Mitral Valve Prolapse
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is mitral valve prolapse (MVP)?
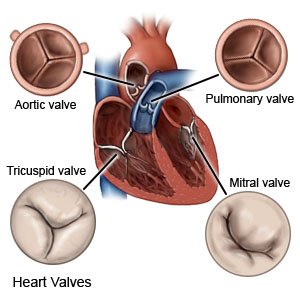
MVP is a weak or bulging mitral valve in your heart. Your mitral valve has 2 flaps that open and close. It allows blood to flow through your heart in one direction. MVP is a common heart condition that often has no signs or symptoms.
 |
What increases my risk for MVP?
Most people who have MVP are born with it. The following may increase your risk for MVP:
- Family history of MVP
- History of rheumatic fever
- Connective tissue disorders, such as Marfan syndrome
- Muscle or skeletal problems, such as some types of muscular dystrophy or scoliosis
- Heart disease or heart attack
- Autoimmune conditions such as Graves disease
What signs and symptoms may I have with MVP?
Many people do not have symptoms. You may have any of the following if MVP gets worse:
- A fast or pounding heartbeat, or heart flutters
- Feeling dizzy, lightheaded, or faint
- Fatigue or anxiety
- Feeling out of breath
- Chest pain
How is MVP diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will examine you and listen to your heart. He or she will ask what medicines you take, and if you have other health conditions. You may also need any of the following:
- An echocardiogram is a type of ultrasound. Sound waves are used to show the structure, movement, and blood vessels of your heart.
- A heart monitor is also called an ECG or EKG. Sticky pads placed on your skin record your heart's electrical activity.
How is MVP treated?
You may not need any treatment if you do not have any symptoms. If you have symptoms, you may need any of the following:
- Medicines may be given to help your heart beat more strongly or regularly. You may need blood thinning medicines to lower your risk of blood clots. You may instead be given medicines to make your blood vessels dilate (open).
- Surgery may be needed if you have severe MVP that causes blood to flow back into your atrium. Your mitral valve may need to be repaired or replaced during surgery.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
How can I manage MVP?
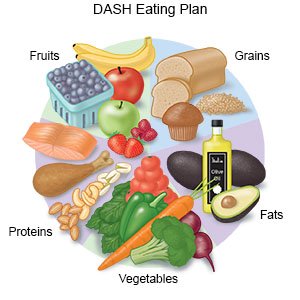
- Eat heart-healthy foods. Heart-healthy foods include fresh fruits and vegetables, low-fat dairy products, chicken (without skin), lean meats, and fish. Eat two 4-ounce servings of fish high in omega-3 fats each week. Examples are salmon, fresh tuna, and herring. Ask for more information on a heart-healthy diet.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight makes your heart work harder. Ask your healthcare provider what a healthy weight is for you. Ask him or her to help you create a weight loss plan if you are overweight.
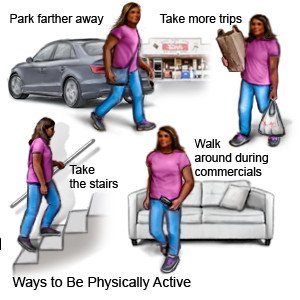
- Stay active. Ask your healthcare provider which activities are best for you.
- Do not use caffeine. Caffeine can make your MVP symptoms worse.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can cause damage to your heart. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) for any of the following:
- You have shortness of breath or chest pain.
- You have any of the following signs of a stroke:
- Numbness or drooping on one side of your face
- Weakness in an arm or leg
- Confusion or difficulty speaking
- Dizziness, a severe headache, or vision loss
When should I seek immediate care?
- You faint.
- You have new symptoms or your symptoms get worse.
When should I call my doctor?
- Your heart beats faster than normal for you, or skips beats.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Mitral Valve Prolapse
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
