath. It can progress and in severe cases, it can destroy bone and lead to tooth loss. Gum disease is usually caused by the buildup of plaque on your teeth and gums. Plaque contains bacteria that are harmful to the gum tissue.
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Contact your dental provider if:
- Your gums bleed regularly when you floss or brush your teeth.
- Your gums are swollen or tender.
- Your gums start to move away from your teeth.
- Your teeth become loose.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Prevent gum disease:
- Brush your teeth 2 times every day. Brush for 2 minutes each time.
- Floss daily. Your dental provider can teach you how to floss properly.
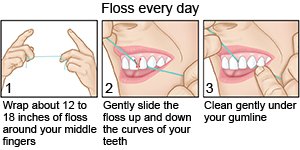
- Use a toothpaste that contains fluoride. You may also need to use a mouth rinse that contains fluoride.
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush. Hard bristles may damage your gums.
- Change your toothbrush every 3 to 4 months. Worn out toothbrushes can damage your gums and do not remove plaque well.
- Eat healthy foods. Avoid sweets between meals to decrease your risk for gum disease. Healthy foods do not form plaque as easily as foods high in sugar. Eat a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean meats, fish, low-fat dairy products, whole-grain breads, and cooked beans.
- Do not smoke, and do not use chewing tobacco. Tobacco increases your risk for gum disease. It is never too late to quit using tobacco. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you need help quitting.
- Visit your dentist every 6 months, or more often as directed, for cleaning and preventive care. Regular visits will help find problems early.
Follow up with your dental provider as directed:
You may need more treatment. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
