Partial Nail Avulsion for Ingrown Nail
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What do I need to know about a partial nail avulsion?
A partial nail avulsion is a procedure to remove an ingrown nail. An ingrown nail is when the edge of your fingernail or toenail grows into the skin next to it.
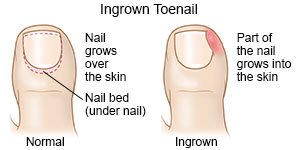 |
How do I prepare for a partial nail avulsion?
Your healthcare provider will talk to you about how to prepare for the procedure. Your provider may tell you not to eat or drink anything after midnight on the day of your surgery. Your provider will tell you what medicines to take or not take on the day of your surgery. You may need someone to drive you home and stay with you.
What will happen during a partial nail avulsion?
- You will be given local anesthesia around the nail to numb the area. Your healthcare provider will cut the nail along the edge that is growing into the skin. Your provider will remove the nail from your finger or toe. Your provider may apply a solution or small electric charge to your nail bed. This keeps the nail from growing into your skin again.
- You may need a matricectomy. This is when part of your nail matrix is destroyed so a small section of your nail stops growing. Your nail matrix is the area that your nail grows from. It is the pale or white color at the base of your nail. Most of the matrix cannot be seen because it is underneath your skin. A chemical, laser, or instrument may be used to destroy the nail matrix.
What will happen after a partial nail avulsion?
Your healthcare provider may put antibiotic ointment and a bandage on your finger or toe. Your provider may want to look at your finger or toe again within 24 hours after your procedure. You may have yellowish drainage for 2 to 6 weeks after your procedure.
What are the risks of a partial nail avulsion?
You may bleed more than expected or develop an infection. Your ingrown nail may happen again. You may have damage to surrounding tissue. Your nail may look disfigured or you may have a scar. You may develop a cyst or it make take longer than expected to heal.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
