Ovarian Torsion
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
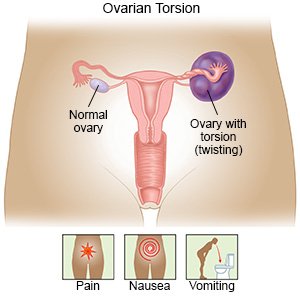
Ovarian torsion is a condition that causes twisting of a ligament that supports the ovary. The ovary may also become twisted with the fallopian tube. Blood flow to the ovary is reduced or blocked. The lack of blood flow can cause ovary necrosis (tissue death). Ovarian torsion needs immediate care to prevent this from happening. Torsion usually happens to only one ovary but can happen to both.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Seek care immediately if:
- You have a fever that is getting higher.
- You have new or worsening symptoms, such as increased pain or vomiting.
Call your doctor or gynecologist if:
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
You may need the following:
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Prevent ovarian torsion:
- Know what to do if you are at high risk for ovarian torsion. An ovarian cyst, pregnancy, or fertility treatment put you at high risk. Seek immediate care if you have any signs or symptoms of ovarian torsion, such as sudden, severe pelvic pain.
- Birth control pills may be prescribed if you are a person of childbearing age. Certain birth control pills help prevent ovulation. This helps prevent ovarian cysts that may lead to ovarian torsion. Talk to your healthcare provider about family planning, if needed.
Follow up with your doctor or gynecologist as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
