ORIF of a Hip Fracture in Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) of a hip fracture is surgery to fix a broken bone in your child's hip. Open reduction means that healthcare providers move the bone back into the right place with surgery. Internal fixation means that hardware (such as screws, rods, or pins) is used to hold the broken bone together. ORIF of a hip fracture is also called percutaneous hip pinning.
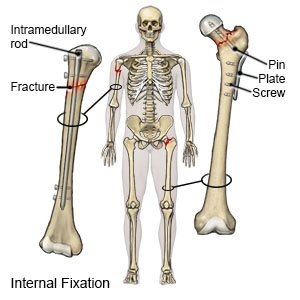 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- Your child feels lightheaded, short of breath, and has chest pain.
- Your child coughs up blood.
Seek care immediately if:
- Your child tells you that his or her leg feels tender or painful. It may feel warm to the touch, and look swollen and red.
- Your child has a cast and his or her toes become swollen, cold, or numb. His or her toes may also look pale or blue.
- Your child has blood or pus leaking from the surgery wound.
Call your child's doctor or surgeon if:
- Your child has pain that does not go away with medicine or gets worse.
- Your child has a fever.
- Your child has stomach pain or is vomiting.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Medicines:
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your child's healthcare provider how to give this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not give your child other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to a healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your child's healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- Do not give aspirin to children younger than 18 years. Your child could develop Reye syndrome if he or she has the flu or a fever and takes aspirin. Reye syndrome can cause life-threatening brain and liver damage. Check your child's medicine labels for aspirin or salicylates.
- Give your child's medicine as directed. Contact your child's healthcare provider if you think the medicine is not working as expected. Tell the provider if your child is allergic to any medicine. Keep a current list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs your child takes. Include the amounts, and when, how, and why they are taken. Bring the list or the medicines in their containers to follow-up visits. Carry your child's medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Wound and cast care:
Ask how to care for your child's wound. If your child has a hip spica cast, he or she will be taught how to use the bathroom and take a bath. You will learn how to help him or her do these activities and how to clean the cast and keep it dry. You will also learn how to help your child move and get dressed.
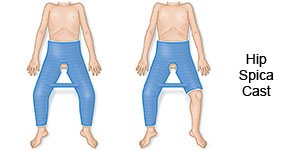 |
Activity:
Your child may need to use crutches or a cane. He or she may only bear weight on the toes of his or her injured leg when he or she first starts to walk. If your child is in a spica cast, he or she may need to use a wheelchair.
Physical therapy:
Your child may need physical therapy after his or her cast is removed. A physical therapist teaches your child exercises to help improve movement and strength, and to decrease pain.
For more information:
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
6300 North River Road
Rosemont , IL 60018-4262
Phone: 1- 847 - 823-7186
Web Address: http://www.aaos.org/
Follow up with your child's doctor or surgeon as directed:
Your child may need to return to have his or her stitches, staples, or cast removed. He or she may also need x-rays or other imaging tests to check for bone healing. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
