Patellar Fracture in Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
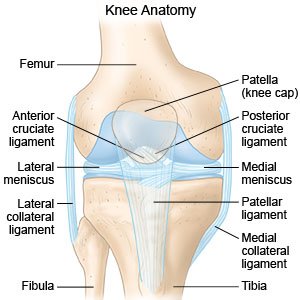
A patellar fracture
is a break in your child's kneecap. Treatment depends on how the kneecap breaks. Broken pieces may move out of line or break through the skin.
 |
Common signs and symptoms of a patellar fracture in children:
- Pain when your child's knee is touched or when he or she moves the leg
- Swelling and bruising around the knee
- Not being able to put weight on the leg
- Not being able to raise the leg when he or she is lying down
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- Your child suddenly feels lightheaded and short of breath.
- Your child has chest pain when he or she takes a deep breath or coughs.
- Your child coughs up blood.
Seek immediate care if:
- Your child's cast or splint breaks or gets damaged.
- Your child says that his or her foot or toes feel numb.
- Your child's foot or toes are swollen, cold, or turn white or blue.
Call your child's doctor or bone specialist if:
- Your child has a fever.
- Your child's knee pain gets worse, even after treatment.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Treatment
may include any of the following:
- A brace, cast, or splint may be needed. These supportive devices stop the kneecap from moving and help it heal. Your child may also need to use crutches to help him or her move around while the kneecap heals.
- Medicines can help prevent or fight pain or a bacterial infection. Your child may also need a Td vaccine. This vaccine is a booster shot to help prevent tetanus. He or she may need the Td vaccine if bone broke through the skin.
- Closed reduction may be used to move the broken pieces back to their correct places without surgery. External fixation may be used to hold your child's kneecap in place, and then removed.
- Surgery may be used to move the broken pieces back into their correct positions. Wires, pins, screws, or bands may be used to hold the pieces in place. Surgery may also be used to remove part or all of your child's kneecap.
- Physical therapy may be recommended. A physical therapist teaches your child exercises to help improve movement and strength, and to decrease pain.
Care for your child:
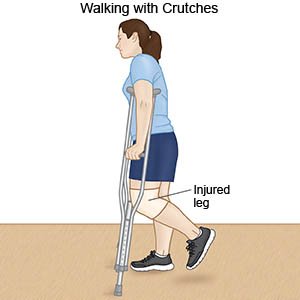
- Have your child rest his or her knee as directed. Crutches help rest and support your child's knee when he or she walks. Your child's healthcare provider will tell you when your child can start to use crutches. Follow instructions about how much weight your child can put on the leg.
- Apply ice to help decrease swelling and pain. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover it with a towel before you place it on your child's knee or supportive device. Apply ice for 15 to 20 minutes every hour for 2 days, or as directed.
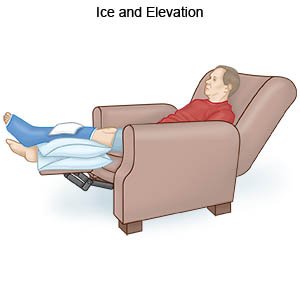
- Elevate your child's knee above the level of his or her heart as often as you can. This will help decrease swelling and pain. Prop your child's leg on pillows or blankets to keep it elevated comfortably. Do not put pillows directly under your child's knee.

Brace, cast, or splint care:
- Check the skin around the device every day. Apply lotion to any red or sore areas.
- Ask your child's healthcare provider when he or she can bathe. Do not get the device wet. Cover it with a plastic bag. Tape the bag above the device to prevent water from getting in. Help your child keep his or her knee out of the water as much as possible.
- Tell your child not to push or lean on any part of a cast or splint.
- Do not let your child put any sharp or pointed objects inside the cast.
Follow up with your child's doctor or bone specialist as directed:
Your child may need to return to have his or her stitches removed. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your child's visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
